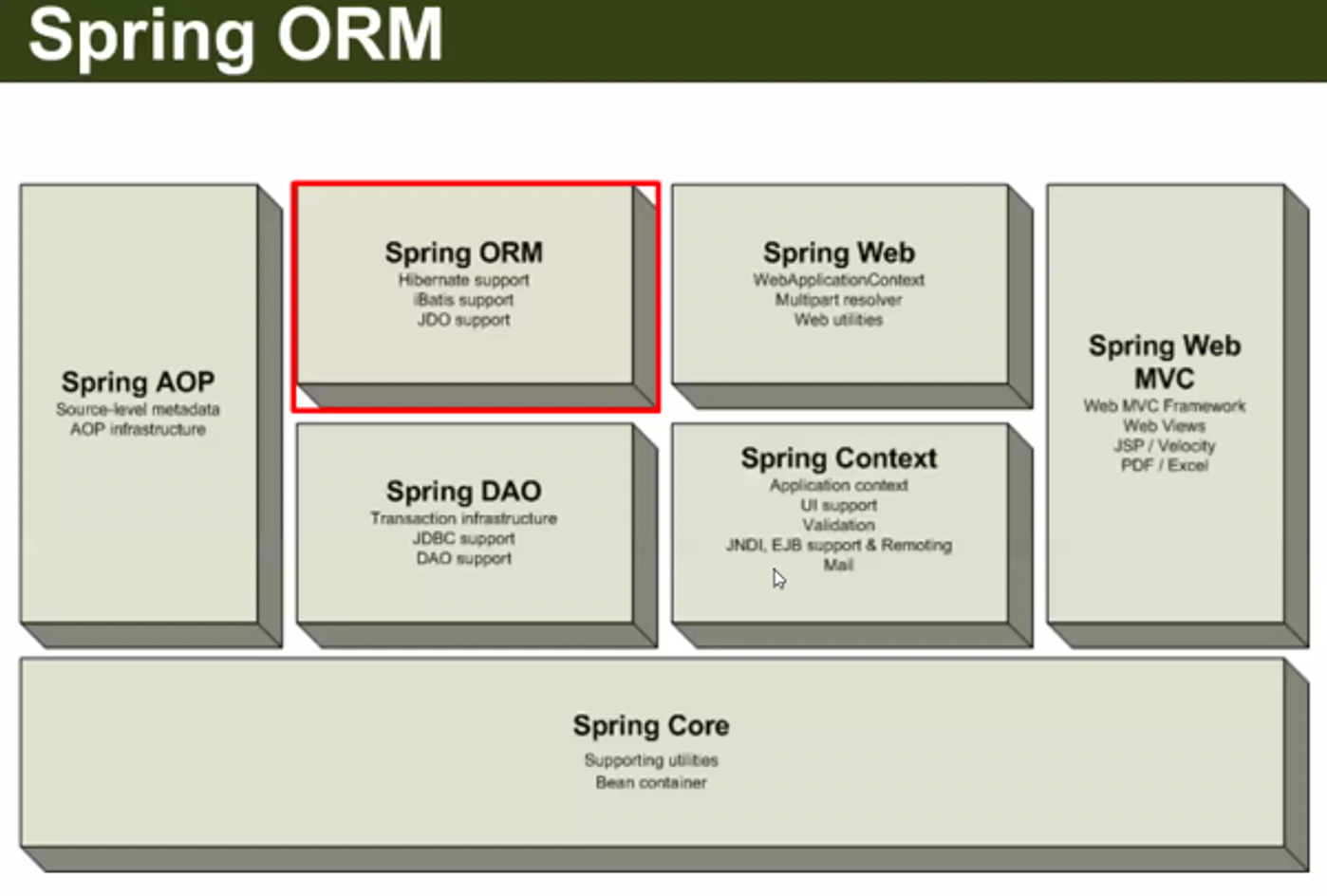
Spring ORM
-
