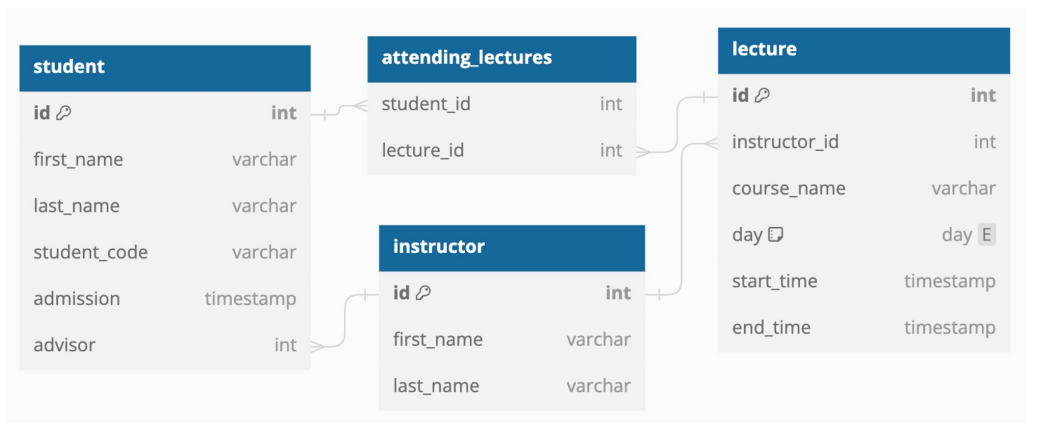
외래키
외래키(Foreign Key)는 관계형 데이터베이스에서 한 테이블의 열(또는 열의 집합)로 다른 테이블의 기본키를 참조하는 열을 의미한다.
기본키란?
DB에서 기본키(Primary Key)는 데이터베이스 테이블의 각 레코드(행)를 고유하게 식별하는 열(또는 열의 집합)을 의미한다.
테이블에서 관계는 외래키를 이용하여 표현한다.
외래키를 통해 맺어지는 관계는 크게 3가지로 나눌 수 있다.
1:1 One to One 관계
- 테이블의 하나의 레코드가 다른 테이블의 하나의 레코드와 연관된다.
- 데이터베이스의 성능이나 보안을 위해 테이블을 나누는 경우가 많다.
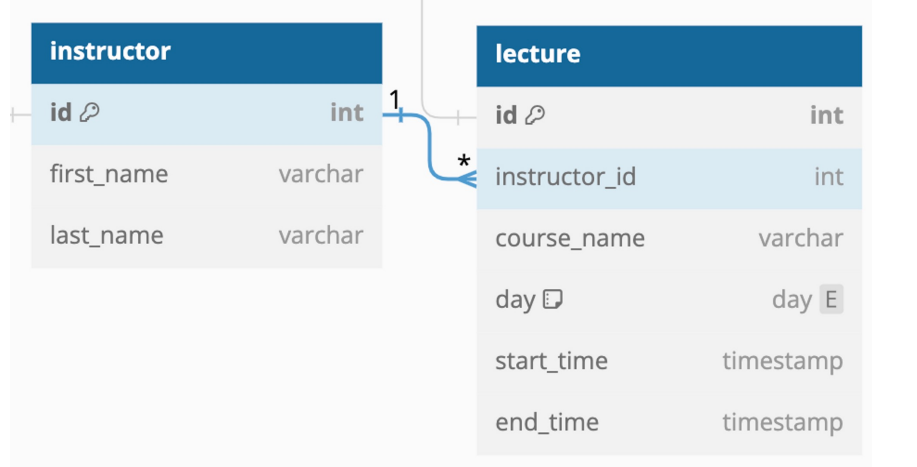
N:1 Many to One 관계
- 테이블의 레코드 0개 이상이 다른 테이블 레코드 1개와 연관된다.
- ex) 게시글과 댓글, 가게와 상품 관계
M:N Many to Many 관계
- 테이블의 레코드 0개 이상이 다른 테이블 레코드 0개 이상과 연관된다.
- 두 테이블의 PK들를 외래키로 가진 테이블을 Associative Table, Join Table이라고 부른다.
ORM
-
객체 관계 매핑(Object-Relational Mapping)
-
객체 지향 프로그래밍 언어와 관계형 데이터베이스 간의 데이터 변환을 자동화하는 기술
-
테이블의 데이터를 표현하기 위해 등장한 기술이다.
-
ORM을 사용하면 테이블간 관계를 Entity의 필드로 표현이 가능.
