4주차 과제: 제어문
📌 목표
자바가 제공하는 제어문을 학습하세요.
📌 학습할 것
📑 학습할 것 (필수)
선택문
반복문
✏️ 과제 (옵션)
과제 0. JUnit 5 학습하세요.
과제 1. live-study 대시 보드를 만드는 코드를 작성하세요.
📜 시작에 앞서
- 백기선 님의 라이브 스터디(2020년 11월부터 2021년 3월까지) 커리큘럼을 따라 진행한 학습입니다
- 뒤늦게 알게 되어 스터디 참여는 못했지만 남아있는 스터디 깃허브 주소와 유튜브 영상을 참고했습니다
📑 선택문
- 조건에 따라 프로그램의 흐름을 바꾸는 역할
if
//if-else
if(조건식1) { // 조건식의 결과는 true나 false
수행문 // 조건식이 true일때 수행
} else { //(else문 없이 그냥 if문만 가능)
수행문 // 위의 조건식 false일 때
}
//if-if
if(조긴식1){
수행문
} if(조건식2){
수행문
}- 가독성 위해 일반적인 경우를
else절 아닌if절에 작성 - 항상
else문이 필요한지 고려하고,else문이 필요 없지만 그 이유가 불분명하다면 주석으로else절이 필요 없는 이유 작성
if-else
if(조건식1){ // 조건식의 결과는 true나 false
수행문 // 조건식이 true일때 수행
} else if(조건식2){
수행문
} else if(조건식2){ // if-if문과 달리 if-else if문은 하나의 조건 만족하면 나머지 조건 비교X
수행문
else { // 위의 조건식 모두 false일 때
수행문
}if-else문은 하나의 조건 만족하면 나머지 조건 비교X- 가장 흔한 경우를 앞에 놓으면 가독성과 최적화 모두 챙길 수 있다
- 조건식이 복잡하다면
boolean값을 리턴하는 메서드를 호출해 단순화 하자 - 모든 경우를 다뤘는지 확인 ->
else절에는 오류 메시지나 어셜션 작성
switch
//switch
switch(조건식){ // 조건식 계산
case 값1: // 조건식 결과와 일치하는 case문으로 이동
수행문 // 수행문 실행
break; // switch문 탈출
case 값2: // break 없다면 아래로 break 만날 때까지 쭉 수행
수행문
break;
default: // 결과와 일치하는 case 없을 때 수행
수행문
break;
}switch문은 쉽게 분류할 수 있는 간단한 데이터에 대해 사용, 그러지 않다면if-else문 사용case에 사용하기 위해 가짜 변수 생성Xcase순서는 의미있게 나열(알파벳순, 가정 정상적인 경우순, 빈도순 등)default는 유일한 기본 값을 찾거나 오류를 검출할 때만 사용- java12, java13 에서의 변화는 3주차 과제: 연산자: Java 13. switch 연산자 참고
📑 반복문
- 조건에 따라 프로그램의 흐름을 반복
for
for(초기화;조건식;증감식){ // 조건식의 결과는 true나 false
수행문 // 조건식의 결과가 true인 동안 실행
}for-each loop
for(Element e : elements) { //대입받을 변수 : 순회할 객체
수행문 // 순회할 객체 전체를 순회하는 동안 반복
}- 순회할 객체는
Iterable구현한 객체와 배열 사용 가능 for문을 사용했다면for(Iterator<Element> i = elements.iterator() ; i.hasNext(); ){...}와 같이 복잡했을 것iterator를 숨기기 때문에 내부 원소에 대해 제거나 변형 불가- 제거 예 -> 자바8 부터는
Collection의removeIf()를 사용해 컬렉션을 명시적으로 순회하지 않고 원하는 원소 제거 가능,iterator사용 - 변형 예 -> 리스트의 반복자나 배열의 인덱스 사용
- 제거 예 -> 자바8 부터는
- 여러 컬렉션을 병렬 순회하여 각각의 반복자와 인덱스 변수를 사용해 엄격하고 명시적으로 제어해야 한다면
for사용
while, do-while
//while
while(조건식){
수행문
}
//do-while
do{
수행문 //최소 1번 실행 후, 조건식 결과가 true인 동안 실행
} while(조건식);반복문에서 break, continue문
break: 속한 반복문 탈출continue: 속한 반복문에 해당 반복 탈출(다음 반복 계속 진행)
✏️ JUnit 5 학습하세요.
JUnit docs: JUnit 5 User Guide
JUnit docs의 예제
- For Gradle and Java, check out the
junit5-jupiter-starter-gradleproject.