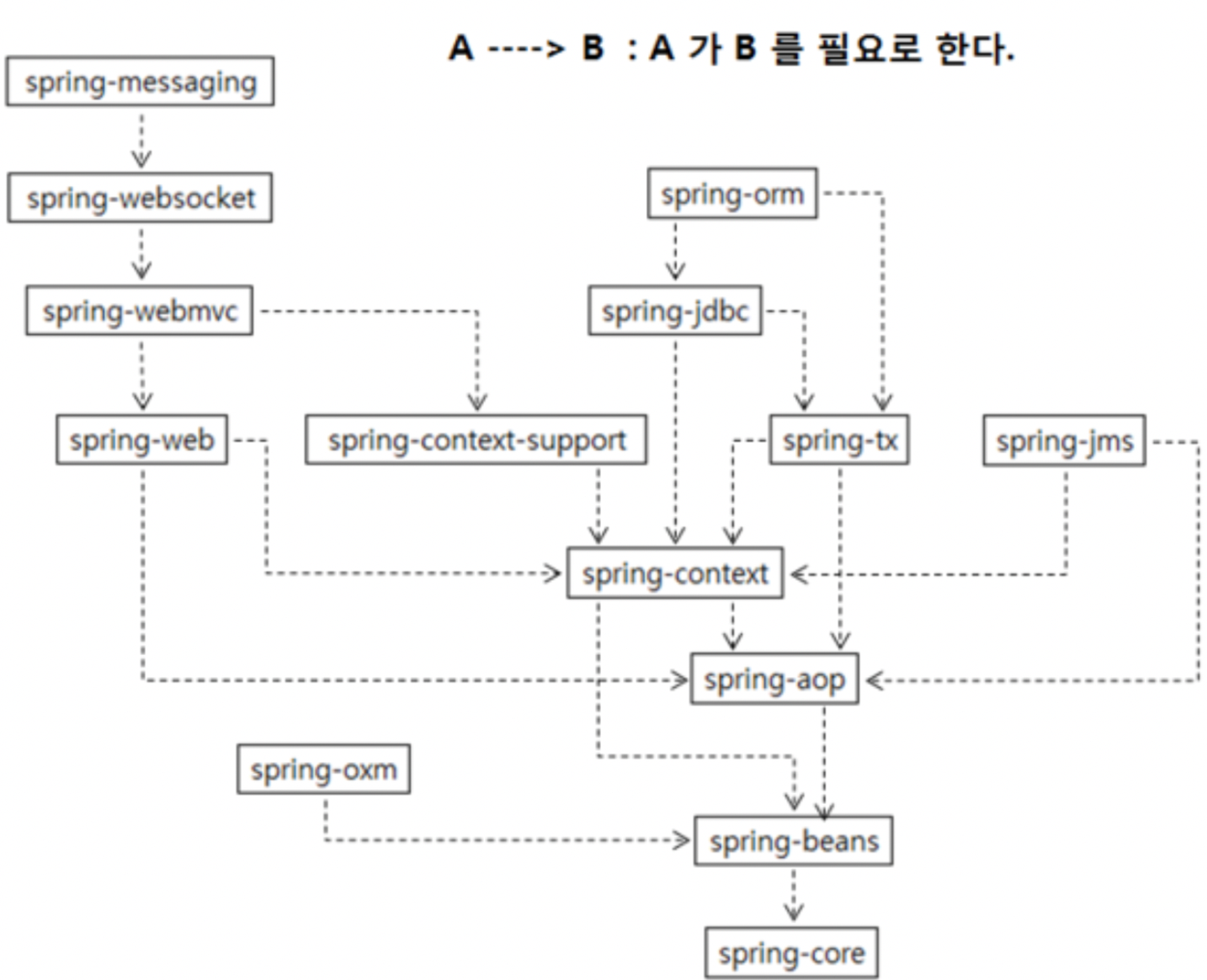
Spring은 여러 개의 모듈로 이루어져 있으며, 각 모듈은 서로간의 의존관계를 가집니다.
