클래스 구조
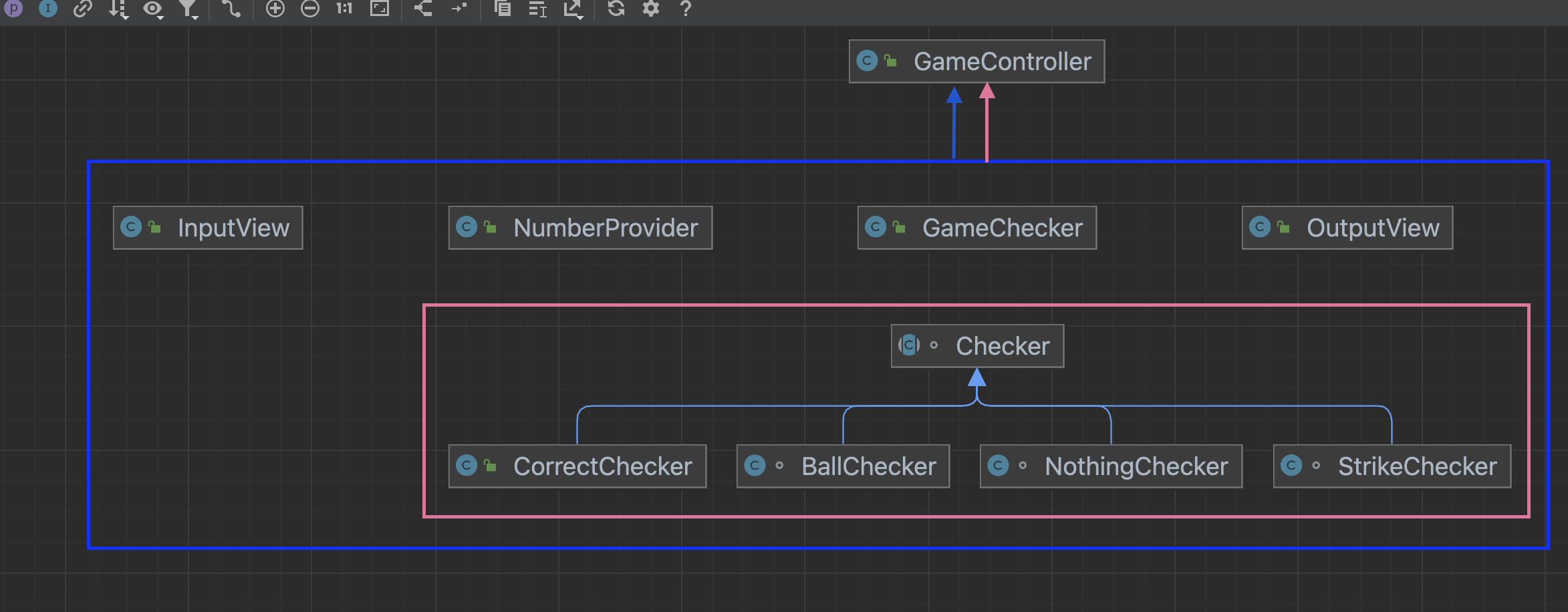
1. 사용자의 인펏을 받는 InputView
public class InputView {
private final BufferedReader br;
public InputView() {
this.br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
public String getInput() throws IOException {
System.out.println("숫자를 입력 해 주세요");
String input = br.readLine();
if (!isProperInput(input)) {
getInput();
}
return input;
}
public boolean wantContinue() throws IOException {
String input = br.readLine();
return input.equals("1");
}
public boolean isProperInput(String s) {
if (s.length() != 3) {
System.out.println("3자리 숫자를 입력해주세요");
return false;
}
try {
Integer.parseInt(s);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("숫자만 입력해주세요");
return false;
}
return true;
}
}- BufferedReader 이용, 사용자의 입력을 받는 부분
- OutputView 와 연결을 끊고싶어서 sout이 여기도 존재하는데, 이게 좋은 방식인지는 모르겠다
- "인풋을 받는다"의 책임이, 사용자에게 "인풋하라"라고 알리는 것 + 인풋을 실제로 받는 것 이렇게 두 개로 나뉘는 책임이라면, 조금 구조의 수정이 필요할 듯 하다
2. NumberProvider
public class NumberProvider {
public String makeRandomAnswer() {
List<Integer> digits = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
digits.add(i);
}
Collections.shuffle(digits);
int firstDigit = digits.get(0);
int secondDigit = digits.get(1);
int thirdDigit = digits.get(2);
int answer = firstDigit * 100 + secondDigit * 10 + thirdDigit;
return String.valueOf(answer);
}
}-
사용자와의 게임을 위해서 임의의 숫자를 만들고, String 타입으로 리턴하는 책임
-
임의의 숫자 만들기 + 숫자를 받아서 리턴하기 의 책임을 나누지 않은 이유는...너무 간단하니까 그러긴 했는데
-
그래도 나누는 게 좋겠다.