Calculator
/*
* Copyright 2015-2018 the original author or authors.
*
* All rights reserved. This program and the accompanying materials are
* made available under the terms of the Eclipse Public License v2.0 which
* accompanies this distribution and is available at
*
* http://www.eclipse.org/legal/epl-v20.html
*/
package com.example.project;
public class Calculator {
public int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
}CalculatorTest
/*
* Copyright 2015-2018 the original author or authors.
*
* All rights reserved. This program and the accompanying materials are
* made available under the terms of the Eclipse Public License v2.0 which
* accompanies this distribution and is available at
*
* http://www.eclipse.org/legal/epl-v20.html
*/
package com.example.project;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.params.ParameterizedTest;
import org.junit.jupiter.params.provider.CsvSource;
class CalculatorTests {
@Test
@DisplayName("1 + 1 = 2")
void addsTwoNumbers() {
Calculator calculator = new Calculator();
assertEquals(2, calculator.add(1, 1), "1 + 1 should equal 2");
}
@ParameterizedTest(name = "{0} + {1} = {2}")
@CsvSource({
"0, 1, 1",
"1, 2, 3",
"49, 51, 100",
"1, 100, 101"
})
void add(int first, int second, int expectedResult) {
Calculator calculator = new Calculator();
assertEquals(expectedResult, calculator.add(first, second),
() -> first + " + " + second + " should equal " + expectedResult);
}
}실행 결과
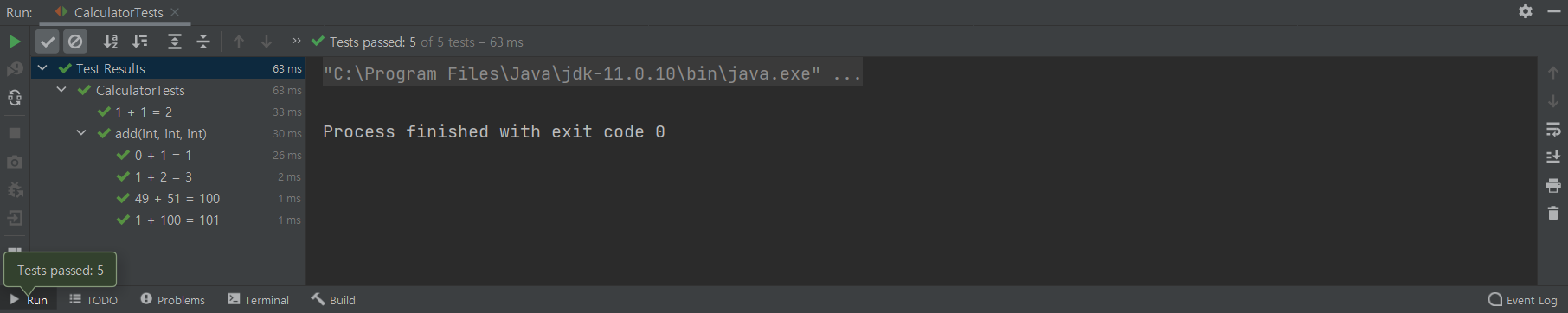
- 인텔리J에서 테스트 실행 결과
no tests found for given includes xxxx.someThingTest에러가 뜬다면- Settings > ...Gradle 검색... > Gradle > Run Test Using 항목을 IntelliJ 로 변경
어노테이션
| Annotation | description |
|---|---|
| @Test | 메서드가 테스트 메서드임을 나타낸다 |
| @ParameterizedTest | 메서드가 매개변수가 있는 테스트임을 나타낸다 |
| @DisplayName | 테스트 클래스 또는 테스트 메서드를 사용자가 지정한 이름으로 표시한다. 공백, 특수문자, 이모지도 사용 가능 |
| @DisplayNameGeneration | 테스트 클래스를 사용자가 지정한 이름으로 표시한다 |
| @BeforeEach | 각 테스트가 실행되기 전에 한 번 씩 실행 |
| @AfterEach | 각 테스트가 실행된 후에 한 번 씩 실행 |
| @BeforeAll | 모든 테스트가 실행되기 이전 한 번 실행 |
| @AfterAll | 모든 테스트가 실행된 후 한 번 실행 |
| @Tag | 필터링 테스트를 위한 태그 선언 |
| @Disabled | 테스트 클래스 또는 테스트 메서드를 무시 |
| @Order | 테스트 실행시 우선순위 지정 전체 또는 일부분에 대해 statefull test 가능 |
어설션
org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*assertEquals(expected, actual)등 방식- JUnit4에 있던 메서드와 Java8의 람다와 사용하기 적합한 몇몇 기능 추가
- JUnit5 doc: org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions 참고
org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.*assertThat(actual).isEqualTo(expected)등 방식- AssertJ docs 참고
✏️ live-study 대시 보드를 만드는 코드를 작성하세요.
