
👩🏻💻 GITHUB 레포지토리
👩🏻💻 GITHUB Argument Passing 이슈
👊 진입 전 읽어보면 좋을 포스팅
테스트 방법
- /pintos-kaist
source ./activate - /pintos-kaist/userprog
make - /pintos-kaist/userprog/build
pintos --fs-disk=10 -p tests/userprog/args-single:args-single -- -q -f run 'args-single onearg'
사전 환경 설정
✔️ 테스트 방법을 참고하여 미리 테스트 돌려보자!
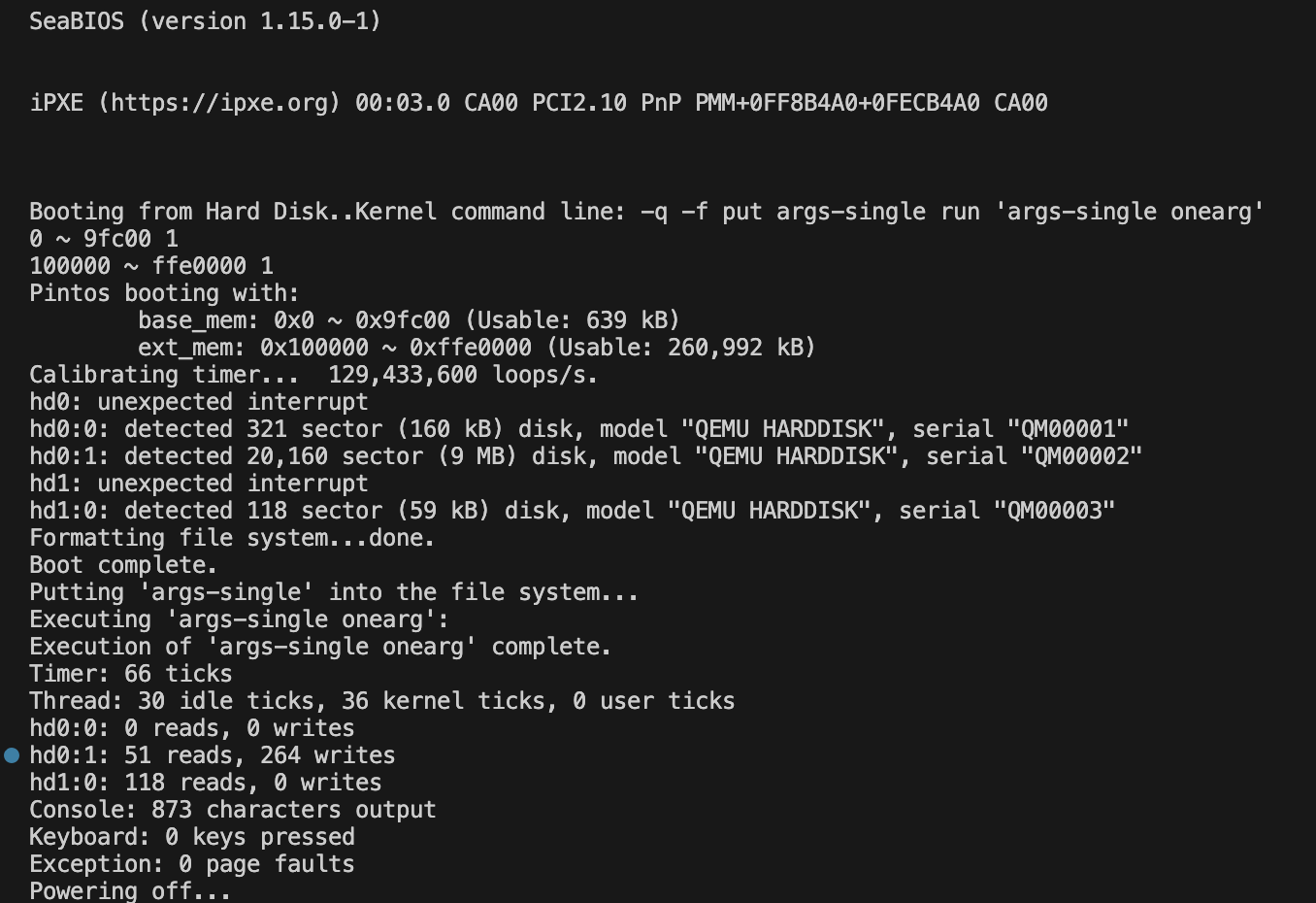
이렇게 뜬다면 이제 프로젝트를 시작 가능!!!
밑에 처럼 panic이 뜬다...? 같이 고쳐보자....
