🎈Querydsl 사용
프로젝트 진행 중 검색 기능에 조건별 필터 기능이 필요하게 되었다. 초기에는 각각의 조건별 SQL을 미리 다 작성하여 하나씩 가져다 사용했지만, 매우 비효율적이었다.
이를 해결하기 위해 기존 프로젝트에 Querydsl을 이용한 동적쿼리를 적용하기로 했다.
Maven(pom.xml) 의존성 추가
의존성 추가
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.querydsl</groupId>
<artifactId>querydsl-apt</artifactId>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.querydsl</groupId>
<artifactId>querydsl-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>build plugin 추가
<plugin>
<groupId>com.mysema.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>apt-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.1.3</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>process</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<outputDirectory>target/generated-sources/java</outputDirectory>
<processor>com.querydsl.apt.jpa.JPAAnnotationProcessor</processor>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>플러그인에서 outputDirectory는 @Entity가 붙은 Q타입의 클래스가 생성되는 위치다.
설정 후 mvn compile을 실행하면, outputDirectory에 Q타입 클래스가 생성된 것을 확인할 수 있다.
📍QClass 인식 해결(Intellij)
Intellij에서 Querydsl을 사용할 때, mvn compile을 통해 생성된 QClass가 존재함에도 불구하고, 인식하지 못하는 문제가 종종 발생한다.
이경우, 실제 실행을 하면 실행은 잘되지만 자동완성 기능을 이용할 수 없기에 작업시 많은 불편을 야기한다.
해결
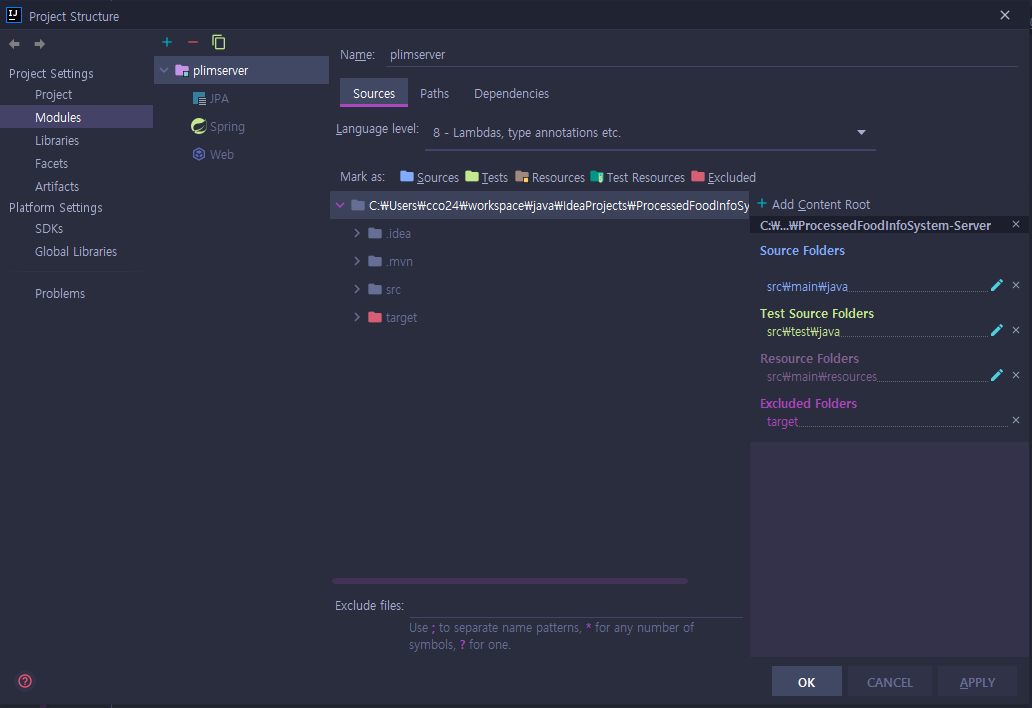
Intellij의 File → Project Structure로 이동하자.