- 라이브 스터디가 오래전 끝나기도 했고, 지금 쓸 수 있는 걸 만들고 싶어서 다른 과제로 대체
- GitHub에서 사용자 아이디와 저장소 이름으로 검색해 저장소 이름, 저장소 설명, 커밋 메시지, 커밋 날짜를 md 표로 출력
import org.kohsuke.github.*;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class App {
private static final String PERSONAL_TOKEN = "YOUR-API-KEY-HERE";
private static final String GITHUB_USER_MYSELF = "myself";
private static final Scanner SCANNER = new Scanner(System.in);
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
App app = new App();
app.run();
}
private void run() throws IOException {
GitHub github = new GitHubBuilder().withOAuthToken(PERSONAL_TOKEN).build();
String userId = getUserId();
Map<String, GHRepository> repos = getRepos(github, userId);
String repoNameKeyword = getRepoNameKeyword();
getCommitInfo(repos, repoNameKeyword);
}
private void getCommitInfo(Map<String, GHRepository> repos, String repoNameKeyword) throws IOException {
for (String key : repos.keySet()) {
GHRepository repo = repos.get(key);
String repoName = repo.getName();
if(repoName.contains(repoNameKeyword)){
System.out.printf("**%s**\n", repoName);
System.out.printf("|%s|%s|\n", repo.getDescription(), "커밋 날짜");
System.out.println("|---|---|");
PagedIterable<GHCommit> ghCommits = repo.listCommits();
for (GHCommit commit : ghCommits) {
Date commitDate = commit.getCommitDate();
System.out.printf("|%s|%d년 %d월 %d일|\n",
commit.getCommitShortInfo().getMessage().replace("\n", " "),
commitDate.getYear()+1900,
commitDate.getMonth()+1,
commitDate.getDate());
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
private Map<String, GHRepository> getRepos(GitHub github,String userId) throws IOException {
if (!userId.equals(GITHUB_USER_MYSELF)) { // !equals 주의
GHUser user = github.getUser(userId);
return user.getRepositories();
} else {
GHMyself myself = github.getMyself();
return myself.getAllRepositories();
}
}
private String getRepoNameKeyword(){
System.out.println("저장소 주소 검색 키워드를 입력하세요.");
return getUserInput();
}
private String getUserId(){
System.out.println("저장소를 검색할 유저 아이디를 입력하세요. 본인 검색할 경우 " + GITHUB_USER_MYSELF);
return getUserInput();
}
private static String getUserInput() {
return SCANNER.nextLine();
}
}private static final String PERSONAL_TOKEN = "YOUR-API-KEY-HERE"
- GitHub Docs: Creating a personal access token
- 본인 저장소 검색시 비공개 저장소까지 결과에 포함하고 싶다면 토큰 권한 설정시 repo 전체 선택
실행 결과
- 저작권 위해 비공개 저장소에 저장한 커밋 이력 md 표로 출력 예시
저장소를 검색할 유저 아이디를 입력하세요. 본인 검색할 경우 myself
myself
저장소 주소 검색 키워드를 입력하세요.
JPA
C2L-JPA-basic
| 자바 ORM 표준 JPA 프로그래밍 - 기본편 / 김영한님 강의 | 커밋 날짜 |
|---|---|
| 섹션 11. 객체지향 쿼리 언어2 - 중급 문법 | 2021년 5월 26일 |
| 섹션 10. 객체지향 쿼리 언어1 - 기본 문법 | 2021년 5월 25일 |
| 섹션 9. 값 타입 | 2021년 5월 24일 |
| 섹션 8. 프록시와 연관관계 관리 | 2021년 5월 23일 |
| 섹션 7. 고급 매핑 | 2021년 5월 22일 |
| 섹션 6. 다양한 연관관계 매핑 | 2021년 5월 21일 |
| 섹션 5. 연관관계 매핑 기초 | 2021년 5월 20일 |
| 섹션 4. 엔티티 매핑 | 2021년 5월 19일 |
| 섹션 3. 영속성 관리 - 내부 동작 방식 | 2021년 5월 18일 |
| 섹션 2. JPA 시작하기 | 2021년 5월 17일 |
| 섹션 1. JPA 소개 | 2021년 5월 16일 |
📑📌📜✏️

