
bfs 문제로, 몇 가지 제한사항만 지켜준다면 쉽게 풀 수 있는 문제다.
- 아기 상어는 자신의 크기 이하의 길을 지나갈 수 있다.
- 아기 상어는 자신의 크기 미만의 물고기를 먹을 수 있다.
- 같은 거리에 먹을 수 있는 물고기가 2마리 이상이라면 더 높이 있는(작은 행의), 같은 높이라면 더 왼쪽에 있는(작은 열의) 물고기를 먼저 먹는다.
- 각 물고기를 먹은 후 어떤 물고기를 먹을지 다시 탐색을 시작한다.
이 조건을 만족하기 위해 상하좌우를 탐색하는 bfs에서 정점을 방문하는 순서가 중요해진다. 작은 행, 작은 열 순서로 우선순위가 정해지므로 상좌우하 순으로 방문할 필요가 있다.
하지만 다음과 같은 경우를 생각해보자.
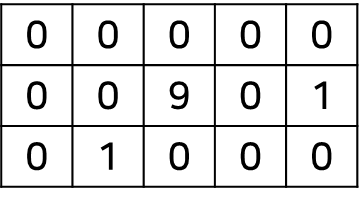
상좌우하 순으로 방문하는 규칙으로 bfs를 돌린다면 {2, 5}에 있는 물고기보다 {3, 2}에 있는 물고기를 먼저 먹게 된다. 하지만 {3, 2}가 더 낮은 행에 있으므로 기본 규칙에 위배된다.
이 예외를 처리해주기 위해 최소 거리로 이동할 수 있는 정점을 찾았다면 그 지점을 기억하여 minDist라는 변수에 그 거리를, nextPoint라는 변수에 그 좌표를 저장했다. 이후 정점을 계속 방문해서 nextPoint보다 더 작은 행 또는 열에 방문할 수 있는지를 검사한다.
만약 방문한 정점이 minDist와 같은 거리에 있다면 그 정점에서부터 이동할 수 있는 정점은 minDist보다 머 거리에 있는 정점일 것이므로 탐색을 중단하고 해당 정점에서부터 다시 다음 방문 지점을 탐색한다.
위 내용을 모두 적용한 코드 전문은 아래와 같다.
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#define MAX 10000
// 상좌우하 순으로 방문
std::pair<int, int> direction[4] = { {-1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}, {1, 0} };
std::queue<std::pair<int, int>> q;
// 외벽 설정을 위해 n 최대 크기보다 더 큰 배열을 생성
int map[23][23];
int visit[23][23] = { 0, };
int dist[23][23] = { 0, };
int n;
int moveCnt;
int sharkSize;
int feadCnt;
int totalDist;
std::pair<int, int> nextPoint;
int minDist;
void init() {
for (int row = 0; row <= n + 1; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col <= n + 1; col++) {
map[row][col] = MAX; // 외벽 설정
}
}
sharkSize = 2; // 어린 상어의 크기
feadCnt = 0; // 먹은 물고기의 수
moveCnt = 1; // 탐색 카운트. 물고기를 먹을 때마다 카운트를 올려
// visit 초기화 없이 탐색할 수 있게 함.
totalDist = 0; // 이동한 총 거리
minDist = MAX; // 다음 지점으로 이동하는 최소 거리
nextPoint = { MAX, MAX };
}
void bfs() {
while (!q.empty()) {
int curRow = q.front().first;
int curCol = q.front().second;
q.pop();
// 이번 정점과 도달할 수 있는 최단 거리 정점이 같은 거리라면 탐색 중지
if (minDist == dist[curRow][curCol]) {
feadCnt++;
moveCnt++;
map[nextPoint.first][nextPoint.second] = 0;
if (feadCnt == sharkSize) {
feadCnt = 0;
sharkSize++;
}
while (!q.empty()) {
q.pop();
}
totalDist += dist[nextPoint.first][nextPoint.second];
minDist = MAX;
dist[nextPoint.first][nextPoint.second] = 0;
q.push({ nextPoint.first, nextPoint.second });
visit[nextPoint.first][nextPoint.second] = moveCnt;
nextPoint = { MAX, MAX };
continue;
}
for (auto dir : direction) {
int nextRow = curRow + dir.first;
int nextCol = curCol + dir.second;
dist[nextRow][nextCol] = dist[curRow][curCol] + 1;
if (visit[nextRow][nextCol] < moveCnt && map[nextRow][nextCol] <= sharkSize) {
// 상어의 크기보다 더 작은 물고기라면 방문 리스트에 추가
if (map[nextRow][nextCol] > 0 && map[nextRow][nextCol] < sharkSize) {
minDist = dist[nextRow][nextCol];
// 같은 거리에 있더라도 더 작은 행 또는 열이라면 방문 정점 변경
if (nextPoint.first == nextRow) {
if (nextPoint.second > nextCol) {
nextPoint.second = nextCol;
}
}
else if (nextPoint.first > nextRow) {
nextPoint = { nextRow, nextCol };
}
}
q.push({ nextRow, nextCol });
visit[nextRow][nextCol] = moveCnt;
}
}
}
}
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
std::cin.tie(NULL);
std::cout.tie(NULL);
std::cin >> n;
init();
for (int row = 1; row <= n; row++) {
for (int col = 1; col <= n; col++) {
std::cin >> map[row][col];
if (map[row][col] == 9) {
q.push({ row, col });
map[row][col] = 0;
visit[row][col] = moveCnt;
}
}
}
bfs();
std::cout << totalDist;
}