Kernel panic in run:
PANIC at ../../threads/thread.c:338 in thread_yield():
assertion `!intr_context ()' failed.인터럽트 핸들러가 켜져있는 상태에서 스레드 교체(thread_yield) 가 발생하여 디버깅 함수가 동작한 문제이다.
- threads/thread.c -
text_max_priority()함수 수정
void
test_max_priority (void)
{
if (list_empty(&ready_list))
return;
struct thread *th = list_entry(list_front(&ready_list), struct thread, elem);
if (thread_current()->priority < th->priority) {
/** Project 2: Panic 방지 */
if (intr_context())
intr_yield_on_return();
else
thread_yield();
}
}다시 돌려보고 정상 작동한다면 프로젝트 시작~!!!!!!
과제 설명
유저 프로그램을 실행하기 전에, 커널은 레지스터에다가 맨 처음 function의 argument를 저장해야 한다. process_exec()은 유저가 입력한 명령어를 수행할 수 있도록 프로그램(=process)을 메모리에 적재하고 실행하는 함수이다. 해당 프로그램은 f_name에 문자열로 저장되어 있으나 현재 상태에서 process_exec() 은 새로운 프로세스에 대한 인자 passing을 제공하지 않는다. 이 기능을 구현하는 것이 이번 과제이다. process_exec() 에 코드를 추가해서 간단히 프로그램 파일 이름을 인자로 넣는것 대신에, space가 올 때마다 단어를 parsing하도록 만들어야 한다. 이때, 첫 번째 단어는 프로그램 이름이고 두세 번째 단어는 각각 첫 번째, 두 번째 인자이다.
ex) process_exec("grep foo bar"): process_exec()에서 두 인자 foo, bar로 parsing되어야 한다.
수정할 함수
int process_exec(void *f_name)int process_wait(tid_t child_tid UNUSED)
추가할 함수
void argument_stack(char **argv, int argc, struct intr_frame *if_)
구현
1. process_exec() 수정
- userprog/process.c
process_exec()은 유저가 입력한 명령어를 수행할 수 있도록, 프로그램을 메모리에 적재하고 실행하는 함수이다.- 파일 네임을 인자로 받아서 저장한다. 하지만 실행 프로그램 파일과 옵션이 분리되지 않은 상황이다.
- thread의 이름을 실행 파일 명으로 저장하기 위해 실행 파일 명만 분리하기 위해 파싱해야한다.
- 실행 파일 명은 cmd line 안에서 첫번째 공백 전에 해당한다.
- 파일명을 분리해야하지만, 다른 인자들 역시 프로세스를 실행하는 데 필요하므로 함께 user stack에 담아줘야한다.
- arg_list라는 배열을 만들어서, 각 인자의 char*를 담아준다. 프로그램 명은 arg_list[0]에 들어갈 것이며, 2번째 인자는 arg_list[1]에 들어갈 것이다.
- load가 성공적으로 이뤄졌을 때, argument_stack함수를 이용하여, user stack에 인자들을 저장한다.
int
process_exec (void *f_name) {
char *file_name = f_name;
bool success;
/* We cannot use the intr_frame in the thread structure.
* This is because when current thread rescheduled,
* it stores the execution information to the member. */
struct intr_frame _if;
_if.ds = _if.es = _if.ss = SEL_UDSEG;
_if.cs = SEL_UCSEG;
_if.eflags = FLAG_IF | FLAG_MBS;
/* We first kill the current context */
process_cleanup ();
/** project2-Command Line Parsing */
char *ptr, *arg;
int arg_cnt = 0;
char *arg_list[32];
for (arg = strtok_r(file_name, " ", &ptr); arg != NULL; arg = strtok_r(NULL, " ", &ptr))
arg_list[arg_cnt++] = arg;
/* And then load the binary */
success = load (file_name, &_if);
/** project2-Command Line Parsing */
argument_stack(arg_list, arg_cnt, &_if);
/* If load failed, quit. */
palloc_free_page (file_name);
if (!success)
return -1;
/* Start switched process. */
do_iret (&_if);
NOT_REACHED ();
}2. argument_stack() 함수 선언
- include/userprog/process.h
- process_exec 에서 불러온 argument_stack() 함수를 구현하기 위해 선언부터 해준다.
.
.
./** project2-Command Line Parsing */
void argument_stack(char **argv, int argc, struct intr_frame *if_);
.
.
.3. argument_stack() 함수 구현 & load() 함수 수정
- userprog/process.c
- 인자값을 스택에 올리는 함수이다.
- argument_stack 함수는 char **argv로 받은 문자열 배열과 int argc로 받은 인자 개수를 처리한다.
