combinations
python 기본 libaray인 itertools의 함수이다.
사용
iterable한 객체와 조합물의 길이를 매게변수로 받으며,
tuple에 조합물을 담아 반환하는 Generator를 반환한다.
예시
코드
from itertools import combinations
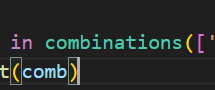
for comb in combinations(['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'], 3):
print(comb)결과
('a', 'b', 'c')
('a', 'b', 'd')
('a', 'b', 'e')
('a', 'c', 'd')
('a', 'c', 'e')
('a', 'd', 'e')
('b', 'c', 'd')
('b', 'c', 'e')
('b', 'd', 'e')
('c', 'd', 'e')동작 원리
코드
def combinations(iterable, r):
# combinations('ABCD', 2) → AB AC AD BC BD CD
# combinations(range(4), 3) → 012 013 023 123
pool = tuple(iterable)
n = len(pool)
if r > n:
return
indices = list(range(r))
yield tuple(pool[i] for i in indices)
while True:
for i in reversed(range(r)):
if indices[i] != i + n - r:
break
else:
return
indices[i] += 1
for j in range(i+1, r):
indices[j] = indices[j-1] + 1
yield tuple(pool[i] for i in indices)동작 설명
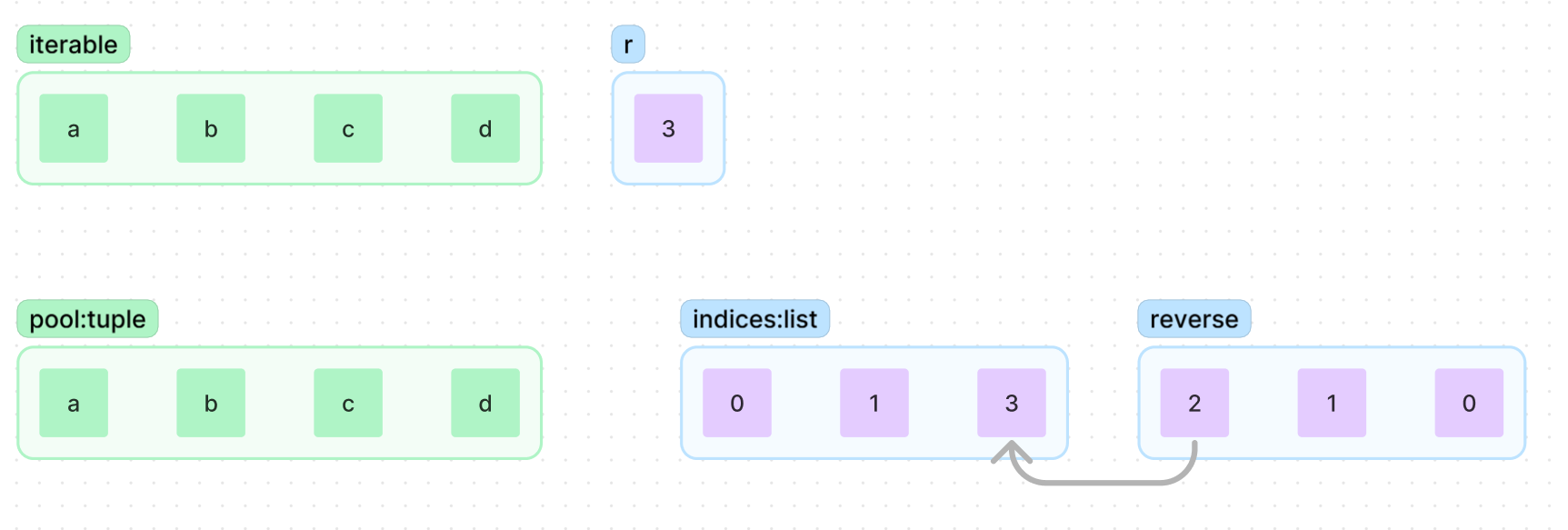
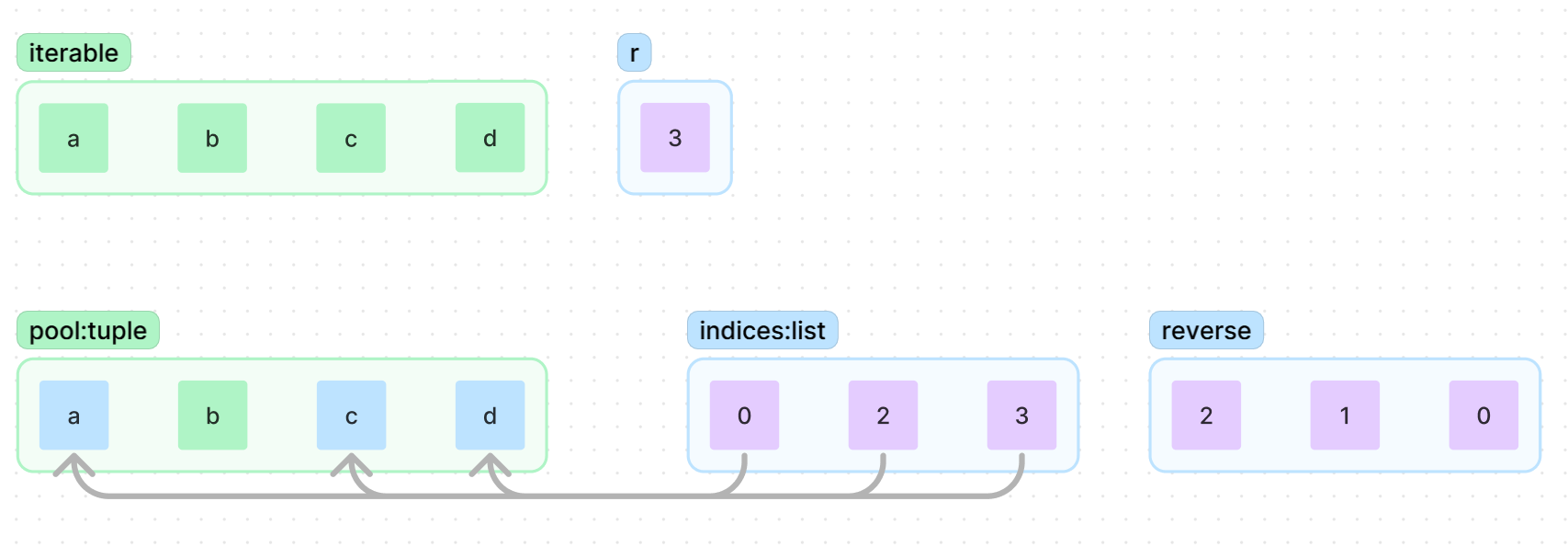
r의 길이 만큼의 indices배열이 생성되며,
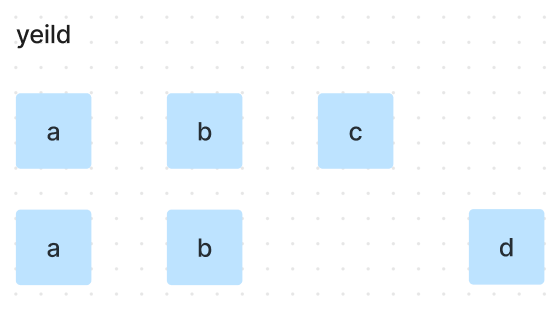
indices의 요소들이 가르키는 pool의 값들이 yeild됨

{a, b, c}를 사용하여 조합을 만들었으나,
{a, b, d}조합을 완성 할 수 있음
그러니 indices[2]의 값을 올려 {a, b, d}를 yeild
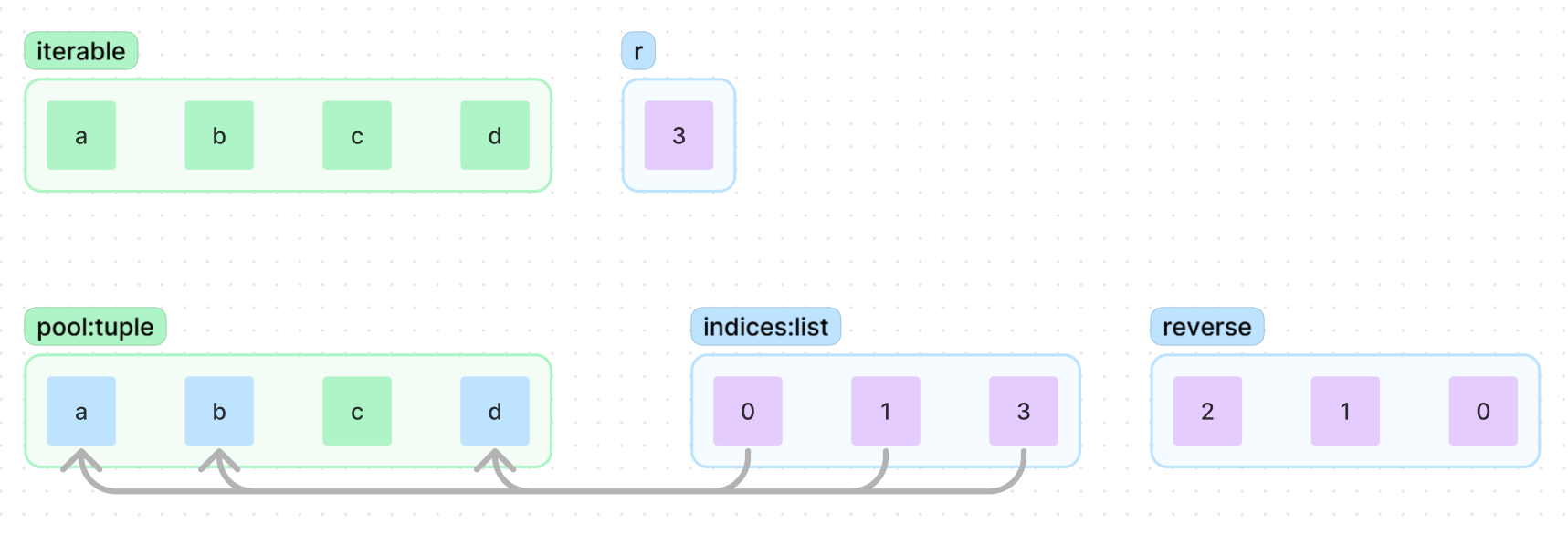
그 후 {a, b}를 사용한 조합은 모두 사용하였으니 indices[1]의 값을 올린 뒤
indices[1:]까지 indices[1]을 기준으로 정렬