아래의 이미지를 확인해보면, Modules의 Sources 탭의 우측의 Source Folders를 확인하면 src\main\java만 포함되어 있는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
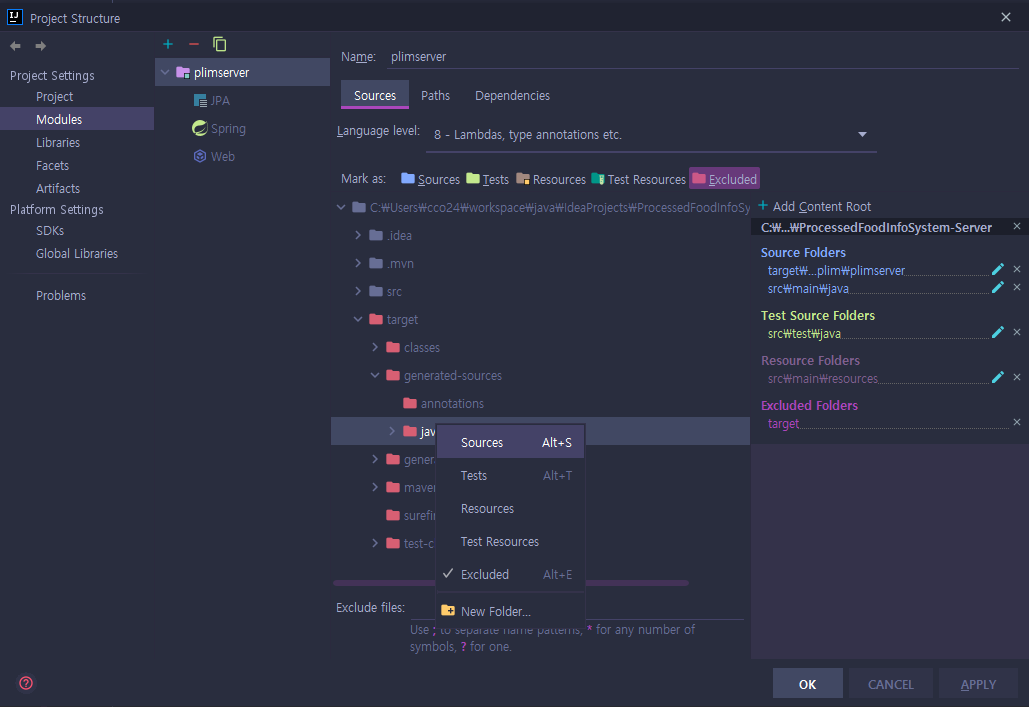
하단의 이미지와 같이, QClass가 추가된 target의 java쪽 폴더 중 원하는 폴더를 우클릭하여 Sources를 클릭한다.
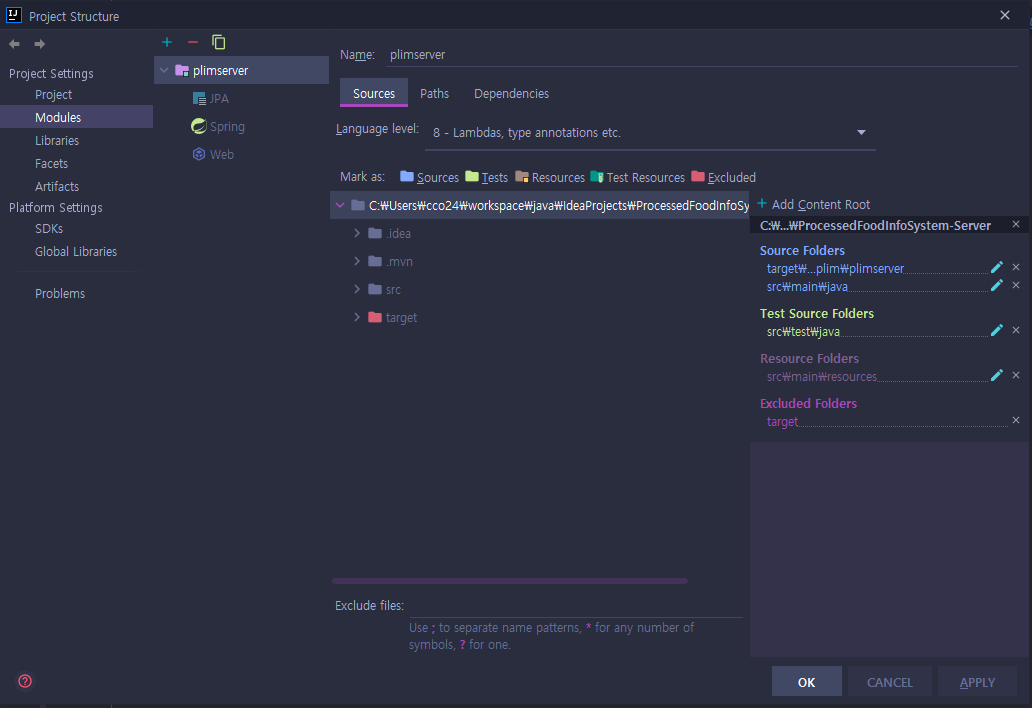
추가가되면 하단의 이미지와 같이 추가가 되며, 자동완성에서 작동하게 된다.
