🐈 Setup
npm i @nestjs/cli- Nest.js CLI를 사용하기 위한 라이브러리 다운nest new [project-name]- 새로운 프로젝트 생성- 만약 이미 폴더를 생성했다면
nest new ./
- 만약 이미 폴더를 생성했다면
- 생성되는 디렉토리와 파일들이다.
├── README.md
├── nest-cli.json
├── node_modules
├── package-lock.json
├── package.json
├── .gitignore
├── .eslintrc.js
├── .prettierrc
├── src
│ ├── app.controller.spec.ts
│ ├── app.controller.ts
│ ├── app.module.ts
│ ├── app.service.ts
│ └── main.ts
├── test
│ ├── app.e2e-spec.ts
│ └── jest-e2e.json
├── tsconfig.build.json
└── tsconfig.json🐈 Controller
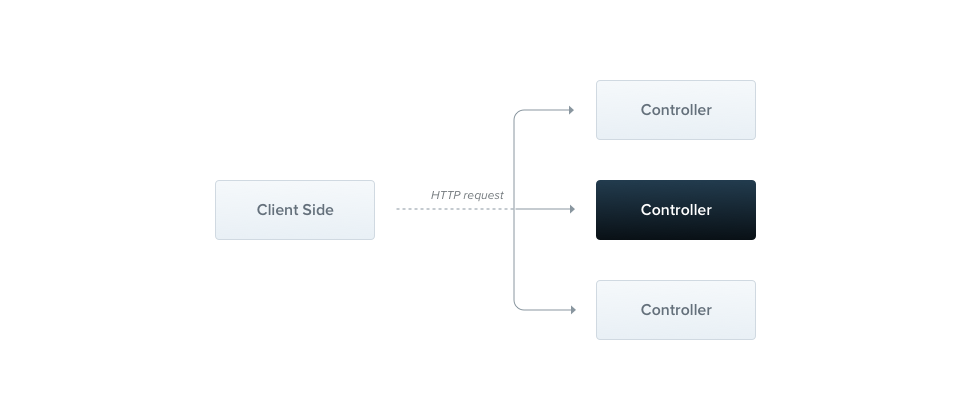
Controller는 클라이언트로부터 들어오는 request를 처리하고, 클라이언트에게 response를 반환해주는 역할을 한다.
- Nest.js에서 controller가
@Post, @Get, @Put, @Patch, @Delete데코레이터를 통해 routing 처리를 같이 해준다. nest g controller [name]으로 파일과 테스트 파일을 생성할 수 있다.
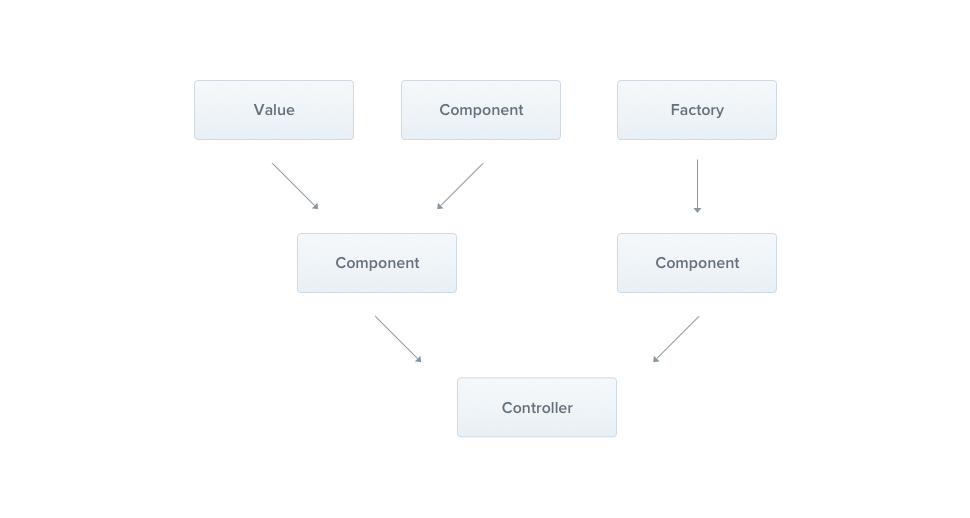
🐈 Provider
Provider는 Service, Respository, Factory, Helper 등등을 모두 포함하는 Nest의 기본이 되는 컨셉이다. 의존성 주입이 될 수 있는 모든 것들을 provider라고 생각하면 좋다. 즉, 다른 시스템과 연관성을 가지는 객체이다.