public class NumberProvider {
private int makeInteger() {
List<Integer> digits = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
digits.add(i);
}
Collections.shuffle(digits);
int firstDigit = digits.get(0);
int secondDigit = digits.get(1);
int thirdDigit = digits.get(2);
return firstDigit * 100 + secondDigit * 10 + thirdDigit;
}
public String makeRandomAnswer(){
return String.valueOf(this.makeInteger());
}
}- 나눈 모습. 난수 생성은 프라이빗으로 닫는다
3. Checker
이 녀석은(Checker) 입력받은 숫자가 정답(생성된 난수)랑 일치하는지 여부를 판별한다. 즉, 낫싱(아예 틀림) 볼(숫자는 맞는데 순서가 틀림) 개수, 스트라이크(숫자, 순서 둘 다 맞음) 개수, 정답(모든 숫자와 순서가 동일함) 을 판별한다.
비슷한 책임을 가지는 녀석이 여러개로 나뉘어서, 상속으로 구현했다 (조금 후회하긴 한다)
abstract class Checker {
public Checker() {
}
}- 상위 추상
class StrikeChecker extends Checker{
private int checkStrike(String aInput, String aAnswer){
return aInput.equals(aAnswer) ? 1 : 0;
}
public int countStrike(String input, String answer){
String[] inputs = input.split("");
String[] answers = answer.split("");
int strikeCount = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < inputs.length; i++) {
strikeCount += checkStrike(inputs[i], answers[i]);
}
return strikeCount;
}
}- 스트라이크 체커
class BallChecker extends Checker {
private int checkBall(String s, String answer){
return answer.contains(s) ? 1 : 0;
}
public int countBall(String input, String answer, int strikeCount){
String[] given = input.split("");
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(given));
int count = 0;
for (String s : set) {
count += checkBall(s, answer);
}
if (strikeCount != 0) count -= strikeCount;
return count;
}
}
- 볼체커
- Checker 를 상속하는 녀석들은 접근제한자가 없는데, 이것은 protected 로 설정된다 (즉, 자세한 구현체에 대한 접근은 다른 패키지에서 불가능하다. 오직 게임체커에 의존한다)
- 스트라이크인 숫자를 "빼야지" 온전한 볼이 된다
- 예를 들어 답이 123, 사용자가 321 을 입력했다면 3볼 1스트라이크 처리가 된다 (2는 스트라이크 조건 + 볼의 조건에 부합하므로)
- 따라서 스트라이크 카운트가 0이 아니라면, 해당 카운트를 빼줘야한다.
