Consumer
Consumer는 accept라는 추상 메소드를 가지고 있다.
accept는 별도의 return 값을 가지고 있지 않다. 즉 함수 내부에서 모든 동작을 마무리 한다.
예를 들면 다음과 같다.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
Consumer<String> stringConsumer = x -> System.out.println(x);
stringConsumer.accept("hello world");
}
}
제네릭 타입과 연계 - ForEach 만들기
Consumer와 제네릭 타입을 조합하면 ForEach를 구현할 수 있다.
ForEach는 이터러블한 객체를 돌면서 각 요소마다 넘겨받은 함수를 실행시켜주는 함수다.
예를 들어 Integer List와 Double List를 넘겨주고 각각 출력해주는 ForEach 함수를 구현하면 아래와 같다.
public class ForEach {
public static void main(String[] args){
List<Integer> iList = Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4,5);
List<Double> dList = Arrays.asList(1.5,2.5,3.5,4.5,5.5);
forEach(iList, (x) -> {
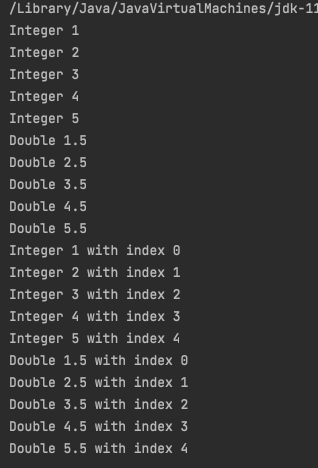
System.out.println("Integer " + x);
});
forEach(dList, (x) -> {
System.out.println("Double " + x);
});
}
public static <T> void forEach(
List<T> list, Consumer<T> processor
){
for(T t : list){
processor.accept(t);
}
}
}
BiConsumer
BiConsumer는 파라미터 값이 두개인 Consumer다.
이 BiConsumer를 사용하면 index 값을 추가로 넘겨줄 수 있는 ForEach를 만들 수 있다.
오버로딩을 사용해서 BiConsumer를 파라미터로 받는 ForEach를 구현할 수 있다.
public class ForEach {
public static void main(String[] args){
List<Integer> iList = Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4,5);
List<Double> dList = Arrays.asList(1.5,2.5,3.5,4.5,5.5);
forEach(iList, (x) -> {
System.out.println("Integer " + x);
});
forEach(dList, (x) -> {
System.out.println("Double " + x);
});
forEach(iList, (i, x) -> {
System.out.println("Integer " + x + " with index " + i);
});
forEach(dList, (i, x) -> {
System.out.println("Double " + x + " with index " + i);
});
}
public static <T> void forEach(
List<T> list, Consumer<T> processor
){
for(T t : list){
processor.accept(t);
}
}
public static <T> void forEach(
List<T> list, BiConsumer<Integer, T> processor
){
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++){
processor.accept(i,list.get(i));
}
}
}