Service
- Service layer에는 비지니스 로직이 담기게 된다.
nest g service [name]으로 파일과 테스트 파일을 생성할 수 있다.
Repository
- Repository layer에는 DB의 쿼리를 직접 실행하는 메서드들이 들어있다.
- 파일은 직접 생성한다.
- Mongo를 사용하는 경우 Repository 사용법을 해당 블로그 포스팅에서 확인할 수 있다.
- TypeORM 관련 버전 이슈: 이전 버전에서는 존재했던
@EntityRepository데코레이터가 deprecated되면서 직접 typeORM에서 제공하는Repository클래스를 상속받아서 사용하여야 한다. 사용법은 해당 블로그 포스팅에 나와있다. (우리는 MySQL을 선택하였기 때문에 TypeORM을 기준으로 설명하도록 하겠다.)
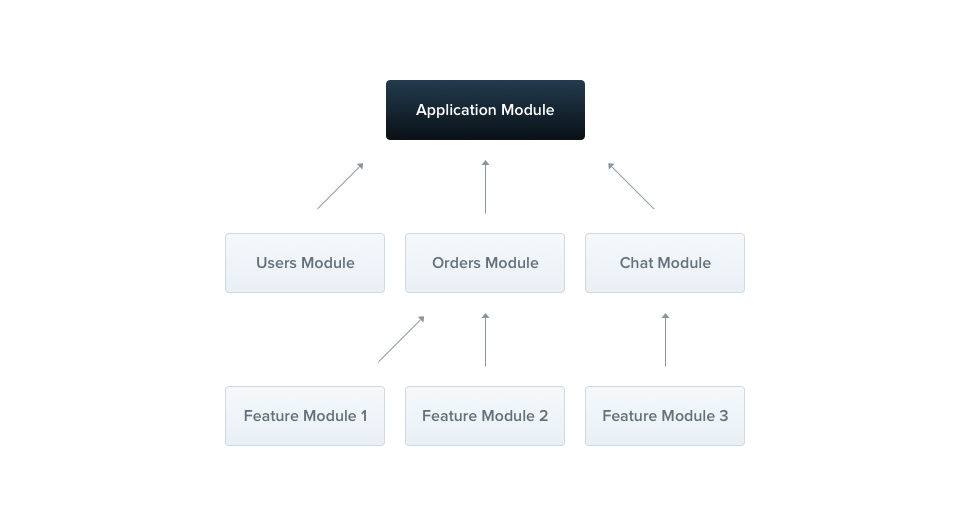
🐈 Module
Module은 Nest가 어플리케이션 구조를 관리하기 위해 사용되는 metadata들을 제공한다. 각 어플리케이션은 1개 이상의 root module을 가지고 있고, 이는 module과 provider의 관계성과 의존성을 정의해준다.
npm g module [name]으로 파일을 생성할 수 있다.- TypeORM 기준, 각 모듈들의 module.ts 파일을 다음과 같이 수정해주어야 한다.
@Module({
imports: [TypeOrmModule.forFeature([EntityName])],
controllers: [SomethingController],
providers: [SomethingService, SomethingRepository],
})
export class HospitalsModule {}TypeOrmModule.forFeature([EntityName])을 imports에 넣어준다.- providers에 repository를 넣어준다.