- char *arg_addr[100];는 문자열 주소를 저장하는 배열이다.
- for 루프는 argv 배열을 역순으로 스택에 넣는다. 그리고 각 문자열의 길이에 1을 더한 만큼의 공간을 할당하여 문자열을 복사한다.
- while 루프는 스택을 8바이트로 정렬한다.
- 두 번째 for 루프는 arg_addr 배열의 주소를 스택에 넣는다. 이때 마지막으로 NULL 포인터를 넣어 인자들의 끝을 표시한다.
- 스택에는 인자의 개수가 RDI 레지스터에, 그리고 인자들의 주소가 RSI 레지스터에 저장된다.
/** project2-Command Line Parsing */
// 유저 스택에 파싱된 토큰을 저장하는 함수
void argument_stack(char **argv, int argc, struct intr_frame *if_) {
char *arg_addr[100];
int argv_len;
for (int i = argc - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
argv_len = strlen(argv[i]) + 1;
if_->rsp -= argv_len;
memcpy(if_->rsp, argv[i], argv_len);
arg_addr[i] = if_->rsp;
}
while (if_->rsp % 8)
*(uint8_t *)(--if_->rsp) = 0;
if_->rsp -= 8;
memset(if_->rsp, 0, sizeof(char *));
for (int i = argc - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if_->rsp -= 8;
memcpy(if_->rsp, &arg_addr[i], sizeof(char *));
}
if_->rsp = if_->rsp - 8;
memset(if_->rsp, 0, sizeof(void *));
if_->R.rdi = argc;
if_->R.rsi = if_->rsp + 8;
}
static bool
load (const char file_name, struct intr_frame if_) {
struct thread t = thread_current();
struct ELF ehdr;
struct file file = NULL;
off_t file_ofs;
bool success = false;
int i;
/* Allocate and activate page directory. */
t->pml4 = pml4_create();
if (t->pml4 == NULL)
goto done;
process_activate(thread_current());
/* Open executable file. */
file = filesys_open(file_name);
if (file == NULL) {
printf("load: %s: open failed\n", file_name);
goto done;
}
/** project2-System Call - 파일 실행 명시 및 접근 금지 설정 */
t->runn_file = file;
file_deny_write(file); /** Project 2: Denying Writes to Executables */
/* Read and verify executable header. */
if (file_read(file, &ehdr, sizeof ehdr) != sizeof ehdr || memcmp(ehdr.e_ident, "\177ELF\2\1\1", 7) || ehdr.e_type != 2 || ehdr.e_machine != 0x3E // amd64
|| ehdr.e_version != 1 || ehdr.e_phentsize != sizeof(struct Phdr) || ehdr.e_phnum > 1024) {
printf("load: %s: error loading executable\n", file_name);
goto done;
}
/* Read program headers. */
file_ofs = ehdr.e_phoff;
for (i = 0; i < ehdr.e_phnum; i++) {
struct Phdr phdr;
if (file_ofs < 0 || file_ofs > file_length(file))
goto done;
file_seek(file, file_ofs);
if (file_read(file, &phdr, sizeof phdr) != sizeof phdr)
goto done;
file_ofs += sizeof phdr;
switch (phdr.p_type) {
case PT_NULL:
case PT_NOTE:
case PT_PHDR:
case PT_STACK:
default:
/* Ignore this segment. */
break;
case PT_DYNAMIC:
case PT_INTERP:
case PT_SHLIB:
goto done;
case PT_LOAD:
if (validate_segment(&phdr, file)) {
bool writable = (phdr.p_flags & PF_W) != 0;
uint64_t file_page = phdr.p_offset & ~PGMASK;
uint64_t mem_page = phdr.p_vaddr & ~PGMASK;
uint64_t page_offset = phdr.p_vaddr & PGMASK;
uint32_t read_bytes, zero_bytes;
if (phdr.p_filesz > 0) {
/* Normal segment.
* Read initial part from disk and zero the rest. */
read_bytes = page_offset + phdr.p_filesz;
zero_bytes = (ROUND_UP(page_offset + phdr.p_memsz, PGSIZE) - read_bytes);
} else {
/* Entirely zero.
