오늘은 알고리즘 문제를 풀면서 사용한 트라이 자료구조를 한 번 정리해두려고 한다 !
트라이란 ?
트라이는 트리 자료구조의 일종으로 연관 배열을 저장하는데에 사용되는 자료구조이다.
연관 배열이란 key-value로 이루어진 자료구조로 java에서는 map을 떠올리면 쉽게 이해할 수 있을 것 같다. 결국 트라이는 트리의 노드에 map을 저장하여 map에 자식 노드들의 key를 저장하여 빠른 검색을 장점으로 갖는 자료구조이다. 아래의 그림을 보면 직관적으로 이해할 수 있을 것이다.
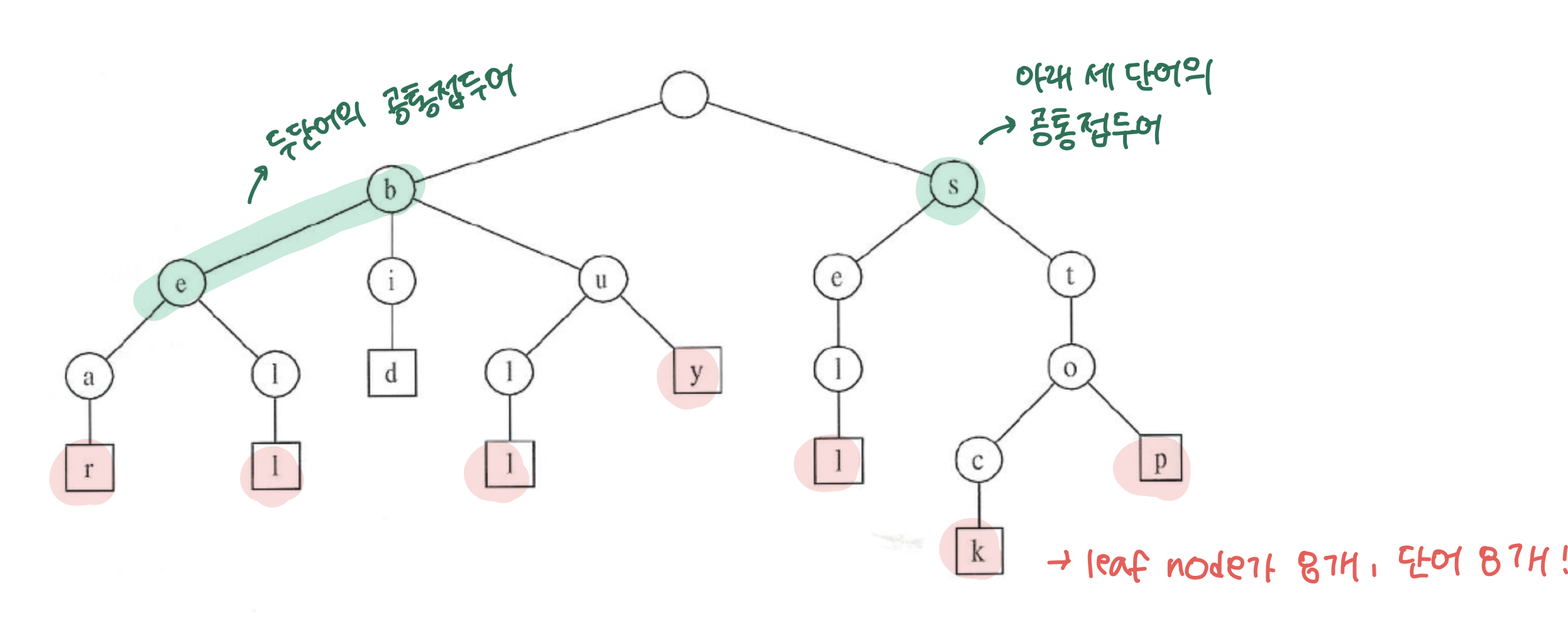
그림은 트라이를 자주 사용하는 문자열의 예시이다. 총 여덟개의 단어를 위와 같이 저장하여 빠르게 문자열을 탐색할 수 있다. 그림처럼 공통된 접두어를 같은 노드로 처리하기 때문에 자동 검색어 완성, 사전 찾기, 문자열 검사 등과 같은 상황에서 좋은 시간복잡도를 위해서 사용된다.
트라이를 자바로 구현해보자 !
그럼 트라이를 어떻게 구현하면 좋을지 알아보자 ! 본인은 자바로 구현하려고 한다. 하지만 필요한 구성 요소와 메소드, 로직, 주의할 점 등을 정리할테니 다른 언어를 사용하는 사람들은 직접 구현해보면 좋을 것 같다 !
트라이가 트리를 기반으로 한 자료구조이기 때문에 노드가 될 클래스와 트라이 자료 구조를 관리할 클래스 두 개를 구현해야 한다. 하나씩 알아보자 !
TrieNode
먼저 트라이의 노드 역할을 할 클래스부터 알아보자 ! 가장 중요한 구성 요소는 두 가지이다.
