문제 💁🏻♂️
해결 과정
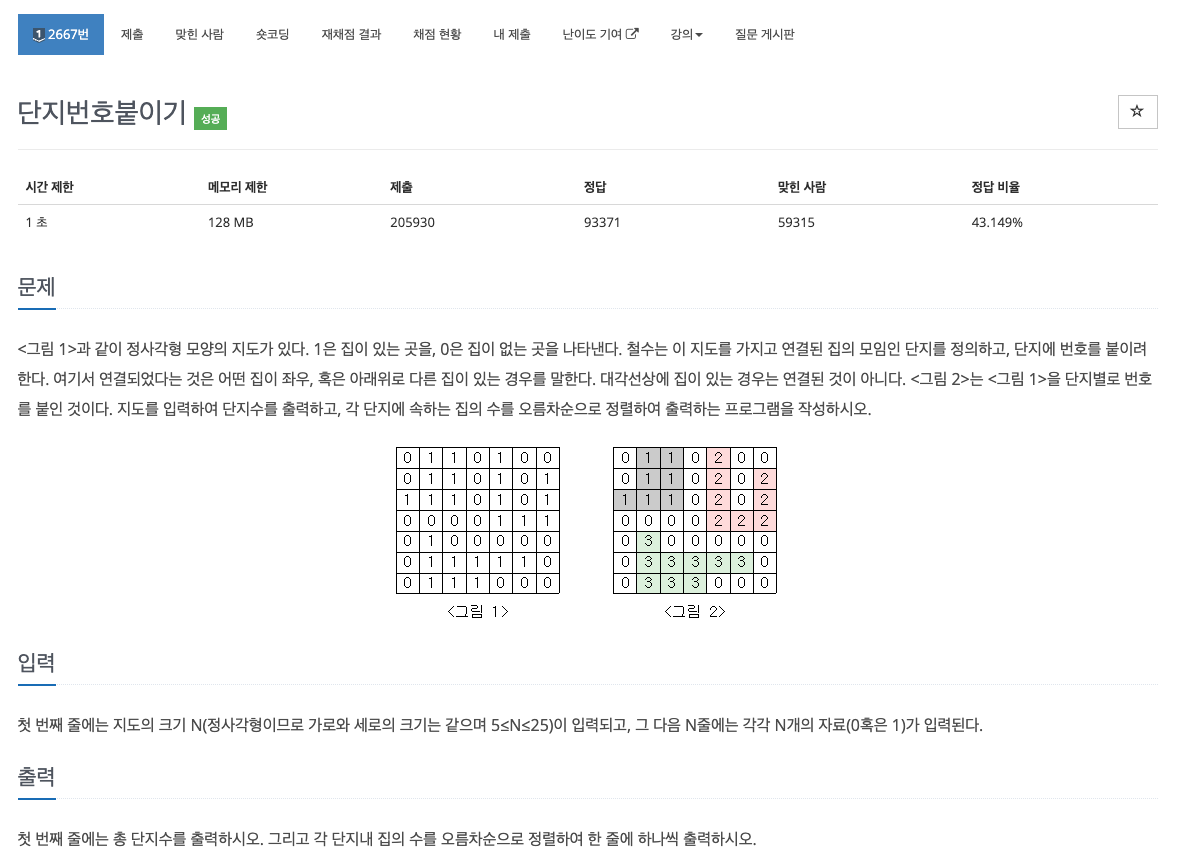
이 문제는 그림에서부터 탐색 문제라는 느낌이 바로 온다. 문제 풀이 핵심을 간략하게 적어보자면, 결국 상하좌우에 있는 1들을 모두 모아 하나의 묶음으로 만들고, 묶음 개수와 각 묶음의 요소들을 오름차순으로 정렬하여 출력하면 끝나는 문제이다.
사고 과정 ❗️
이 문제를 풀기 위해서 최초의 방문하지 않은 1을 만났을 때, DFS 탐색을 하여 인접한 1들을 모두 탐색하도록 구현했다. 탐색을 들어가기 전에 묶음 개수를 1 증가시키고, 탐색을 하면서 묶음 내부의 개수들을 카운팅한다. 이 과정을 모든 탐색이 끝날 때까지 반복한다.
즉, 이 문제는 DFS 탐색을 구현할 줄만 알면 풀 수 있는 알고리즘 기초 문제이다! 이 문제를 통해서 DFS 로직을 이해했다!
코드
정답 코드 (Java)
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
static StringTokenizer st;
static int N, MAX;
static int[] dys = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
static int[] dxs = {0, 0, -1, 1};
static char[][] map;
static boolean[][] visited;
static ArrayList<Integer> lst;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
map = new char[N][N];
visited = new boolean[N][N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
String line = br.readLine();
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
map[i][j] = line.charAt(j);
}
}
lst = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
// 방문한 적이 없고, 1인 경우 -> 탐색
if (!visited[i][j] && map[i][j] == '1') {
MAX = 1;
visited[i][j] = true; // 시작점 방문 처리
dfs(i, j);
lst.add(MAX);
}
}
}
Collections.sort(lst);
bw.write(lst.size() + "\n");
for (int num : lst) {
bw.write(num + "\n");
}
bw.close();
br.close();
}
private static void dfs(int y, int x) {
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nxtY = y + dys[i];
int nxtX = x + dxs[i];
// 범위를 벗어나지 않고, 방문한 적이 없는 경우 -> 탐색 진행
if (inRange(nxtY, nxtX) && !visited[nxtY][nxtX] && map[nxtY][nxtX] == '1') {
visited[nxtY][nxtX] = true; // 방문 처리
MAX++;
dfs(nxtY, nxtX);
}
}
}
private static boolean inRange(int y, int x) {
return 0 <= y && y < N && 0 <= x && x < N;
}
}정답 코드 (Python)
from sys import stdin, setrecursionlimit
setrecursionlimit(2_500)
input = stdin.readline
def dfs(cur_y, cur_x):
global cnt
MAP[cur_y][cur_x] = 0
cnt += 1
dys, dxs = [0, 0, -1, 1], [-1, 1, 0, 0]
for dy, dx in zip(dys, dxs):
nxt_y, nxt_x = cur_y + dy, cur_x + dx
if 0 <= nxt_y < n and 0 <= nxt_x < n and MAP[nxt_y][nxt_x] == 1:
dfs(nxt_y, nxt_x)
n = int(input().rstrip())
MAP = [list(map(int, input().rstrip())) for _ in range(n)]
home_cnt = []
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
if MAP[i][j] == 1:
cnt = 0
dfs(i, j)
home_cnt.append(cnt)
print(len(home_cnt))
print(*sorted(home_cnt), sep='\n')
Reference
- 내 머릿 속