4. GameChecker
가장 아쉬운 녀석. 아쉬움이 남음
public class GameChecker {
private NothingChecker nothingChecker;
private CorrectChecker correctChecker;
private StrikeChecker strikeChecker;
private BallChecker ballChecker;
private void init() throws IOException {
this.ballChecker = new BallChecker();
this.correctChecker = new CorrectChecker();
this.nothingChecker = new NothingChecker();
this.strikeChecker = new StrikeChecker();
}
public String check(String input, String answer) throws IOException {
init();
if (this.correctChecker.isCorrect(input, answer)) return "정답";
int strikeCount = strikeChecker.countStrike(input, answer);
int ballCount = ballChecker.countBall(input, answer, strikeCount);
if (nothingChecker.isNothing(strikeCount, ballCount)) return "낫싱";
String ball = ballCount + "볼";
if (strikeCount == 0 && ballCount != 0) return ball;
String strike = strikeCount + "스트라이크";
if (ballCount == 0 && strikeCount != 0) return strike;
return strike + ball;
}
}-
체커를 의존 주입 형식으로 받는다면, nothingChecker 등을 protected로 해둔 의미가 없어진다...(밖에서 꺼내가지 못하도록 막아두는 차원에서 checker의 하위 패키지에서만 사용 가능하게 했다)
-
그러나, init() 이라는 매서드를 통해서 체크할 때마다 초기화 하는것도 이상하다.
-
이 부분은...그냥 게임체커 인스턴스가 생성 될 때 (생성자가 호출 될 때) 함께 초기화하는것으로 해야할 듯 하다...
package baseboll.checker;
import java.io.IOException;
public class GameChecker {
private NothingChecker nothingChecker;
private CorrectChecker correctChecker;
private StrikeChecker strikeChecker;
private BallChecker ballChecker;
public GameChecker() {
init();
}
private void init() {
this.ballChecker = new BallChecker();
this.correctChecker = new CorrectChecker();
this.nothingChecker = new NothingChecker();
this.strikeChecker = new StrikeChecker();
}
public String check(String input, String answer){
if (this.correctChecker.isCorrect(input, answer)) return "정답";
int strikeCount = strikeChecker.countStrike(input, answer);
int ballCount = ballChecker.countBall(input, answer, strikeCount);
if (nothingChecker.isNothing(strikeCount, ballCount)) return "낫싱";
String ball = ballCount + "볼";
if (strikeCount == 0 && ballCount != 0) return ball;
String strike = strikeCount + "스트라이크";
if (ballCount == 0 && strikeCount != 0) return strike;
return strike + ball;
}
}- 정말 이게 최선인가???
- 강의 듣고 개선하자...
5. OutputView
public class OutputView {
public void nothing(){
System.out.println("낫싱");
}
public void gameEnd(){
System.out.println("3개의 숫자를 모두 맞히셨습니다! 게임 종료" + "\n" + "게임을 새로 시작하려면 1, 종료하려면 2를 입력하세요.");
}
public void sendOutput(String checkResult){
if (checkResult.equals("정답")) {
gameEnd();
return;
}
if (checkResult.equals("낫싱")) {
nothing();
return;
}
if (checkResult.equals("")) return;
System.out.println(checkResult);
}
}-
정말 출력만 해주는 녀석
-
사실상 제일 깔끔한것 아닐까?...
6. GameController
public class GameController {
private final InputView inputView;
private final OutputView outputView;
private final GameChecker gameChecker;
private final NumberProvider numberProvider;
public GameController(InputView inputView, OutputView outputView, GameChecker gameChecker, NumberProvider numberProvider) {
this.inputView = inputView;
this.outputView = outputView;
this.gameChecker = gameChecker;
this.numberProvider = numberProvider;
}
private boolean correct(String input, String answer) {
return input.equals(answer);
}
public void game() throws IOException {
String answer = numberProvider.makeRandomAnswer();
System.out.println(answer);
String input = "";
while (!correct(input, answer)){
input = inputView.getInput(); // 인펏부터 받는다
String checked = gameChecker.check(input, answer);
outputView.sendOutput(checked);
}
if (inputView.wantContinue()) game();
}
}-
여기서도 protected 로 숨긴 폐해가 나온다 (correct가 저기 왜있음?)
-
어쨌든, 위의 모든 요소들을 의존 주입 받아서 사용자에게 game() 이라는 매서드만 노출해주는 녀석
어려워!!!