- 자식 노드들을 담고있는 Map ( 문자열을 저장한다면 문자가 키, 노드가 밸류 )
- 본인 노드가 어떠한 입력값의 말단 노드인지를 나타내는 boolean
이 외에도 기본적인 생성자, getter, setter 등 필요한 요소들을 구현해주면 된다.
import java.util.*;
class TrieNode {
private Map<Character, TrieNode> childNodes = new HashMap<>();
private boolean isLast;
public Map<Character, TrieNode> getChildNodes() {
return childNodes;
}
public boolean isLast() {
return isLast;
}
public void setLast(boolean last) {
isLast = last;
}
}Trie
이제 위의 트라이 노드를 이용하여 트라이 자료 구조를 구현해보자 ! 기본적으로 아래의 코드처럼 root 노드를 초기화 해주어야 한다.
public class Trie {
private TrieNode rootNode;
Trie(){
rootNode = new TrieNode();
}
}
이제 트라이를 사용하기 위한 기본적인 메소드 세 가지를 구현해보자.
1. insert
입력 받은 단어를 문자 순서대로 트리 계층 구조의 자식 노드로 생성하여 넣어준다.
- 이미 자식 노드에 같은 문자가 존재하면 새로 생성해주지 않고 자식 노드로 이동만 한다.
- 단어의 마지막 문자 노드에는 last 체크를 해준다.
void insert(String word){
TrieNode node = this.rootNode;
for(int i=0; i<word.length(); i++) node = node.getChildNodes().computeIfAbsent(word.charAt(i), c -> new TrieNode());
node.setLast(true);
}2. contains
특정 단어가 트라이에 존재하는지 확인한다.
- 루트 노드부터 단어의 문자 순서대로 일치하는 자식 노드가 계층별로 있어야 한다.
- 단어의 마지막 문자에 last로 체크가 되어있어야 한다.
위의 두 조건을 모두 만족하면 true, 그렇지 않으면 false
boolean contains(String word){
TrieNode node = this.rootNode;
char cur;
for(int i=0; i<word.length(); i++){
cur = word.charAt(i);
if(!node.getChildNodes().containsKey(cur)) return false;
node = node.getChildNodes().get(cur);
}
return node.isLast();
}3. delete
트라이에 넣었던 단어를 삭제한다.
- 자식 노드는 부모 노드를 모르기 때문에 주어진 단어의 마지막 문자까지 이동하여 거꾸로 문자를 삭제해와야 한다. 이 과정은 재귀로 구현해주었다.
- 당연하게도 다음 문자에 해당하는 자식 노드가 존재해야 한다. 또한 삭제를 시작하는 마지막 노드는 last로 체크되어 있어야 한다. 이 두가지로 존재하지 않는 단어에 대한 삭제 예외를 잡아줄 수 있다.
- 단어 삭제를 의미하기 위해서 기본적으로 마지막 문자 노드의 last 체크를 해제해준 후, 아래의 조건에 맞추어 노드 삭제를 진행한다.
- 자식 노드가 없어야 한다. 자식 노드가 있다면 다른 단어에도 사용되는 문자이므로 제거하면 안된다.
- 자식 노드가 없더라도 last가 체크되어 있다면 다른 단어에 포함되는 문자이므로 제거하면 안된다.
void delete(String word){
delete(this.rootNode, word, 0);
}
private void delete(TrieNode node, String word, int index){
if(index == word.length()){
if(!node.isLast()) throw new Error("not exist");
node.setLast(false);
return;
}
char cur = word.charAt(index);
if(!node.getChildNodes().containsKey(cur)) throw new Error("not exist");
TrieNode child = node.getChildNodes().get(cur);
delete(node.getChildNodes().get(cur), word, index+1);
if(child.getChildNodes().isEmpty()) {
if(!child.isLast()) node.getChildNodes().remove(cur, child);
}
}전체 코드
import java.util.*;
class TrieNode {
private Map<Character, TrieNode> childNodes = new HashMap<>();
private boolean isLast;
public Map<Character, TrieNode> getChildNodes() {
return childNodes;
}
public boolean isLast() {
return isLast;
}
public void setLast(boolean last) {
isLast = last;
}
}
public class Trie {
private TrieNode rootNode;
Trie(){
rootNode = new TrieNode();
}
void insert(String word){
TrieNode node = this.rootNode;
for(int i=0; i<word.length(); i++) node = node.getChildNodes().computeIfAbsent(word.charAt(i), c -> new TrieNode());
node.setLast(true);
}
boolean contains(String word){
TrieNode node = this.rootNode;
char cur;
for(int i=0; i<word.length(); i++){
cur = word.charAt(i);
if(!node.getChildNodes().containsKey(cur)) return false;
node = node.getChildNodes().get(cur);
}
return node.isLast();
}
void delete(String word){
delete(this.rootNode, word, 0);
}
private void delete(TrieNode node, String word, int index){
if(index == word.length()){
if(!node.isLast()) throw new Error("not exist");
node.setLast(false);
return;
}
char cur = word.charAt(index);
if(!node.getChildNodes().containsKey(cur)) throw new Error("not exist");
TrieNode child = node.getChildNodes().get(cur);
delete(node.getChildNodes().get(cur), word, index+1);
if(child.getChildNodes().isEmpty()) {
if(!child.isLast()) node.getChildNodes().remove(cur, child);
}
}
}