📌 Thread 란
실제 프로그램이 수행되는 작업의 최소 단위. 하나의 프로세스는 하나 이상의 Thread를 가진다.
📌 구현방법
1. Thread class 상속
public class ThreadPractice {
public static void main(String[] args) {
A t1 = new A();
A t2 = new A();
t1.start();
t2.start();
System.out.println("finish");
}
}
class A extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
int i;
for(i=0;i<50;i++){
System.out.print(i + "\t");
try {
sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}-
run() 구현 후 start() 를 하면 실행된다.
-
sleep 함수는 interruptedException ( 중간에 멈추는 에러 ) 가 발생할 수 있기에 에러처리 해줘야 한다.
2. Runnable interface 상속
public class ThreadPractice {
public static void main(String[] args) {
A t1 = new A();
A t2 = new A();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(t1);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(t2);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
System.out.println("finish");
}
}
class A implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
int i;
for(i=0;i<50;i++){
System.out.print(i + "\t");
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}-
sleep 함수는 static method이기 때문에 Runnable을 받을 때는 Thread를 붙여주어야 한다.
-
interface를 상속받았기에 run() 구현이 강제된다.
-
인스턴스를 Thread 생성자의 parameter로 넣어주어야 thread가 생성된다.
📌 멀티스레드
-
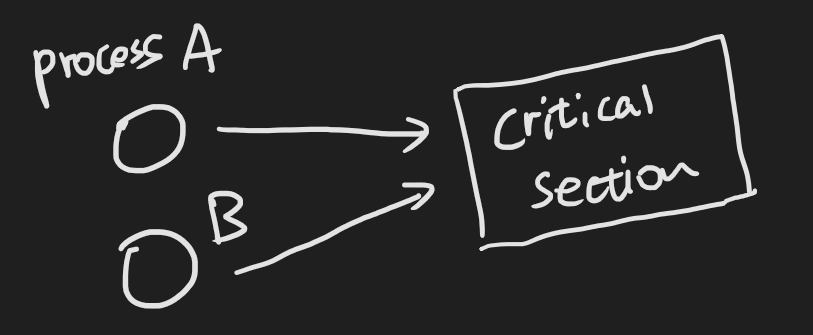
같은 공유자원에 접근할 수 있기 때문에 overwrtting의 문제가 발생할 수 있다.
-
그래서 critical section에 들어갈 수 있는 thread는 한 번에 하나만 있어야 한다.
-
OS에는 Critical Section에 Lock을 거는 세마포어 기법이 있다.
-
Java에서는 Synchronization을 제공
-
공유 자원이 있는 경우 race condition이 발생한다. ( 경쟁 )
📌 생명주기
-
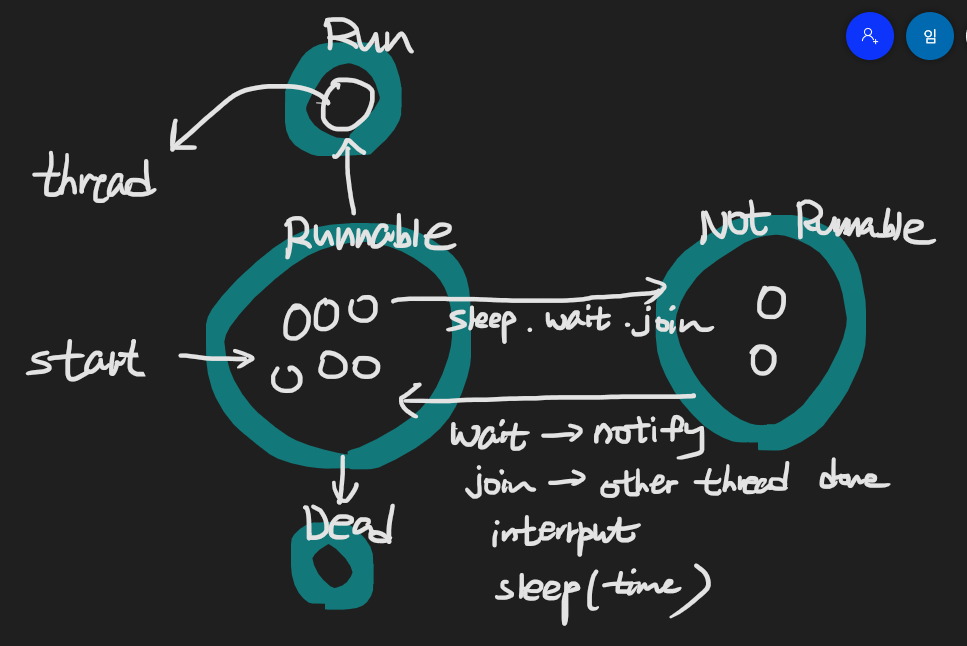
작은 동그라미 하나 하나는 쓰레드
-
sleep() , wait() , join() method들에 의해서 not runnable 상태로 갈 수 있다.
