Stack 계산기
중위표기법 계산
일반적인 수식
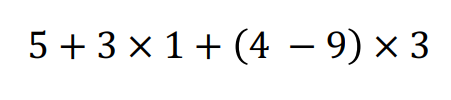
후위표기법 계산
컴퓨터는 중위표기법에서 연산의 우선순위를 판단할 수 없다.
연산자의 우선순위를 고려하여 연산자를 뒤쪽에 배치하는 방식이다.
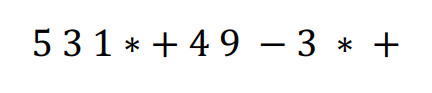
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Stack;
public class PostfixCalculation {
public void solution() throws IOException {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String input = reader.readLine();
Stack<Integer> digitStack = new Stack<>();
for (int i = 0; i < input.length(); i++) {
char token = input.charAt(i);
// 1. 숫자라면, 스택에 push한다.
// Character.isDigit(token) // token이 숫자가 표현된 글자인지 판단하는 메소드
// token을 int로 변환 => token - '0'
if (Character.isDigit(token)) {
digitStack.push(token - '0');
}
// 2. 숫자가 아니라면, (연산자) 스택에서 두 번 pop하고 계산한다.
else {
int numRight = digitStack.pop();
int numLeft = digitStack.pop();
switch (token) {
case '+':
digitStack.push(numLeft + numRight);
break;
case '-':
digitStack.push(numLeft - numRight);
break;
case '*':
digitStack.push(numLeft * numRight);
break;
case '/':
digitStack.push(numLeft / numRight);
break;
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("invalid operator");
}
}
}
int answer = digitStack.pop();
if (digitStack.empty())
System.out.println(answer);
else System.out.println("error");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
new PostfixCalculation().solution();
}
}

후위표기법 변환
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Stack;
public class InfixToPostfix {
private boolean isOperator(char token) {
return token == '(' || token == '+' || token == '-' || token == '*' || token == '/';
}
public void solution() throws IOException {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String input = reader.readLine();
// 결과를 담아둘 StringBuilder
StringBuilder answerBuilder = new StringBuilder();
// 연산자 담는 스택
Stack<Character> operStack = new Stack<>();
// 문자 단위로 순회
for (int i = 0; i < input.length(); i++) {
char token = input.charAt(i);
// 연산자 (+, -, *, /, '(')일 때
if(token == '(') {
operStack.push(token);
}
// 닫는 괄호일 때
else if(token == '*' || token == '/') {
while(!operStack.empty() && (operStack.peek() == '*' || operStack.peek() == '/'))
answerBuilder.append(operStack.pop());
operStack.push(token);
}
else if(token == '+' || token == '-'){
while(!operStack.empty() && operStack.peek() != '(')
answerBuilder.append(operStack.pop());
operStack.push(token);
}
else if(token == ')'){
char top = operStack.pop();
while(!operStack.empty() && top != '('){
answerBuilder.append(top);
top = operStack.pop();
}
}
else answerBuilder.append(token);
}
while (!operStack.empty()) {
answerBuilder.append(operStack.pop());
}
System.out.println(answerBuilder);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
new InfixToPostfix().solution();
}
}
DFS(깊이 우선 탐색)
한 쪽 갈림길을 택해서 갈 수 있는 최대의 깊이로 들어가면서 그래프를 탐색하는 방법이다.
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Stack;
public class DepthFirstSearch {
public void solution() throws IOException {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
// 첫 입력은 정점의 개수
int maxNodes = Integer.parseInt(reader.readLine());
// 정점간 연결 정보
int[][] edgeMap = new int[maxNodes + 1][maxNodes + 1];
// 1 2 1 3 2 4 2 5 4 6 5 6 6 7 3 7
String[] edges = reader.readLine().split(" ");
// 두 개씩 순회
for (int i = 0; i < edges.length / 2; i++) {
int leftNode = Integer.parseInt(edges[i * 2]); // 0, 2, 4, ...
int rightNode = Integer.parseInt(edges[i * 2 + 1]); // 1, 3, 5, ...