ERD
N:1
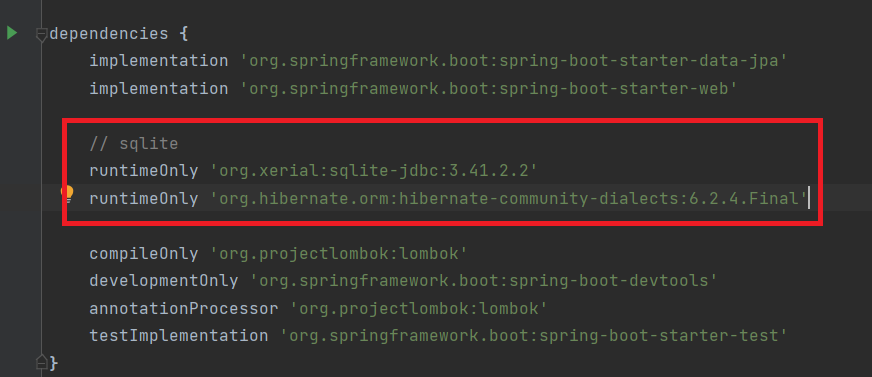
build.gradle
Entity 생성하기
@Data
@Entity
public class Instructor {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
}@Data
@Entity
public class Lecture {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String name;
private String day;
private Integer startTime;
private Integer endTime;
}
- N : 1 관계를 맺을 Entity인
Lecture에 해당 필드를 추가

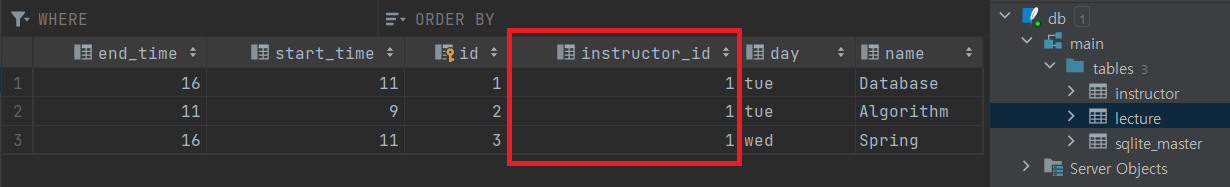
실행하면 아래와 같이 추가했던 Instructor instructor 필드가 아닌 instuctor_id로 변환되어 들어갔음을 알 수 있다.
data.sql 생성
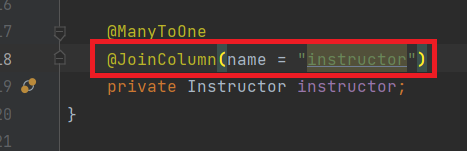
@JoinColumn 이란 OneToOne, OneToMany, ManyToMany 등의 관계에서 외래 키(Foreign Key)를 지정하는데 사용할 수 있다. (FK 이름 변경)
Lecture Controller
// 로거 설정
@Slf4j
// Spring Boot 요청 URL 엔드포인트
@RestController
@RequestMapping("lectures")
// 의존성 주입 위한 생성자 자동 생성
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class LectureController {
private final LectureRepository lectureRepository;
private final InstructorRepository instructorRepository;
// 강의에 강사를 배정한다.
@PutMapping("{id}/instructor/{instructorId}")
// 응답 바디가 없을 것이다.
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT)
public void updateLectureInstructor(
@PathVariable("id") Long id,
@PathVariable("instructorId") Long instructorID
) {
Optional<Lecture> optionalLecture
= lectureRepository.findById(id);
if (optionalLecture.isEmpty()) throw new ResponseStatusException(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
Optional<Instructor> optionalInstructor = instructorRepository.findById(instructorID);
if (optionalInstructor.isEmpty()) throw new ResponseStatusException(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
Lecture lecture = optionalLecture.get();
Instructor instructor = optionalInstructor.get();
// 그냥 Java 객체 쓰듯이
// 데이터를 할당 후 save 해준다.