(🔥blocked) -
wait은 notify() 에 의해, join은 다른 쓰레드 뒤에 넣어주는 메서드 이므로 다른 쓰레드가 끝나면, sleep은 시간이 지나면 runnable상태로 가진다. interrupt에 의해 runnable에 가질 수도 있다.
📌 Thread 우선순위
기본 우선순위 = 5
- setPriority() 를 통해 우선순위를 높게 줄 수 있다 ( MAX = 10 )
📌 currentThread
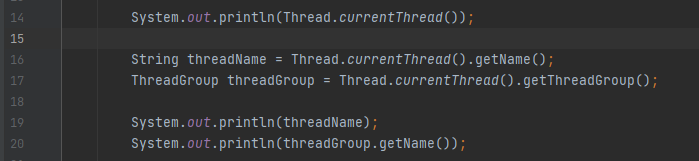
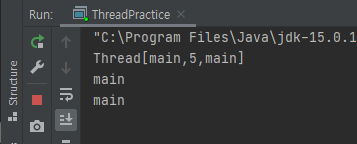
- 첫번째는 thread 이름, 마지막은 threadGroup이 출력됨. 가운데 5는 우선순위를 의미한다.
📌 Join
class B extends Thread{
int start;
int end;
int sum;
B(int start,int end){
this.start=start;
this.end=end;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i=start;i<end;i++){
sum += i;
}
}
}
public class ThreadJoinPractice {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
B t1 = new B(1,50);
B t2 = new B(51,100);
int sum=0;
t1.start();
t2.start();
t1.join();
t2.join();
System.out.println(t1.sum);
System.out.println(t2.sum);
sum = t1.sum + t2.sum;
System.out.println(sum);
}
}- Runnable로 sum을 구하는 방법을 모르겠다.
📌 interrupt()
sleep 인 상태일 때 interrupt()를 걸어주면 바로 깨어난다
📌 Thread 멈추기
-
Thread.stop() 은 쓰지 않는다.
-
대신에 flag를 이용해서 thread를 멈춘다.
public class TerminateThread extends Thread {
String word;
boolean flag = false;
public TerminateThread(String name,String word){
super(name);
this.word=word;
}
public void run(){
try {
while(!flag){
sleep(1000);
System.out.println(word);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TerminateThread t1 = new TerminateThread("A","A 입니다");
TerminateThread t2 = new TerminateThread("B","B 입니다");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}- 이렇게 되면 무한반복되는 쓰레드가 생성
public class TerminateThread extends Thread {
String word;
boolean flag = false;
public TerminateThread(String name,String word){
super(name);
this.word=word;
}
public void run(){
try {
while(!flag){
sleep(1000);
System.out.println(word);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
TerminateThread t1 = new TerminateThread("A","A 입니다");
TerminateThread t2 = new TerminateThread("B","B 입니다");
t1.start();
t2.start();
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String s = br.readLine();
while(true){
if(s.equals("A")){
t1.flag=true;
t2.flag=true;
}
}
}
}- flag의 값을 바꾸어주어서 쓰레드를 멈춘다.
📌 Synchronization
임계 영역에 여러 Thread 가 접근하는 경우 한 Thread가 작업을 수행하는 동안 다른 Thread에는 Lock해서 자원을 동시에 접근하지 못하도록 한다.
- 동기화를 잘못 구현하면 Deadlock에 빠질 수 있다.
