📌 단방향 LinkedList 구현
🔥 Idea
🧿 Code
public class OnePathLinkedList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node n = new Node(1);
n.append(2);
n.append(3);
n.append(3);
n.append(4);
n.retrieve();
n.delete(3);
n.retrieve();
}
static class Node{
int val;
Node next;
Node(int val){
this.val=val;
}
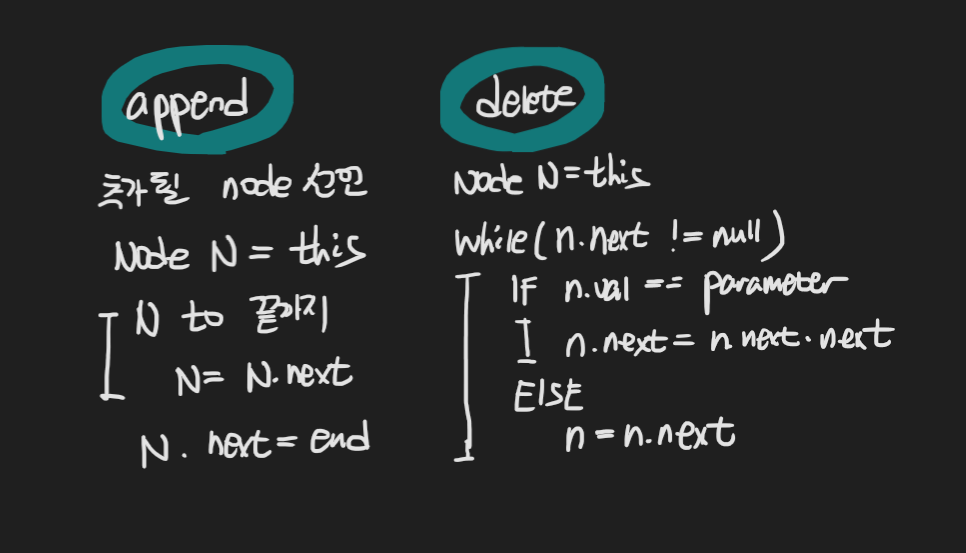
void append(int d){
Node end = new Node(d);
Node n = this;
while(n.next!=null){
n=n.next;
}
n.next=end;
}
void delete(int d){
Node n = this;
while(n.next!=null){
if(n.next.val==d){
n.next=n.next.next;
}else{
n=n.next;
}
}
}
void retrieve(){
Node n = this;
while(n.next!=null){
System.out.println("n.val -> " + n.val);
n=n.next;
}
System.out.println(n.val);
}
}
}-
참조 포인터 활용
-
while(n.next!=null)
-
삭제시, 지우기 = 그냥 다음것에 연결해주면 됨
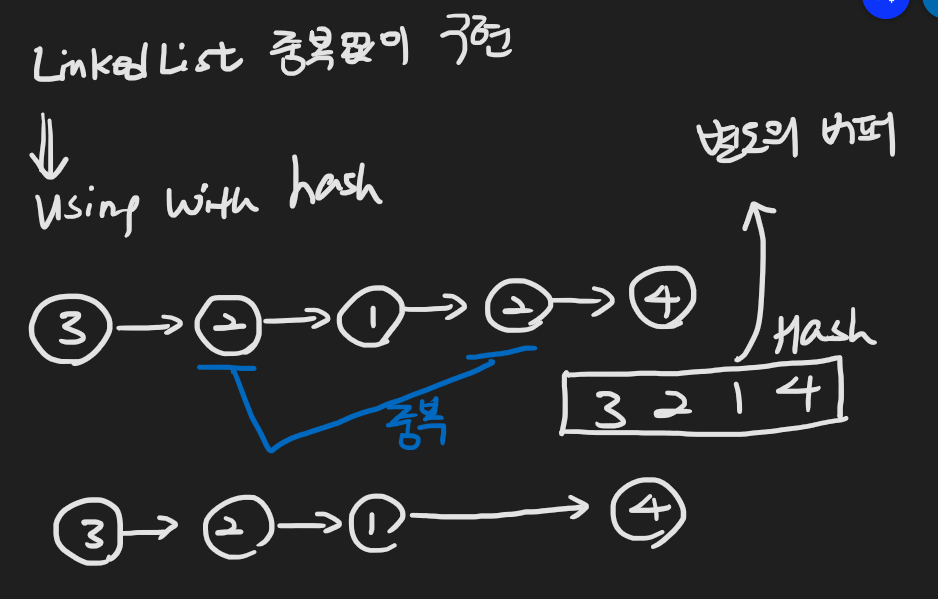
📌 LinkedList 중복 없이 구현
🔥 Hash 이용
🧿 Code
public class LinkedListNode {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList ln = new LinkedList();
ln.append(1);
ln.append(1);
ln.append(3);
ln.append(3);
ln.append(3);
ln.removeDups();
ln.retrieve();
}
static class LinkedList{
Node header;
static class Node{
int data;
Node next = null;
}
LinkedList(){
header = new Node();
}
void append(int d){
Node n = header;
while(n.next!=null){
n= n.next;
}
Node end = new Node();
end.data = d;
n.next=end;
}
void delete(int d){
Node n = header;
while(n.next!=null){
if(n.next.data==d){
n.next=n.next.next;
}else{
n=n.next;
}
}
}
void retrieve(){
Node n = header.next;
while(n.next!=null){
System.out.println("n.data -> " + n.data);
n=n.next;
}
System.out.println("n.data -> " + n.data);
}
/*
버퍼를 사용하지 않고 중복되는 값 삭제하는 방법
pointer 를 이용 ( 강좌에서는 러너라고 부름 )
*/
void removeDups(){
Node n = header;
while(n!=null &&n.next!=null){
Node r = n;
while(r.next!=null){
if(n.data==r.next.data){
r.next=r.next.next;
}else{
r=r.next;
}
}
n=n.next;
}
}
}
}📌 뒤에서 n번째 값 찾기
🔥 1번째 방법
전체 길이 센 다음에, 앞에서부터 들어가서 몇 번째(K)인지 찾고 전체 길이 - K
🧿 Code
public class FindLinkedListDESC {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node node = new Node(1);
node.append(2);
node.append(3);
node.append(4);
int k=2;
Node solution = solution(node, k);
System.out.println(solution.val);
}
private static Node solution(Node node, int k) {
Node n = node;
int total=0;
while(n.next!=null){
n=n.next;
total++;
}
total++;
n=node;
// 예시로 따라가보면 범위 값이 정해짐.