edgeMap[leftNode][rightNode] = 1;
edgeMap[rightNode][leftNode] = 1;
}
// 다음에 방문할 점들을 담아주는 스택
Stack<Integer> toVisit = new Stack<>();
// 방문을 기록하는 용도의 배열
boolean[] visited = new boolean[maxNodes + 1];
// 여기부터 DFS
// 첫 방문 대상 선정 (1)
int next = 1;
// 대상을 스택에 push
toVisit.push(next);
// 스택이 비어있을 때까지 반복하는 while
while (!toVisit.empty()) {
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
new DepthFirstSearch().solution();
}
}
MyBatis
객체 지향 언어인 자바의 관계형 데이터베이스 프로그래밍을 좀 더 쉽게 할 수 있게 도와 주는 개발 프레임 워크이다.
mybatis 프로젝트 생성
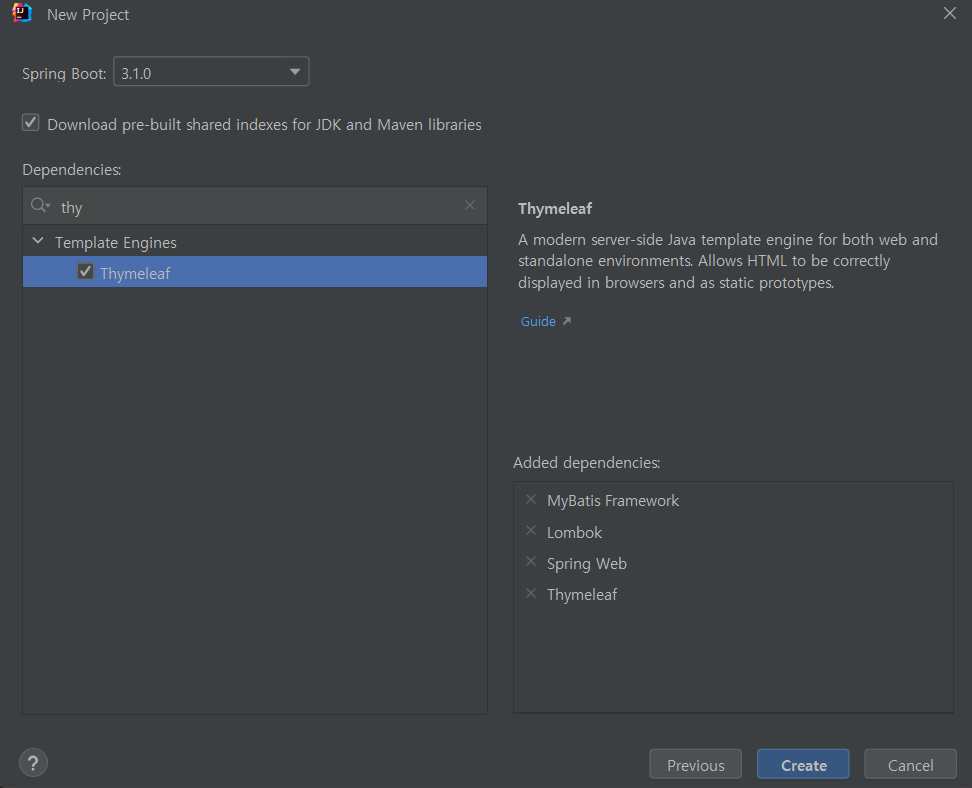
build.gradle의 dependencies에 SQLite관련 라이브러리 추가
db등록 - Database - SQLite 생성
application.yaml 생성 후 설정
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:sqlite:db.sqlite
driver-class-name: org.sqlite.JDBC
# username: sa
# password: password
mybatis:
mapper-locations: "classpath:mybatis/mappers/*.xml"
type-aliases-package: "com.example.mybatis.model"
configuration:
map-underscore-to-camel-case: truedml.sql 작성 후 db.sqlite에 데이터 추가
INSERT INTO students (name, age, phone, email)
VALUES ('alex', 35, '010-1234-5678', 'alex@gmail.com');
INSERT INTO students (name, age, phone, email)
VALUES ('brad', 35, '010-1234-5678', 'brad@gmail.com');
INSERT INTO students (name, age, phone, email)
VALUES ('chad', 35, '010-1234-5678', 'chad@gmail.com');
select * from students;Mybatis Mapper 방법
@Mapper 어노테이션 사용
StudentMapper.interface
package com.example.mybatis.mapper;
import com.example.mybatis.model.Student;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.*;
import java.util.List;
@Mapper // MyBatis가 Mapper가 붙은 클래스를 데이터베이스 통신에 사용할 준비
public interface StudentMapper {
// INSERT INTO students (name, age, phone, email)
// VALUE (?, ?, ?, ?);
@Insert("INSERT INTO students (name, age, phone, email)" +
"VALUES (#{name}, #{age}, #{phone}, #{email})")
void insertStudent(Student student);
// SELECT * FROM students; 를 실행할 메소드를 만드는데
// 복수 개의 Students를 반환하게 하는 반환 return 타입 -> List<Student>
@Select("SELECT * FROM students")
List<Student> selectStudentAll();
@Select("SELECT * FROM students WHERE id = #{id}")
Student selectStudent(Long id);
@Update("UPDATE students SET " +
"name = #{name}, " +
"age = #{age}, " +
"phone = #{phone}, " +
"email = #{email}, " +
"WHERE id = #{id}")
void updateStudent(Student student);
@Delete("DELETE FROM students " +
"WHERE id = #{id}")
void deleteStudent(Long id);
}
XML 파일 사용
StudentMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.example.mybatis.mapper.StudentXmlMapper">
<select id="selectStudentAll" resultType="Student">
SELECT * FROM students;
</select>
<select id="selectStudentAll" resultType="Student" parameterType="Long">
SELECT * FROM students WHERE id = #{id};
</select>
</mapper>
- 디렉토리 생성 시 "." 주의 할 것. (패키지와 다르게 이름으로 판단됨)
Student.class
package com.example.mybatis.model;
import lombok.*;
@Data
//@Getter
//@Setter
//@RequiredArgsConstructor
//@ToString
//@EqualsAndHashCode