-
예를 들어,
1) Spring의 DI 기능만 필요하다면 의존성으로 Spring Core, Spring Context를 추가해주면 되고
2) Spring의 AOP 기능만 필요하다면 의존성으로 Spring Core, Spring Beans를 추가해주면 되며
3) Spring Web MVC 기능은 Spring Context Support와 Spring Web
4) Spring ORM 을 쓰려면, Spring Core, Spring Context, Spring AOP, Spring DAO ( DB 연결 및 Transaction 관리 ) 가 있어야 합니다.
DataSource & DBCP
-
DBCP는 데이터베이스 커넥션 풀의 약자로, 클라이언트 요청마다 DB에서의 인증 및 커넥션 생성을 하여 진행하는 것이 아닌, 미리 커넥션을 여러 개 만들어서 웹 어플리케이션 환경에서 응답속도를 개선하기 위해 사용합니다. ( 커넥션 만드는 비용을 줄일 수 있기 떄문 )
- 10번의 트랜잭션이 있다면, 10번
DB_ID,DB_PW로 인증하는 시간 낭비, 자원 낭비
- 10번의 트랜잭션이 있다면, 10번
-
이러한 Connection Pool의 라이브러리로 Apache Commons DBCP를 많이 사용합니다.
-
기존 코드에서는
ojdbc6.jar의OracleDataSource를 직접 의존 ( new로 생성 )하여 커넥션 풀을 만들고, 해당 커넥션에서 물어온 Connection으로 DB연결을 수행했습니다. -
이러한 DataSource를 Spring Context에 Bean으로 등록하여 사용한다면, 추후 요구사항 변경 시 코드 수정을 줄여 유지보수성을 좋게할 수 있습니다.