코드상 사용
Querydsl Config 파일 생성
후에 기술할 실제 구현단에서 사용할 JPAQueryFactory를 생성자를 통해 주입받기 위해, Config 전용 클래스를 생성한다.
@Configuration
public class QuerydslConfig {
@PersistenceContext
private EntityManager entityManager;
@Bean
public JPAQueryFactory jpaQueryFactory() {
return new JPAQueryFactory(entityManager);
}
}Repository 생성
Querydsl을 이용한 동적쿼리가 적용될 특정 Entity를 위한 Repository가 총 3개 생성된다.
Food라는 Entity Class가 있다고 가정하자.
FoodRepository: 기존 Spring data jpa를 위한 Repository class이다.FoodRepositoryCustom: Querydsl을 위해 생성되는 class이다.FoodRepositoryImpl: Querydsl을 위해 생성되는 class이다.
Querydsl을 이용한 동적쿼리용 SQL메소드를 가장 먼저 FoodRepositoryCustom Interface에 생성한다.
public interface FoodRepositoryCustom {
Page<Food> search(String sortElement, String category, String foodName, String manufacturerName
, List<String> allergyList, String order, Pageable pageable);
}이후 Custom Interface에 생성된 메소드를 Service Class에서 사용해야 하기 때문에, FoodRepository가 FoodRepositoryCustom을 상속받는다.
public interface FoodRepository extends JpaRepository<Food, Long>, FoodRepositoryCustom{
}Custom Interface를 직접 구현한 FoodRepositoryImpl을 생성한다. 이후, Query 작성을 위해 JPAQueryFactory를 생성자 주입 받는다.
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class FoodRepositoryImpl implements FoodRepositoryCustom{
private final JPAQueryFactory queryFactory;
}사용
예시로 언급한 FoodRepositoryCustom의 search 메소드를 구현하는 것을 예로 들겠다.
실제 구현은 위에서 언급한 것처럼 Custom을 구현한 FoodRepositoryImpl에서 구현한다.
import static com.plim.plimserver.domain.food.domain.QFood.food; //QClass사용
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class FoodRepositoryImpl implements FoodRepositoryCustom{
private final JPAQueryFactory queryFactory;
@Override
public Page<Food> search(String sortElement, String category, String foodName, String manufacturerName
, List<String> allergyList, String order, Pageable pageable) {
QueryResults<Food> result = queryFactory.selectFrom(food)
.where(eqFoodName(foodName), eqManufacturerName(manufacturerName)
, eqAllergies(allergyList), eqCategory(category))
.orderBy(orderType(sortElement, order))
.offset(pageable.getOffset())
.limit(pageable.getPageSize())
.fetchResults();
return new PageImpl<>(result.getResults(), pageable, result.getTotal());
}
}사용방법은 기존의 SQL 작성과 굉장히 유사한 것을 확인할 수 있다.
여기서 눈 여겨 봐야할 코드는 where절이다. where절에서는 동적쿼리를 위해, 매개변수로 받은 foodName, manufacturerName, category의 존재여부(null인가 아닌가) 확인을 해야한다. 또한, List로 들어오는 매개변수인 allergyList의 경우에는 각각의 리스트 요소들에 대한 조건(예시에서는 각각의 알러지들을 1개라도 가지고 있지 않은 경우)도 확인해줄 수 있어야 한다.