public class Student {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String phone;
private String email;
}
StudentXmlMapper.interface
package com.example.mybatis.mapper;
import com.example.mybatis.model.Student;
import java.util.List;
public interface StudentXmlMapper {
List<Student> selectStudentAll();
Student selectStudent(Long id);
}
StudentDao.class
package com.example.mybatis.dao;
import com.example.mybatis.mapper.StudentMapper;
import com.example.mybatis.mapper.StudentXmlMapper;
import com.example.mybatis.model.Student;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.List;
@Repository
public class StudentDao {
private final SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory;
public StudentDao(SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory) {
this.sessionFactory = sessionFactory;
}
public List<Student> readStudentsAll() {
try (SqlSession session = sessionFactory.openSession()) {
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
return studentMapper.selectStudentAll();
}
}
public void createStudent(Student student) {
try (SqlSession session = sessionFactory.openSession()) {
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
studentMapper.insertStudent(student);
}
}
public Student readStudent(Long id) {
try (SqlSession session = sessionFactory.openSession()){
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
return studentMapper.selectStudent(id);
}
}
public List<Student> readAllXml() {
try (SqlSession session = sessionFactory.openSession()){
StudentXmlMapper studentXmlMapper = session.getMapper(StudentXmlMapper.class);
return studentXmlMapper.selectStudentAll();
}
}
}
MybatisApplication.class
package com.example.mybatis;
import com.example.mybatis.dao.StudentDao;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class MybatisApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext
= SpringApplication.run(MybatisApplication.class, args);
StudentDao dao = applicationContext.getBean(StudentDao.class);
// System.out.println(dao.readStudentsAll());
//
// System.out.println(dao.readStudent(1L));
// System.out.println(dao.readStudent(2L));
// System.out.println(dao.readStudent(3L));
System.out.println(dao.readAllXml());
}
}
인사이트 타임
문자열로 변환
https://school.programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/181845
class Solution {
public String solution(int n) {
return String.format("%d", n);
}
}easy
연속된 수의 합
https://school.programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/120923
생각해낸 첫 번째 방법은 반복문의 i의 합이 total과 같아지면 i의 값을 배열에 넣기 - 실패
두 번째 방법은 num이 홀수라면 결과 값의 가운데의, 짝수라면 가운데 +1의 인덱스에 total / num 을 넣고 나머지 인덱스 채우기 - 실패
구상은 할 수 있었지만 코드를 못 짜서 못 풀었다.
이 어려운걸 원기님과 태환님이 각 방법으로 풀어 주셨다 ㄷㄷ
다음에 재도전!
review
오늘은 오전 오후 수업 내용이 전부 어려웠다. 어제가 위키 작성일인게 정말 천만다행이라고 생각하게 된 하루였다. 배운 내용 전부 처음 보는 것들이었고 수강생 대부분이 많은 오류로 고생하는 수업이었는데 그나마 오류가 안나서 덜 고생한 것 같다. 정말 하루하루 배워야할 것들이 산더미처럼 늘어나는 것 같다.