lecture.setInstructor(instructor);
lectureRepository.save(lecture);
}
// id 강의의 강사를 반환하는 엔드포인트
@GetMapping("{id}/instructor")
public void readLectureInstructor(Long id) {
Optional<Lecture> optionalLecture = lectureRepository.findById(id);
if (optionalLecture.isEmpty()) throw new ResponseStatusException(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
Lecture lecture = optionalLecture.get();
Instructor instructor = lecture.getInstructor();
log.info(instructor.toString());
// 위를 체인 형식으로 엮은 것
// log.info(optionalLecture.get().getInstructor().toString());
}
}Instructor Controller
@RestController
@Slf4j
@RequestMapping("instructor")
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class InstructorController {
private final InstructorRepository instructorRepository;
@GetMapping("{id}/lectures")
public void readInstructorLectures(
@PathVariable("id") Long id
) {
Optional<Instructor> optionalInstructor = instructorRepository.findById(id);
Instructor instructor = optionalInstructor.get();
for (Lecture lecture: instructor.getLecture()) {
log.info(lecture.getName());
}
}
}Postman 요청
PUT /lectures/{id}/instructor/{id}
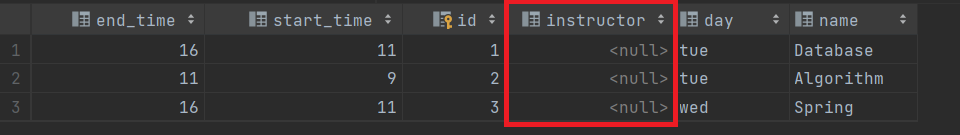

PUT 요청을 보내면 응답은 204 NO_CONTENT 로 뜨면서
lecture 테이블에 instuctor 가 입력되고, lecture 테이블이 instuctor와 관계를 가지고 있음을 확인할 수 있다.
1:N
위에 등장한 ManyToOne에서는 일대다 관계를 설정하는 필드가 Lecture에만 존재한다.
하지만 상황에 따라 Instructor에서 Lecture를 활용하고 싶을 수도 있다.
예를 들어, 어떤 Instructor 의 Lecture 정보를 다 알고 싶다고 가정하면, 테이블을 기준으로 했을 때 해당 Instructor 의 PK를 기준으로 Lecture 테이블의 FK를 검색할 것이다.
위 과정을 두 가지 방법으로 구현이 가능하다.
1. JpaRepository 에 Query Method 추가
Entity (수정 X)
LectureRepository
public interface LectureRepository extends JpaRepository<Lecture, Long> {
List<Lecture> findAllByInstructor(Instructor entity);
List<Lecture> findAllByInstructorId(Long id);
}InstructorController
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("instructor")
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class InstructorController {
private final InstructorRepository instructorRepository;
@GetMapping("{id}/lectures")
public void readInstructorLectures(
@PathVariable("id") Long id
) {
Optional<Instructor> optionalInstructor = instructorRepository.findById(id);
Instructor instructor = optionalInstructor.get();
for (Lecture lecture: instructor.getLectures()) {
log.info(lecture.getName());
}
}
}2. Instructor 에 @OneToMany 추가
Entity 수정
@Data
@Entity
public class Instructor {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "instructor")
private List<Lecture> lectures;
}JPA가 서로의 관계가 다르다고 인식할 수 있으므로 같은 관계임을 나타내주는 mappedBy를 써준다.
이 때, mappedBy 는 반대쪽 @ManyToOne 어노테이션이 붙은 필드의 이름이 작성된다. 이는 각각 entity의 관계가 저장될 때, 어느 쪽 데이터가 우선되어 저장될지를 정의하기 위한 요소이다.
(@ManyToOne 필드 쪽을 우선시 하도록 개발하는게 권장함)
M:N
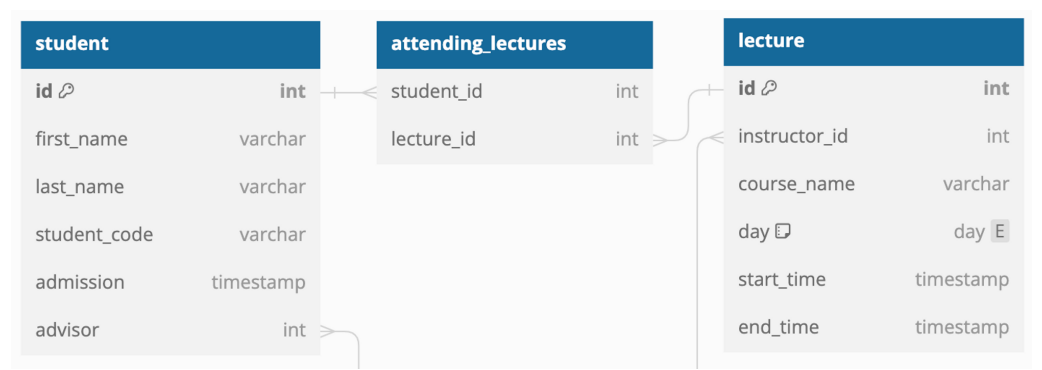
Entity 생성하기
@Entity
public class Student {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
@ManyToMany
private List<Lecture> attending;
}Student 객체에서 자신이 속한 강의를 조회하기 위해 List<Lecture> 타입의 필드를 가져야 한다.