📌 예제
class Bank{
int money=10000;
public int getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(int money) {
this.money = money;
}
public void saveMoney(int money) throws InterruptedException {
int m = getMoney();
Thread.sleep(3000);
setMoney(m+money);
}
public void minusMoney(int money) throws InterruptedException {
int m = getMoney();
Thread.sleep(200);
setMoney(m-money);
}
}
class Man extends Thread{
public void run(){
System.out.println("man's thread start");
try {
SyncTest.kakaoBank.saveMoney(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("after man : " + SyncTest.kakaoBank.getMoney());
}
}
class Wife extends Thread{
public void run(){
System.out.println("wife's thread start");
try {
SyncTest.kakaoBank.minusMoney(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("after wife : " + SyncTest.kakaoBank.getMoney());
}
}
public class SyncTest {
public static Bank kakaoBank = new Bank();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Man man = new Man();
man.start();
Thread.sleep(200);
Wife wife = new Wife();
wife.start();
}
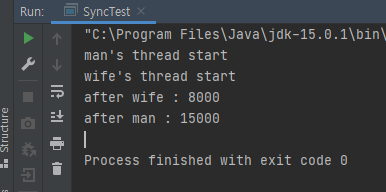
}- 남편이 5000원 저금하고, 아내가 2000원 썼으니 기본 돈 10000원에 3000원 더해서 13000이 돼야한다.
-
그러나 결과는 man과 wife과 따로따로 놀면서 나오는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
-
이 때 Synchronized를 걸어주면 해결 가능하다. 방법은 2가지가 있다.
🔥 synchronized 1번
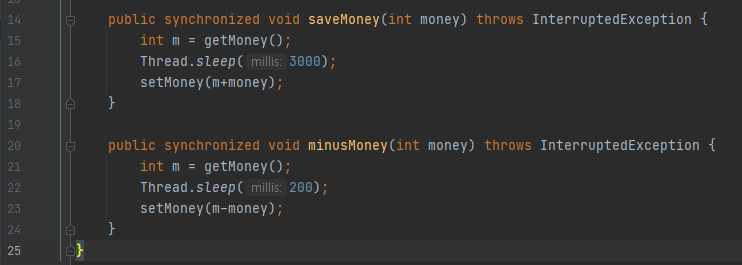
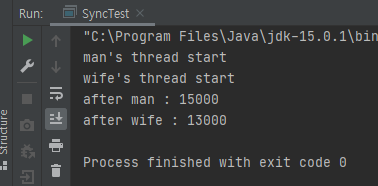
📌 1. Bank class(공유자원) 안의 method 들한테 synchronized를 걸어주기
🔥 synchronized 2번
📌 2. Block안에 synchronized 걸어주고 parameter로 인자 받기
class Man extends Thread{
public void run(){
synchronized (SyncTest.kakaoBank){
System.out.println("man's thread start");
try {
SyncTest.kakaoBank.saveMoney(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("after man : " + SyncTest.kakaoBank.getMoney());
}
}
}
class Wife extends Thread{
public void run(){
synchronized (SyncTest.kakaoBank) {
System.out.println("wife's thread start");
try {
SyncTest.kakaoBank.minusMoney(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("after wife : " + SyncTest.kakaoBank.getMoney());
}
}
}🔥 참고
public synchronized void run(){
}- 위처럼 run에 걸어주면 thread에 lock을 걸어주는 것이므로 의미가 없다.
public void saveMoney(int money) throws InterruptedException {
synchronized (this){
int m = getMoney();
Thread.sleep(3000);
setMoney(m+money);
}
}- 위처럼 bank class 안에서도 block으로 synchronized를 걸어줄 수 있다. 이 객체 ( Bank ) 를 의미하므로 this를 인자로 넘겨준다.
📌 DeadLock
synchronized 된 두 메서드가 서로를 기다리다가 꼬여서 둘다 lock이 발생한 상황. 1번을 실행하려면 2번이 필요하고, 2번을 실행하려면 1번이 필요한데 서로 lock이 돼서 둘다 실행을 하지 못하는 상황.
- 그래서 synchronized method에서는 왠만하면 다른 synchronized method를 부르지 않는 것이 권장된다.
📌 wait() - notifyAll()
-
wait()으로 non-runnable로 넘어간 thread는 notify()가 호출될 때 까지 기다린다.
-
notify() 는 무작위로 하나의 쓰레드를 깨운다. 그래서 확률적으로 못 깨어나는 thread도 있다.
-
그래서 일단 전부 깨우고, 우선순위 기반으로 실행이 되게 notifyAll()이 권장된다.
public void method(){
while(condition==?) wait()
}public void usingMethod(){
notifyAll()
}