// 만약 total=4, k=2 라면 찾는 값의 위치는 total-k+1 임.
// i가 1부터인 이유는 노드의 개수를 구하는게 아니라, 화살표의 갯수를 구하는 것이기 때문
for(int i=1;i<total-k+1;i++){
n=n.next;
}
return n;
}
static class Node{
int val;
Node next;
Node(int val){
this.val=val;
}
void append(int d){
Node end = new Node(d);
Node n = this;
while(n.next!=null){
n=n.next;
}
n.next=end;
}
}
}🔥 2번째 방법 - 규칙성
재귀 이용
마지막까지 간 다음에, 마지막에서 부터 +1 해서 찾음
🧿 Code
public class FindLinkedListDESC_Recursive {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node n = new Node(1);
for(int i=2;i<10;i++){
n.append(i);
}
int k=3;
int solution = solution(n, k);
}
private static int solution(Node n, int k) {
if(n==null) return 0;
int count=0;
count = solution(n.next, k)+1;
if(count==k){
System.out.println("뒤에서 " + k+ "번째 값은 = " + n.val);
}
return count;
}
static class Node{
int val;
Node next;
Node(int val){
this.val=val;
}
void append(int d){
Node end = new Node(d);
Node n = this;
while(n.next!=null){
n=n.next;
}
n.next=end;
}
void retrieve(){
Node n = this;
while(n.next!=null){
System.out.println("n.val = " + n.val);
n=n.next;
}
System.out.println("n.val = " + n.val);
}
}
}근데 위 방법에는 문제가 존재.
count를 return 해야 recursive를 이용할 수 있는데, count를 return 하면 답을 못찾음
🔥 두번째 방법 - Recursive
객체나 배열은 stack frame에 pointer만 저장한다.
count를 객체 안에 넣어서 객체의 주소를 전달
🧿 부분 코드
private static Node solution(Node n, int k,Reference r) {
if(n==null) return null;
Node found = solution(n.next, k,r);
r.count++;
if(r.count==k){
return n;
}
return found;
}
static class Reference{
int count;
}-
Reference라는 참조값을 전달한다.
-
참조값 안의 count를 증가시킨다.
🔥 Recursive
public class Recursive_test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a = new A();
int sum = a.sum(100);
System.out.println(sum);
}
static class A{
int sum(int var){
if(var == 1){
return 1;
}else{
return var + sum(var-1);
}
}
}
}- recursive에는 초기값을 멈춰줄 if condition 과 값을 지속해서 return 해서 쌓을 값을 만들어줄 return 이 필요하다.
🔥 3번째 방법 - pointer
포인터 이용
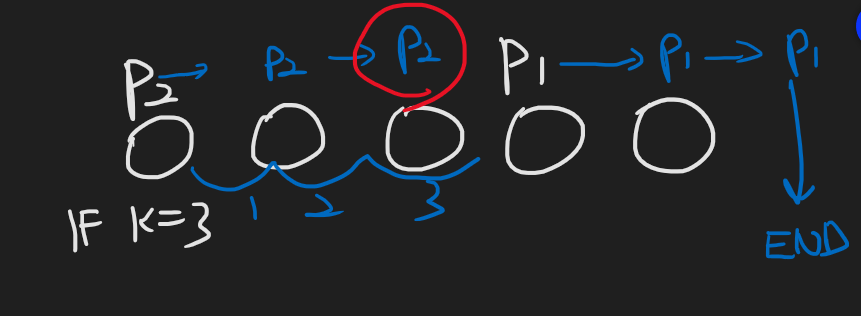
포인터를 두개 선언
하나는 기준 포인터(위에선 P2)에서 K만큼 떨어져서 앞으로 가게 둠
P2와 P1을 같이 가게 둔다
P1의 값이 null 이면 멈춘다
그러면 그 때의 P2의 값이 정답.
🧿 Code
private static Node solution(Node n, int k) {
Node p1 = n;
Node p2 = n;
for(int i=0;i<k;i++){
if(p1==null) return null;
p1=p1.next;
}
while(p1!=null){
p1=p1.next;
p2=p2.next;
}
return p2;
}📌 참조 영상
엔지니어 대한민국