* Don't read anything from disk. */
read_bytes = 0;
zero_bytes = ROUND_UP(page_offset + phdr.p_memsz, PGSIZE);
}
if (!load_segment(file, file_page, (void *)mem_page, read_bytes, zero_bytes, writable))
goto done;
} else
goto done;
break;
}
}
/* Set up stack. */
if (!setup_stack(if_))
goto done;
/* Start address. */
if_->rip = ehdr.e_entry;
success = true;done:
/ We arrive here whether the load is successful or not. /
// file_close(file);
return success;}
4. process_wait() 함수 무한 루프 추가
- userprog/process.c
- 무한 루프를 돌아야 한다. 핀토스는 유저 프로세스를 생성한 후 프로세스 종료를 대기해야 하는데 자식 프로세스가 종료될 때까지 무한 대기한다.
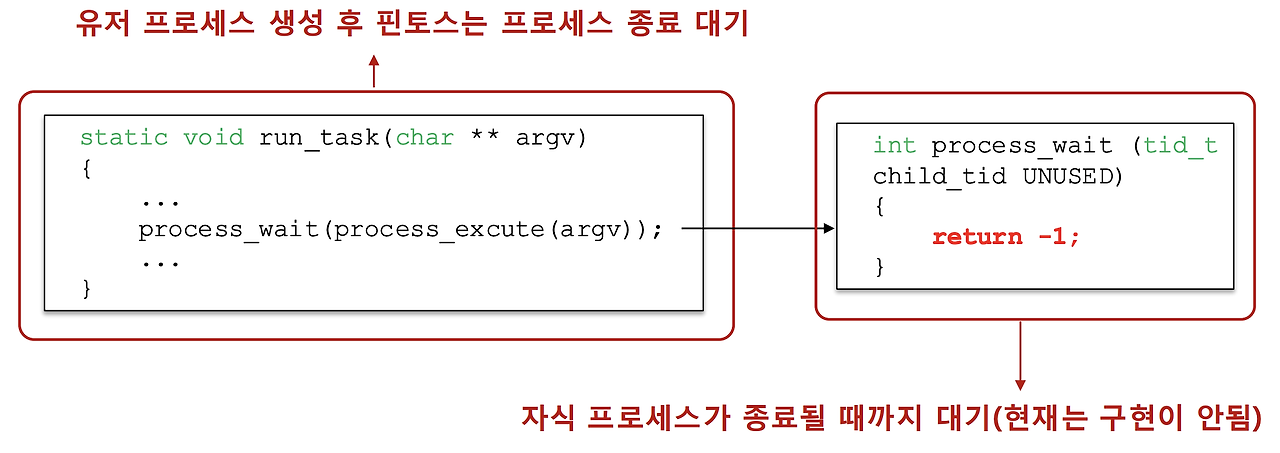
int
process_wait (tid_t child_tid UNUSED) {
/* XXX: Hint) The pintos exit if process_wait (initd), we recommend you
* XXX: to add infinite loop here before
* XXX: implementing the process_wait. */
/** project2-Command Line Parsing */
while (1){}
return -1;
}5. 디버깅을 위한 hex_dump() 추가
- userprog/process.c
- 결과를 확인하기 위해 hex_dump() 함수를 사용한다.
- 이 함수는 메모리의 내용을 16진수 형식으로 출력해줘서 스택에 저장된 값들을 확인할 수 있다.
int
process_exec (void *f_name) {
char *file_name = f_name;
bool success;
/* We cannot use the intr_frame in the thread structure.
* This is because when current thread rescheduled,
* it stores the execution information to the member. */
struct intr_frame _if;
_if.ds = _if.es = _if.ss = SEL_UDSEG;
_if.cs = SEL_UCSEG;
_if.eflags = FLAG_IF | FLAG_MBS;
/* We first kill the current context */
process_cleanup ();
/** project2-Command Line Parsing */
char *ptr, *arg;
int arg_cnt = 0;
char *arg_list[32];
for (arg = strtok_r(file_name, " ", &ptr); arg != NULL; arg = strtok_r(NULL, " ", &ptr))
arg_list[arg_cnt++] = arg;
/* And then load the binary */
success = load (file_name, &_if);
/** project2-Command Line Parsing */
argument_stack(arg_list, arg_cnt, &_if);
/* If load failed, quit. */
palloc_free_page (file_name);
if (!success)
return -1;
hex_dump(_if.rsp, _if.rsp, USER_STACK - _if.rsp, true); // 0x47480000
/* Start switched process. */
do_iret (&_if);
NOT_REACHED ();
}6. make check pass를 위한 process_create_initd() 함수 수정
직접 프로그램을 실행할 때에는 이 함수를 사용하지 않지만 make check에서 이 함수를 통해 process_create를 실행하기 때문에 이 부분을 수정해주지 않으면 Test Case의 Thread_name이 커맨드 라인 전체로 바뀌게 되어 Pass할 수 없다.
tid_t process_create_initd(const char *file_name) {
char *fn_copy;
tid_t tid;
/* FILE_NAME의 사본을 만듭니다.