가장먼저 존재여부에 대한 간단한 메소드를 직접 보자.
import static com.plim.plimserver.domain.food.domain.QFood.food; //QClass사용
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class FoodRepositoryImpl implements FoodRepositoryCustom{
private final JPAQueryFactory queryFactory;
@Override
public Page<Food> search(String sortElement, String category, String foodName, String manufacturerName
, List<String> allergyList, String order, Pageable pageable) {
QueryResults<Food> result = queryFactory.selectFrom(food)
.where(eqFoodName(foodName), eqManufacturerName(manufacturerName)
, eqAllergies(allergyList), eqCategory(category))
.orderBy(orderType(sortElement, order))
.offset(pageable.getOffset())
.limit(pageable.getPageSize())
.fetchResults();
return new PageImpl<>(result.getResults(), pageable, result.getTotal());
}
private BooleanExpression eqFoodName(String foodName) {
return foodName != null ? food.foodName.contains(foodName) : null;
}
private BooleanExpression eqCategory(String category) {
return category != null ? food.category.contains(category) : null;
}
private BooleanExpression eqManufacturerName(String manufacturerName) {
return manufacturerName != null ? food.manufacturerName.contains(manufacturerName) : null;
}
}추가된 3개의 메소드는 foodName, category, manufacturerName에 대해 실제로 매개변수로 주어졌는지 null 체크를 통해 확인 후, 해당 매개변수가 없는 경우에는 null을 반환한다. 반대로 존재하는 경우에는 매개변수로 들어온 foodName을 포함하고 있는 경우라는 것을 BooleanExpression 타입으로 반환해준다.
즉, like %foodName%이 sql 조건에 추가 되었다고 보면 된다.
그 다음으로는 검색해도 잘 나오지 않는 List 타입에 대한 BooleanExpression 적용이다.
일단, 코드가 길어지니 위에서 사용한 foodName, category, manufacturerName에 관한 메소드는 생략하겠다.
import static com.plim.plimserver.domain.food.domain.QFood.food; //QClass사용
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class FoodRepositoryImpl implements FoodRepositoryCustom{
private final JPAQueryFactory queryFactory;
@Override
public Page<Food> search(String sortElement, String category, String foodName, String manufacturerName
, List<String> allergyList, String order, Pageable pageable) {
QueryResults<Food> result = queryFactory.selectFrom(food)
.where(eqFoodName(foodName), eqManufacturerName(manufacturerName)
, eqAllergies(allergyList), eqCategory(category))
.orderBy(orderType(sortElement, order))
.offset(pageable.getOffset())
.limit(pageable.getPageSize())
.fetchResults();
return new PageImpl<>(result.getResults(), pageable, result.getTotal());
}
private BooleanExpression eqAllergies(List<String> allergyList) {
return allergyList != null ? Expressions.allOf(allergyList.stream().map(this::isFilteredAllergy).toArray(BooleanExpression[]::new)) : null;
}
private BooleanExpression isFilteredAllergy(String allergy) {
return food.allergyMaterials.contains(allergy).not();
}
}List 타입의 매개변수인 allergyList를 Expressions를 이용하여 구현한다.
필자의 경우, 여러 개의 알러지를 or의 형태로 포함하고 싶지 않은 경우이다.
allergyList.stream().map(this::isFilteredAllergy).toArray(BooleanExpression[]::new)우선 위의 코드는 매개변수로 들어온 List를 stream으로 만들어 map를 이용하여 각각의 요소를 확인해준 후, BooleanExpression 배열로 만들어준다.
private BooleanExpression isFilteredAllergy(String allergy) {
return food.allergyMaterials.contains(allergy).not();
}위의 코드는 stream을 이용한 각각의 요소에 map 메소드를 적용하는 부분이다. 각각의 알레르기 요소를 포함하지 않는 것을 의미한다.
private BooleanExpression eqAllergies(List<String> allergyList) {
return allergyList != null ? Expressions.allOf(allergyList.stream().map(this::isFilteredAllergy).toArray(BooleanExpression[]::new)) : null;
}여기서 Expressions의 allOf메소드는 각각의 요소별 조건을 합치는 것(or)을 의미한다. 즉, 예를 들어 {"새우", "밀"}이 List로 들어왔다면, 위의 과정을 거치게 된 후에는 where 절에 (not 새우) or (not 밀)의 의미를 포함하게 된다. SQL문으로는 not REGEXP '새우|밀'가 where절에 포함된다.
후기
검색 메소드를 동적쿼리로 변경하면서 많이 어려웠다. where절에 들어갈 BooleanExpression에 대한 예시는 많았지만 대부분 단일 파라미터에 대한 예시였다. 하지만 나는 여러 값을 필터링 해야했기에 List에 대한 BooleanExpression은 예시가 별로 없어 많은 고생을 했다.
하지만 해당 코드를 적용하면서 JPA의 고질점인 N+1문제가 발생하는 것을 확인했다. 아마 select 절의 문제로 보인다. 이후에 시간이 생긴다면 해당 코드를 고칠 것 같다.