🐈 main.ts 파일
const logger = new Logger();
const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule);
// global validation pipe
app.useGlobalPipes(
new ValidationPipe({
whitelist: true, // 페이로드와 DTO 클래스를 비교해 수신해서는 안되는 속성을 자동으로 제거하는 옵션(유효성이 검사된 객체만 수신)
forbidNonWhitelisted: true, // 허용하지 않은 속성을 제거하는 대신 예외를 throw하는 옵션
transform: true, // 네트워크를 통해 받는 페이로드가 DTO 클래스에 따라 지정된 개체로 자동 변환되도록 하는 옵션
}),
);
// global HTTP exception filter
app.useGlobalFilters(new HttpExceptionFilter()); // global filter
// cors
app.enableCors();
// config
const config = app.get<ConfigType<typeof appConfig>>(appConfig.KEY);
const port = config.port;
await app.listen(port);
if (config.mode === 'development') logger.log(`서버 돌아가는 듕~ ${port}`);- 기본 cors 설정을 해주었다.
- validation pipe (validation & transformation)를 global로 정의하였다. (이를 위해 라이브러리 설치가 필요하다:
npm i --save class-validator class-transformer)
🐈 Config 환경 변수 관리
npm i --save @nestjs/config cross-env joi를 설치해준다.ConfigModule에서 제공하는ConfigService와ConfigType을 통해서 환경 변수에 접근할 수 있다.ConfigType을 사용하면ConfigSerivce보다 더 type-safety한 방식으로 환경 변수를 읽어올 수 있으며, 기능별로 환경 변수를 분리하여 관리하기가 용이하다.
🐈 HTTP 요청 Logger 미들웨어 설정
- app.module.ts에서 다음과 같이 설정해주었다. Development 모드일 경우에만 로그를 찍어준다.
export class AppModule implements NestModule {
private readonly isDev: boolean =
process.env.MODE === 'development' ? true : false;
// dev mode일 때 HTTP 요청 로그 남기는 부분
configure(consumer: MiddlewareConsumer) {
if (this.isDev) {
consumer.apply(HTTPLoggerMiddleware).forRoutes('*');
}
}
}- HTTP-logger.middleware.ts는 다음과 같이 설정해주었다.
@Injectable()
export class HTTPLoggerMiddleware implements NestMiddleware {
private logger = new Logger('HTTP'); // HTTP 프로토콜에 대한 logger
use(req: Request, res: Response, next: NextFunction) {
// response가 완료 (finish event)되면 로그를 남김
res.on('finish', () => {
this.logger.log(
`${req.ip} ${req.method}, ${res.statusCode}`,
req.originalUrl,
);
});
next();
}
}🐈 HTTP Exception Filter
Nest.js에서는 기본적으로 HTTP response에 대해 exception filtering을 제공한다. 예를 들면, 서버 에러가 발생할 경우 Nest에서는 이런 에러를 던져준다.
{
"statusCode": 500,
"message": "Internal server error"
}이렇게 Nest.js에서 자체적으로 처리해주는 response와 우리가 throw new HttpException()으로 커스터마이징하여 던져주는 에러 response에 대해 exception filter를 사용해서 처리해줄 수 있다.
import { Catch, HttpException } from '@nestjs/common';
@Catch(HttpException)
export class HttpExceptionFilter {
catch(exception, host) {
const ctx = host.switchToHttp();
const response = ctx.getResponse();
const request = ctx.getRequest();
const status = exception.getStatus();
const error = exception.getResponse() as
| string
| { error: string; statusCode: number; message: string | string[] };
// 우리가 설정한 throw new HttpException()의 경우
if (typeof error === 'string') {
response.status(status).json({
success: false,
error,
statusCode: status,
timestamp: new Date().toISOString(),
path: request.url,
});
}
// nest 자체에서 처리해주는 error handling의 경우
else {
response.status(status).json({
success: false,
...error,
timestamp: new Date().toISOString(),
path: request.url,
});
}
}
}