전 포스팅을 통해 코루틴이 어떻게 작동하는지 알 수 있었다. 이제 그 코루틴이 어느 스레드에서 돌아가게 뭘 어떻게 전달하는지, 코루틴을 어떻게 컨트롤하는지 알아보고자한다!
ref. Kotlin Coroutines Basics | Mouaad Aallam
오늘 알아볼
- CorountineScope
- CoroutineContext
- Job
- Dispatcher
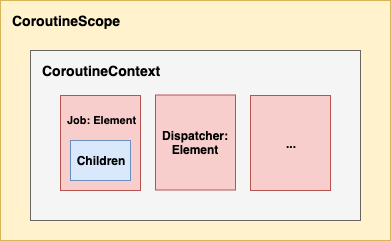
는 위와 같은 관계를 갖고 있다. 하나하나 살펴보자.
CoroutineScope
Data를 갖고있지 않고 CoroutineContext를 잡고 있는 클래스
launch, async 등을 위해 전달하는 암시적 수신자이다. 아래 예시를 보자
runBlocking {
val scope0 = this // top-level 코루틴 scope
scope0.launch {
val scope1 = this // scope1은 scope0의 context를 상속받게 된다
scope1.launch {
val scope2 = this // 위와 동일
}
}
}- "scope1은 scope0의 context를 상속받게 된다"
-> scope0의 Job을 scope1의 Job이 상속받게 된다. 따라서, scope0의 Job을 cancel하면 scope1까지 전파된다
-> 또, runBlocking에서 사용된 Dispatcher를 그대로 유지한다 - launch 시 앞에 scope를 명시해 줬는데 안 붙여도 자동으로 똑같이 된다.(automatically propagate scope)
CoroutineContext
Coroutine을 수행하는 Context
내부에 Job, Dispatcher, Name, ContinuousInterceptor, ExceptionHandler를 갖는다
Job
Coroutine을 컨트롤 할 수 있게 함
- 코루틴 빌더인 launch가 Job을 통해 coroutine을 return 한다
- 따라서, launch로 생성되어 그 block을 실행하고 block의 종료와 함께 끝난다
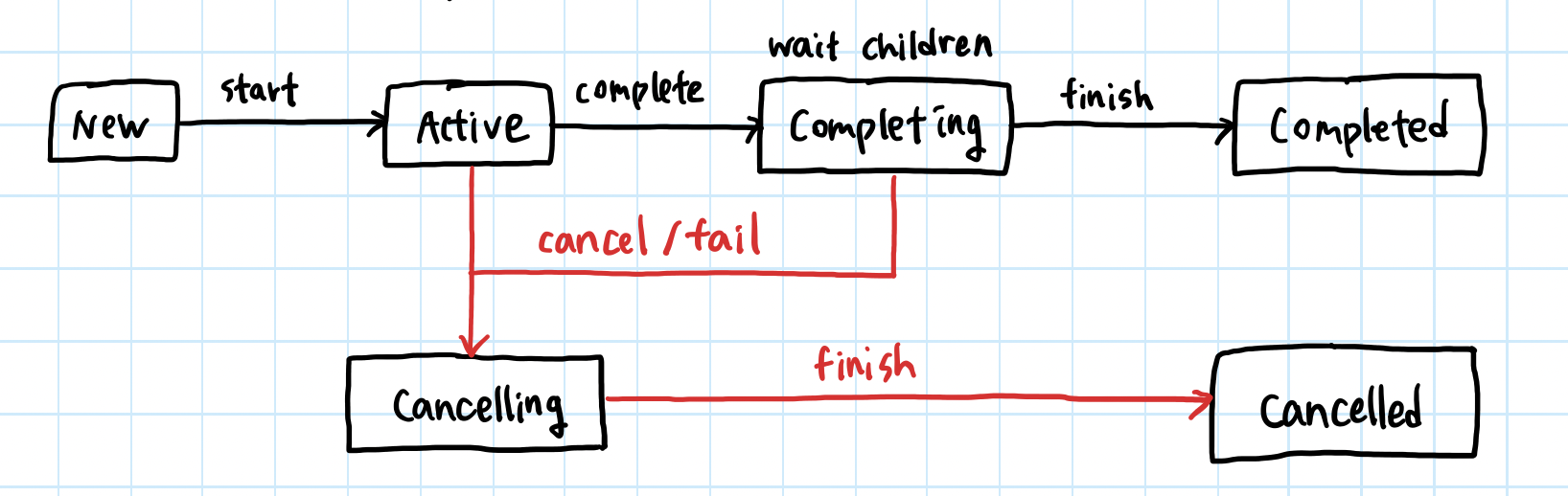
- 위 그림에서 볼 수 있듯, 코루틴을 cancel할 수 있다 !!!
- 언제해야할까? ex. 한 액티비티의 UI를 update하는 코루틴 -> 해당 액티비티 onDestroy에서 cancel 필수
- scope로도 할 수 있지 않나? => 내부에서 context의 Job을 사용한다
public fun CoroutineScope.cancel(cause: CancellationException? = null) {
val job = coroutineContext[Job] ?: error("Scope cannot be cancelled because it does not have a job: $this")
job.cancel(cause)
}- 계층적 구조를 가지며 cancel, exception 발생 시 서로에게 영향을 준다
Dispatcher
Dispatcher가 thread pool을 관리해 coroutine 생성 시 해당 coroutine이 수행될 thread를 지정해 dispatch함
다음 다섯가지 타입을 가짐
1. Dispatchers.Main
2. Dispatchers.IO: 네트워크나 디스크 프로세스처럼 data pulling, pushing에 사용
3. Dispatchers.Default: Main이 아닌 다른 background thread들! 자동으로 할당
4. Dispatchers.Unconfiged: task가 suspend되고 resume될 때 그 target process를 바꿀 수 있는 특별한 디스패처
5. newSingleThreadContext: 유저가 새로은 프로세스를 define하도록 함. 따라서 알아서 close해야 함
type을 전달하면 그에 맞게 dispatch하고, 전달하지 않으면 parent를 따른다
