
Two Sum(twoSum.py)
[문제]
You have a browser of one tab where you start on the homepage and you can visit another url, get back in the history number of steps or move forward in the history number of steps.
Implement the BrowserHistory class:
BrowserHistory(string homepage)Initializes the object with thehomepageof the browser.void visit(string url)Visitsurlfrom the current page. It clears up all the forward history.string back(int steps)Movestepsback in history. If you can only returnxsteps in the history andsteps > x, you will return onlyxsteps. Return the currenturlafter moving back in history at moststeps.string forward(int steps)Movestepsforward in history. If you can only forwardxsteps in the history andsteps > x, you will forward only x steps. Return the currenturlafter forwarding in history at moststeps.
[제한 사항]
1 <= homepage.length <= 201 <= url.length <= 201 <= steps <= 100homepageandurlconsist of '.' or lower case English letters.- At most
5000calls will be made tovisit,back, andforward.
[입출력 예]
Input:
["BrowserHistory","visit","visit","visit","back","back","forward","visit","forward","back","back"]
[["leetcode.com"],["google.com"],["facebook.com"],["youtube.com"],[1],[1],[1],["linkedin.com"],[2],[2],[7]]Output:
[null,null,null,null,"facebook.com","google.com","facebook.com",null,"linkedin.com","google.com","leetcode.com"][입출력 예에 대한 설명]
Explanation:
BrowserHistory browserHistory = new BrowserHistory("leetcode.com");
browserHistory.visit("google.com"); // You are in "leetcode.com". Visit "google.com"
browserHistory.visit("facebook.com"); // You are in "google.com". Visit "facebook.com"
browserHistory.visit("youtube.com"); // You are in "facebook.com". Visit "youtube.com"
browserHistory.back(1); // You are in "youtube.com", move back to "facebook.com" return "facebook.com"
browserHistory.back(1); // You are in "facebook.com", move back to "google.com" return "google.com"
browserHistory.forward(1); // You are in "google.com", move forward to "facebook.com" return "facebook.com"
browserHistory.visit("linkedin.com"); // You are in "facebook.com". Visit "linkedin.com"
browserHistory.forward(2); // You are in "linkedin.com", you cannot move forward any steps.
browserHistory.back(2); // You are in "linkedin.com", move back two steps to "facebook.com" then to "google.com". return "google.com"
browserHistory.back(7); // You are in "google.com", you can move back only one step to "leetcode.com". return "leetcode.com"풀이
1차 시도
접근 방식
- 해시 테이블의 lookup연산의 복잡도가 O(1)임을 이용하면, nums 배열을 한 번만 돌면서 답을 찾을 수 있다고 생각했다.
- nums배열을 돌면서 두 요소의 합이 target이 되는 인덱스 쌍을 찾는 문제이니, 현재 보고있는 요소와, 이전에 보고 저장했던 요소의 합이 target이 되면 답을 찾은 것이다.
- 이전에 보고 저장했던 요소를 찾는 과정을 해시 테이블을 이용하면 잘 풀릴것 같다.
- 우선 요소를 보고, 이전에 보고 저장했던 요소와 지금 보고있는 요소의 합이 target과 같은지 확인해야 하는데, 이전 저장했던 모든 요소를 다 검사하면 시간복잡도가 올라가므로, 저장을 해시테이블에 하고, 바로 합이 target이 되는 값이 해당 테이블에 있는지만 검사하면 될 것 같다.
코드
class Solution:
def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:
hash_table = {}
for i in range(len(nums)):
s = target - nums[i]
if s in hash_table:
return [hash_table[s], i]
hash_table[nums[i]] = i
return [-1, -1]결과
배운점
- 해시 테이블 lookup 복잡도가 O(1)임을 다른 문제에서도 많이 활용하기 좋을 것 같다.
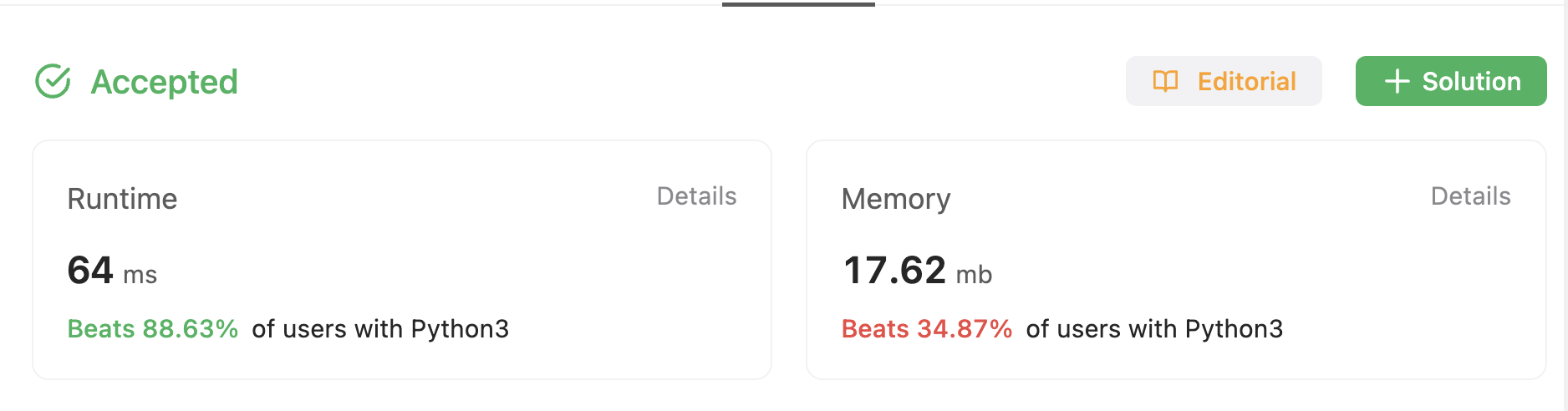

좋은 글 감사합니다.