Callback
Callback 함수(콜백 함수)는 함수의 파라미터에 아규먼트로 전달하는 함수이다.
const sum = (a, b, operation) => {
const result = a + b;
operation(result);
};
const multiplyByTen = (result) => {
console.log(result * 10);
};
const divideByTen = (result) => {
console.log(result / 10);
};
sum(1, 5, multiplyByTen); // 60
sum(2, 5, divideByTen); // 0.7sum함수를 실행하면서 세 번째 인자로multiplyByTen,divideByTen함수를 전달했다.sum함수를 실행하면서 인자로 전달한multiplyByTen,divideByTen함수가 콜백함수이다.sum함수에서 두 매개변수의 값을 더한 결과를 콜백함수에 전달해 콜백함수의 로직에 따라 처리한다.
Callback 사용 이유
콜백 함수를 사용하는 이유
- 콜백 함수를 전달받는 함수(대상 함수) 안에서 실행하고 싶은 로직을 직접 만들어 전달하기 위해
- 대상 함수 안에서 처리한 결과를 콜백 함수가 인자로 받아 콜백 함수의 로직에서 사용하기 위해
위 예시에서 multiplyByTen, divideByTen라는 로직을 직접 만들어 sum 함수를 실행하면서 전달하였다. 또한 sum 함수 내부에서 처리한 결과를 콜백함수가 인자로 받아 콜백 함수의 로직에서 사용하였다.
Callback 방식의 문제점: Callback 지옥
콜백 지옥은 콜백 함수를 익명 함수로 전달하는 과정이 계속 반복되어 코드 들여쓰기 수준이 깊어져 코드 가독성이 굉장히 떨어지는 것을 말한다.
서버 통신과 같은 비동기 작업을 처리하기 위해 콜백 함수를 계속 전달하는 과정에서 콜백 지옥이 발생하는 경우가 많다. 예를 들어 다음과 같은 경우가 있다.
- 첫 번째 GET API 요청의 응답 결과를 받는다.
- 두 번째 GET API 요청 시 첫 번째 GET 요청의 응답 결과를 사용해야 한다.
- 세 번째 GET API 요청 시 두 번쨰 GET 요청의 응답 결과를 사용해야 한다.
위와 같은 경우 콜백 함수를 전달하는 과정에서 코드 들여쓰기 수준이 계속 깊어진다.
const aa = new XMLHttpRequest();
aa.open("get", `http://numbersapi.com/random?min=1&max=200`);
aa.send();
aa.addEventListener("load", (res) => {
// 콜백함수
console.log(res); // API 요청 결과
const num = res.target.response.split(" ")[0]; // 101 (랜덤 숫자)
const bb = new XMLHttpRequest();
bb.open("get", `https://koreanjson.com/posts/${num}`);
bb.send();
bb.addEventListener("load", (res) => {
// 콜백함수
console.log(res); // API 요청 결과
const userId = JSON.parse(res.target.response).UserId;
const cc = new XMLHttpRequest();
cc.open("get", `https://koreanjson.com/posts?userId=${userId}`);
cc.send();
cc.addEventListener("load", (res) => {
// 콜백함수
console.log(res); // 최종 API 요청 결과
});
});
});addEventListener대상 함수에 콜백 함수로 익명 함수를 전달하는 과정에서 계속 코드 들여쓰기가 깊어지고 있다.
이와 같이 콜백 함수로 비동기 결과를 처리하는 경우 콜백 지옥에 빠지는 문제점이 있다.
Promise
Promise는 비동기 작업이 맞이할 미래의 완료 또는 실패와 그 결과 값을 나타내는 객체이다.
- 비동기 작업이 종료된 이후 결과 값과 실패 사유를 처리하기 위한 처리기를 연결할 수 있다.
Promise는 곧바로 얻을 수 없지만, 추후 비동기 작업이 완료되면 받아올 수 있는 데이터에 대한 접근 수단의 역할을 한다.
Promise 객체는 3가지 상태를 갖는다.
- 대기(Pending): 비동기 처리가 아직 완료되지 않고 기다리고 있는 상태
- 이행(Fulfilled): 비동기 처리가 완료되어 결과값을 반환한 상태
- 실패(Rejected): 비동기 처리가 실패 또는 오류가 발생한 상태
Promise 객체를 생성할 때 콜백함수를 전달할 수 있다. 이때 전달하는 콜백함수는 자신의 인자로 비동기 처리 결과의 성공 유무에 따라 실행되는 resolve, reject 함수를 받는다.
new Promise((resolver, reject) => {
try {
// 비동기 API 요청
// ...
const result = "비동기 처리 결과";
resolver(result); // 비동기 처리 성공 시 실행할 함수 => then() 메서드와 연결
} catch (error) {
reject("비동기 처리 실패!"); // 비동기 처리 실패 시 실행할 함수 => catch() 메서드와 연결
}
})
.then(res => {
console.log(res); // 비동기 처리 결과
})
.catch(error => {
console.log(error); // 비동기 처리 실패!