돌려보자
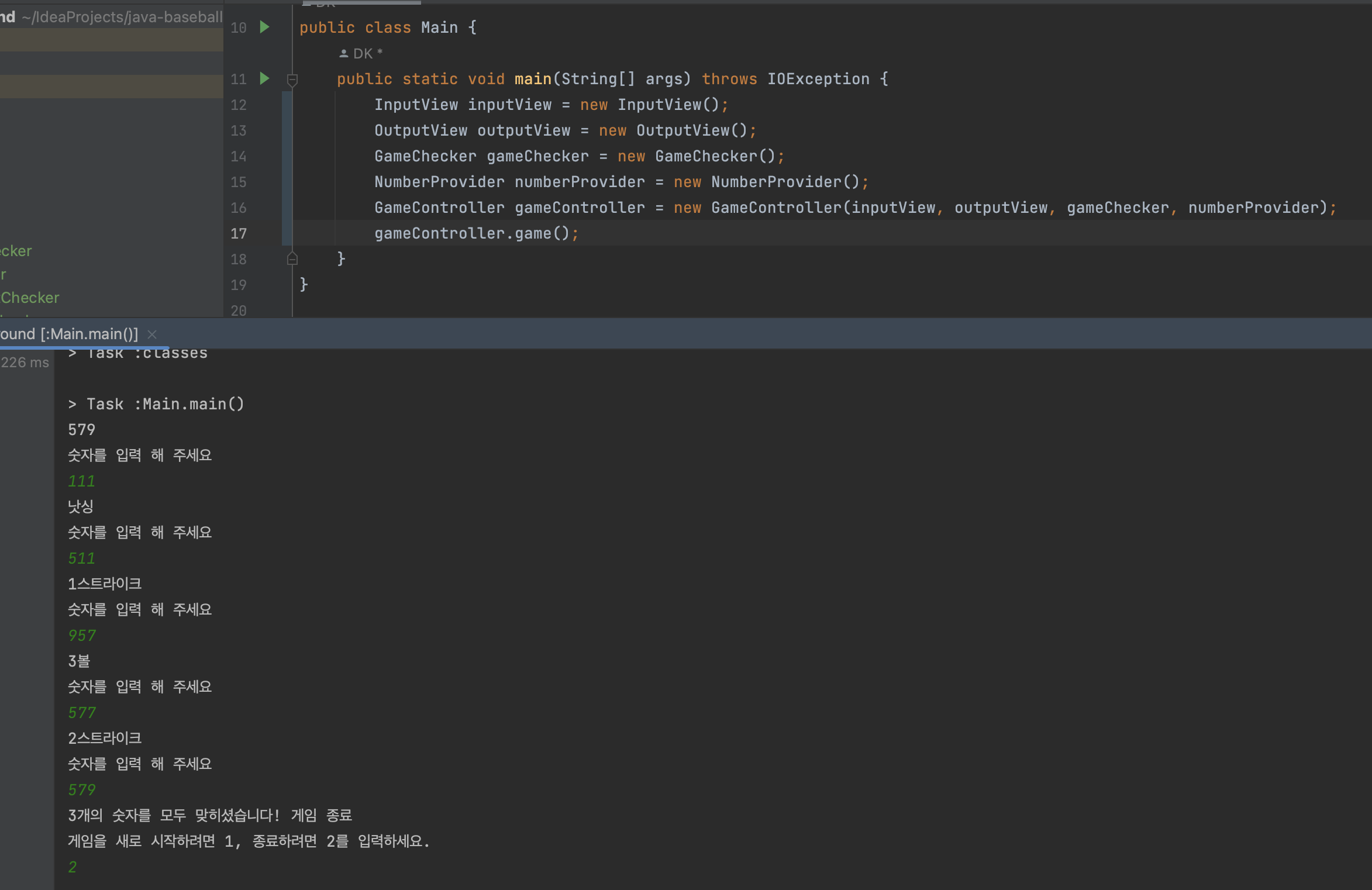
잘 나오는 모습.(답이 먼저 나오는 것은 테스트 용이성을 위해...)
테스트코드도 작성중인데, 어느 정도 범위로 해야할지 모르겠다!