* 그렇지 않으면 호출자와 load() 사이에 race가 발생합니다. */
fn_copy = palloc_get_page(0);
if (fn_copy == NULL)
return TID_ERROR;
strlcpy(fn_copy, file_name, PGSIZE);
/** Project2: for Test Case - 직접 프로그램을 실행할 때에는 이 함수를 사용하지 않지만 make check에서
* 이 함수를 통해 process_create를 실행하기 때문에 이 부분을 수정해주지 않으면 Test Case의 Thread_name이
* 커맨드 라인 전체로 바뀌게 되어 Pass할 수 없다.
*/
char *ptr;
strtok_r(file_name, " ", &ptr);
/** --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
/* FILE_NAME을 실행할 새 스레드를 만듭니다. */
tid = thread_create(file_name, PRI_DEFAULT, initd, fn_copy);
if (tid == TID_ERROR)
palloc_free_page(fn_copy);
return tid;
}테스트 결과
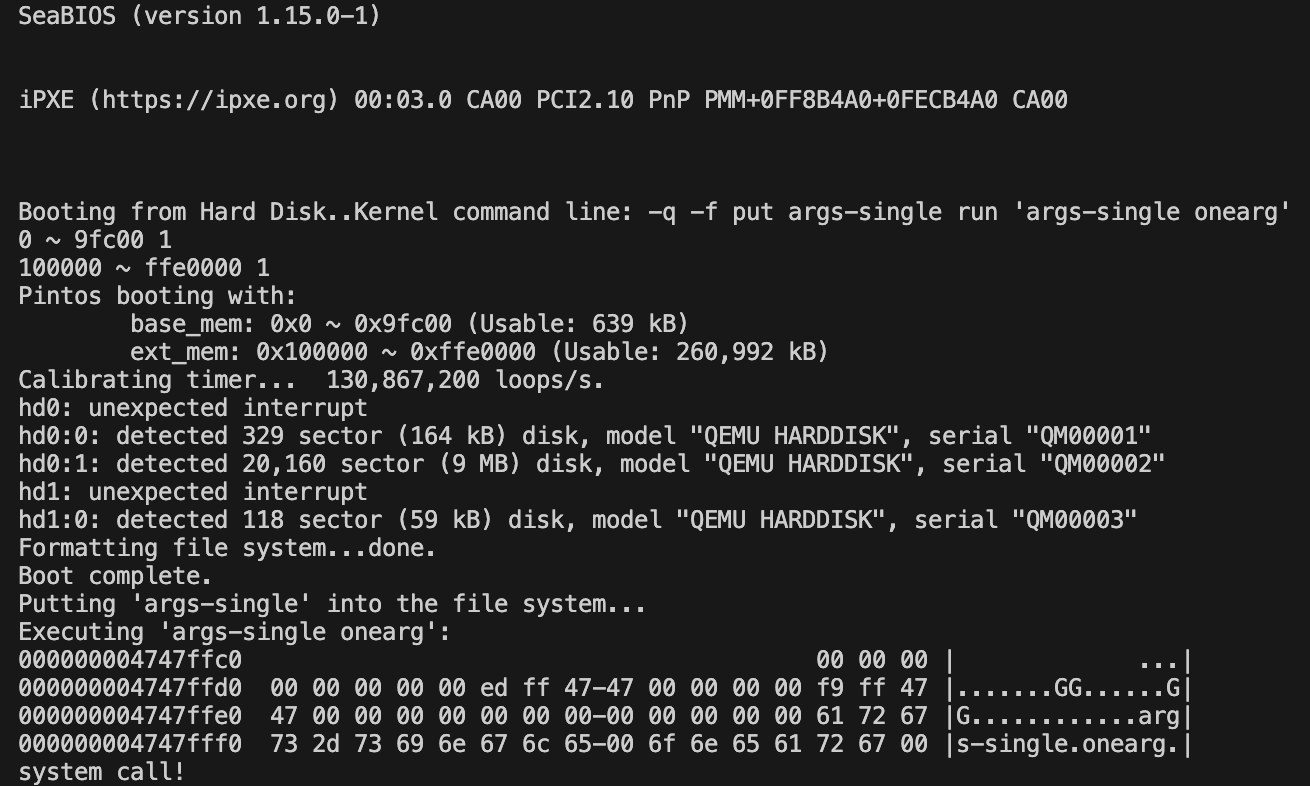
system call! 이 뜨면 성공~~~
무한루프가 돌아가고 있으니 터미널을 종료시켜주자!