-
또한, Oracle의 DataSource를 직접 의존하는 방법 외에 Tomcat 자체에서 제공해주는 DataSource를 사용하는 방법도 있습니다. ( Apache Commons DBCP )
- 이를 사용하기 위해서는
pom.xml에commons-dbcp-1.4.jar,commons pool.jar를 추가해주면 됩니다.
- 이를 사용하기 위해서는
Java 어플리케이션 자체에서 Connection Pool 을 사용해보자. : JNDI
-
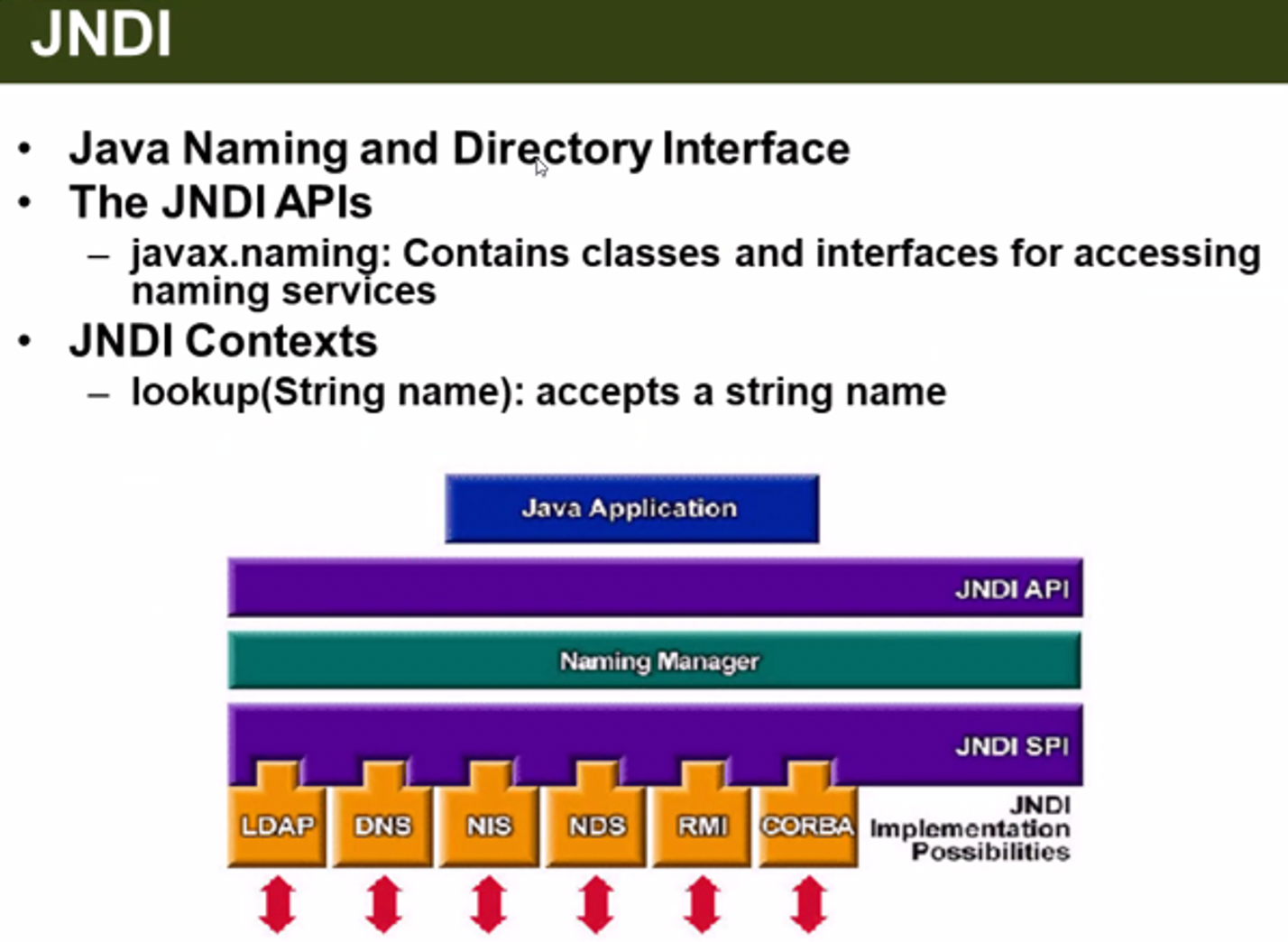
JNDI- Java Naming And Directory Interface -
내 자바 코드에서 남의 자원을 쉽게 사용하고 관리할 수 있게 해준다!
- 내 코드에서 API를 사용하지 않고, jar를 임포트하지 않고, 다른 사람 컴퓨터의 코드를 실행시킨다.
-
이와 관련한 기술로 RMI ( Remote Method Interface )가 있음.
- JNDI를 통해 자원을 lookup 한 뒤에 해당 자원의 메서드를 실행해준다.
- 네트워크 통신에서 사용한다.
-
Java 네트워킹의 가장 핵심, 고급 기술에 해당하는 것이 JNDI + RMI 이다.
-
MyBatis의 Context를 불러올 때 JNDI를 사용하기에 언급하고 감.
-
네트워크 자원에 이름을 통해 접근할 수 있도록 합니다.
-
LDAP (파일 리소스 공유 체계)
-
Low단의 기술에는 JNDI를 기반으로한 응용 기술을 사용합니다.