});-
비동기 처리가 완료되면(
fulfilled)resolver함수가 호출된다. -
이 함수는 Promise 객체의
then()메서드와 연결된다.resolver함수에 전달한 값이then()메서드의 인자로 전달된다. -
비동기 처리가 실패하면(
rejected)reject함수가 호출된다. -
이 함수는 Promise 객체의
catch()메서드와 연결된다.reject함수에 전달한 값이catch()메서드의 인자로 전달된다.
Promise chaining
콜백 지옥의 문제점을 해결하기 위해 Promise를 사용할 수 있다. Promise의 then() 메서드를 사용하면 비동기 처리 결과를 들여쓰기 없이 처리할 수 있다.
axios의 get 메서드는 Promise 객체를 반환한다. 이 get 메서드의 요청에 대한 응답을 성공적으로 받으면 then() 메서드에서 그 응답 결과를 인자로 받을 수 있다.
axios
.get(`http://numbersapi.com/random?min=1&max=200`)
.then((res) => {
const result1 = res.data.split(" ")[0];
return axios.get(`https://koreanjson.com/posts/${result1}`);
})
.then((res) => {
const result2 = res.data.UserId;
return axios.get(`https://koreanjson.com/posts?userId=${result2}`);
})
.then((res) => {
// res 최종 결과
console.log(res);
});- then() 메서드 내부에서 axios의 get 메서드가 반환하는 Promise를 다시 return하면 get 메서드의 요청에 대한 응답 결과를 바로 아래의 then() 메서드의 인자로 전달할 수 있다.
이런 방식으로 then() 메서드를 들여쓰기 없이 계속 이어서 작성할 수 있다. 이것을 Promise chaining이라고 한다. Promise와 then() 메서드를 사용하여 콜백 지옥 문제를 해결할 수 있다.
Promise 방식의 문제점
Promise 방식의 문제점은 코드 실행 결과를 확신할 수 없다는 점이다.
console.log("1번째로 실행!");
axios
.get(`http://numbersapi.com/random?min=1&max=200`)
.then((res) => {
console.log("2번째로 실행!");
const result1 = res.data.split(" ")[0];
return axios.get(`https://koreanjson.com/posts/${result1}`);
})
.then((res) => {
console.log("3번째로 실행!");
const result2 = res.data.UserId;
return axios.get(`https://koreanjson.com/posts?userId=${result2}`);
})
.then((res) => {
console.log("4번째로 실행!");
// res 최종 결과
console.log(res);
});
console.log("5번째로 실행!");실행 결과는 다음과 같다.
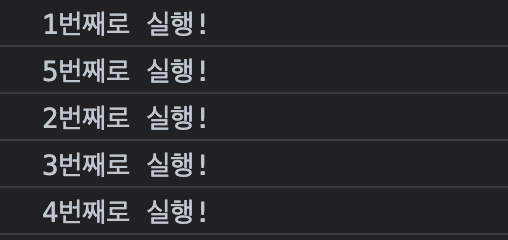
자바스크립트 코드는 동기적으로 실행되지만, axios는 비동기적으로 동작하기 때문에 위와 같은 결과가 나온다. 이런 Promise의 문제점 때문에 async-await이 등장하였다.
async와 await
정리
- 콜백 함수로 비동기 작업 결과를 처리하는 경우 콜백 지옥이 발생할 수 있다.
- 콜백 지옥은 콜백 함수를 익명 함수로 전달하는 과정에서 코드 들여쓰기가 깊어지는 현상으로, 코드 가독성을 매우 떨어뜨린다.
- 콜백 지옥을 해결하기 위해 ES6에서 Promise가 등장하였다.
- Promise는 비동기 작업이 맞이할 미래의 완료 또는 실패와 그 결과 값을 나타내는 객체다.
- Promise는 비동기 작업이 완료되면 받아오는 데이터에 대한 접근 수단의 역할을 한다.
- Promise는 코드 실행 결과를 예측하기 어렵게 한다는 문제점이 있다.
- Promise의 문제점을 해결하기 위해 ES7에서 async-await가 등장하였다.
- await은 Promise를 기다린다. 즉, 비동기 작업 결과를 기다린다.