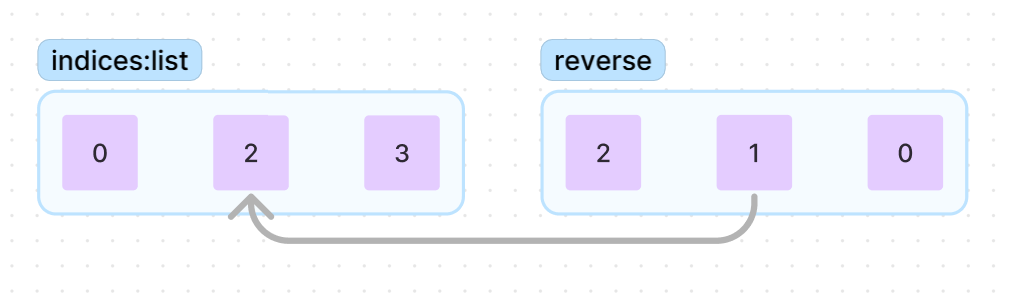
indices의 값을 기준으로 yeild

{a}를 사용한 조합을 모두 완성하였으니,
indices[0]의 값을 올린 뒤
indices[0:]까지 indices[0]을 기준으로 정렬
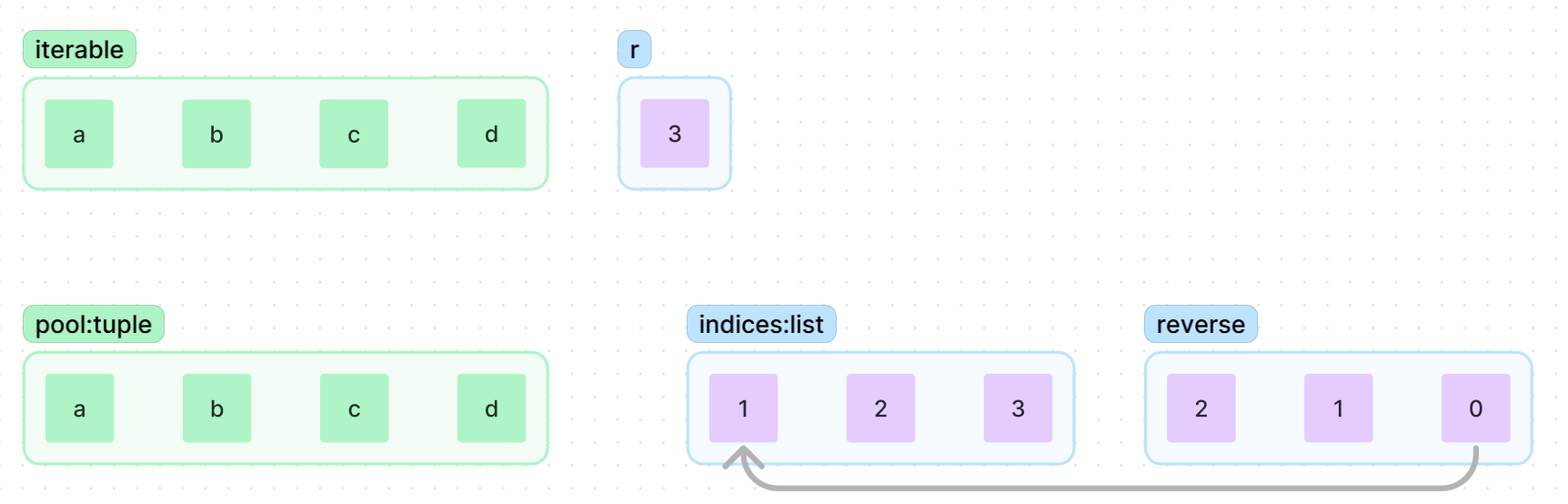
indices의 값을 기준으로 yeild
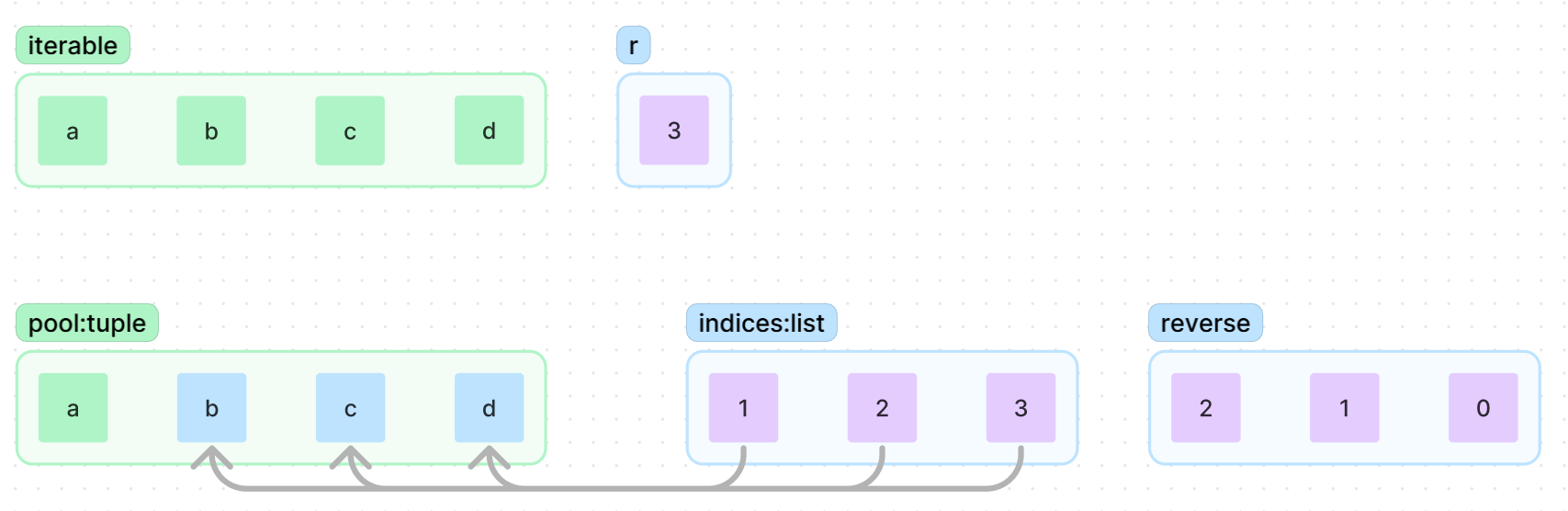
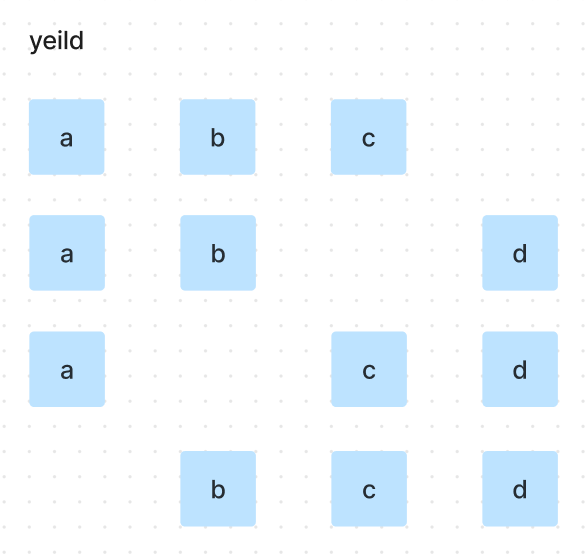
iterable로 길이 M의 모든 조합 완성
정리
흐름만 짚었으니 한번 코드보고 다시 생각해보길 추천함
참조
https://docs.python.org/ko/3/library/itertools.html#itertools.combinations