LectureEntity 수정
@Entity
public class Lecture {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String name;
private String day;
private Integer startTime;
private Integer endTime;
@ManyToOne
// @JoinColumn(name = "instructor")
private Instructor instructor;
@ManyToMany(mappedBy = "attending")
private List<Student> students;
}Lecture 객체에서 자기 수업에 포함된 모든 Student를 조회하려면 List<Student> 타입의 필드를 가져야 한다.
mappedBy의 값은 반대쪽에 자신이 매핑되어 있는 필드명을 써주면 되기 때문에 Student 테이블의 List<Lectures> 객체인 attending 입력한다.
StudentController
@RestController
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@RequestMapping("students")
public class StudentController {
private final StudentRepository studentRepository;
private final LectureRepository lectureRepository;
@PutMapping("{id}/lectures/{lectureId}")
public void updateStudentLectures(
@PathVariable("id") Long id,
@PathVariable("lectureId") Long lectureId
){
Optional<Student> optionalStudent = studentRepository.findById(id);
if(optionalStudent.isEmpty())
throw new ResponseStatusException(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
Optional<Lecture> optionalLecture = lectureRepository.findById(lectureId);
if(optionalLecture.isEmpty())
throw new ResponseStatusException(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
Student student = optionalStudent.get();
Lecture lecture = optionalLecture.get();
student.getAttending().add(lecture);
// student.getAttending().remove(lecture);
studentRepository.save(student);
}
}.add(lecture)를 이용해 컬렉션에 데이터를 넣고 데이터베이스에 저장한다.
.remove(lecture)를 이용해 컬렉션에 넣었던 데이터를 삭제한다.
( 생성된 연결 (Join) 테이블에 데이터를 넣기 위해 필요한 작업으로 Student 엔티티에서 @JoinTable(name = “attending_lectures”)를 붙여주었을 때 연결 테이블에 저장하기 위한 과정 )
Postman 요청
PUT /student/{id}/lectures/{id}
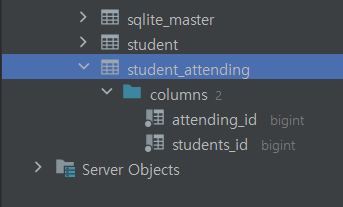
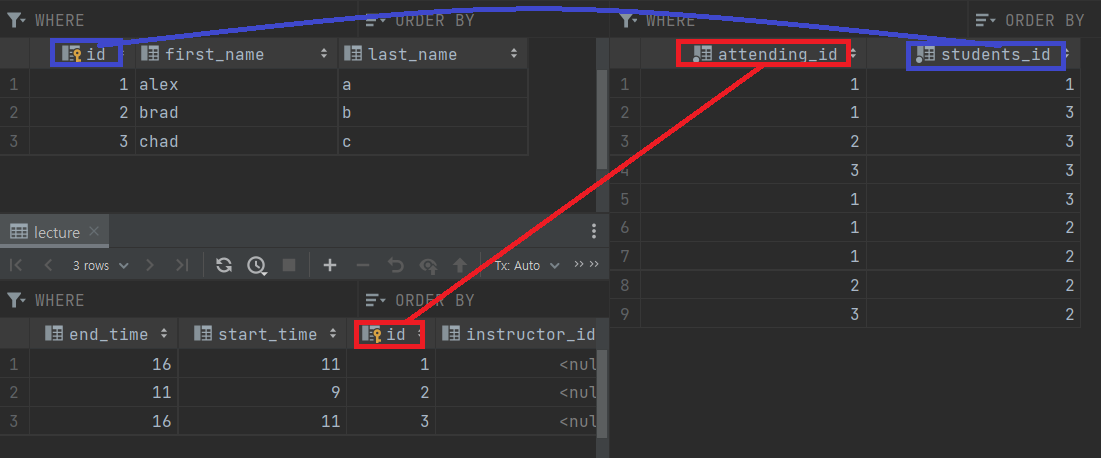
student_attending 테이블에 데이터가 들어온 것을 확인할 수 있으며,
lectureId 에 해당하는 student 들의 목록과, 어떤 강의를 듣는지가 나와있다.
출처 : 멋사 5기 백엔드 위키 6팀 식스센스