-
JNDI를 사용하여 Java 자체 코드에서 DataSource 자원을 사용할 수 있습니다.
static DataSource ds;
public Connection dbConn(){
Connection conn = null;
try {
initialContext ctx = new InitialContext();
Context envCtx = (Context) ctx.lookup("java:/comp/env");
ds = (DataSource) envCtx.lookup("jdbc/MyDataSource_MYNAME");
System.out.println("DataSource Lookup 성공!");
} catch(NamingException e){
System.err.println("lookup 실패 : " + e.getMessage());
}
}- JDNI의 통신 규격 ( "java:/comp/env" 이건
jdbc:thin:...이런 URL 규칙과도 같은 것이다. )
JDNI - web.xml
<!-- 리소스 설정 -->
<resource-ref>
<description>My DataSource</description>
<res-ref-name>jdbc/MyDataSource_MYNAME</res-ref-name>
<res-type>javax.sql.DataSource</res-type>
<res-auth>Container</res-auth>
</resource-ref>- 톰켓 서블릿 컨테이너가 해당 DataSource를 관리한다.
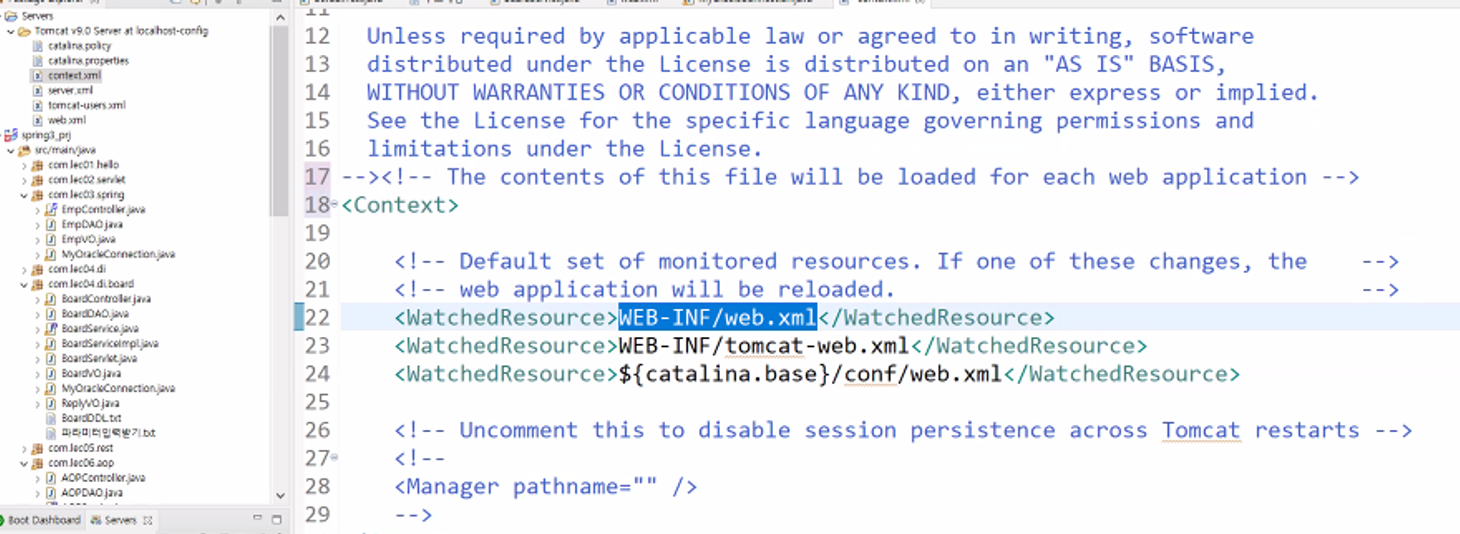
- 톰캣이 지금까지 우리
web.xml을 볼 수 있었던 것은 톰캣의context.xml에WEB-INF/web.xml이 표시되어 있었기 때문.
<!-- Tomcat context.xml -->
<Resource
name="jdbc/MyDataSource_MYNAME"
auth="Container"
type="javax.sql.DataSource"
maxTotal="100" -- 100개의 DataSource ( = Session )
maxIdle="30" -- 대기자 30명까지 대기
maxWaitMillis="10000"
username="it"
password="0000"
driverClassName="oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver"
url="jdbc:oracle:thin:@127.0.0.1:1521:XE"/>-
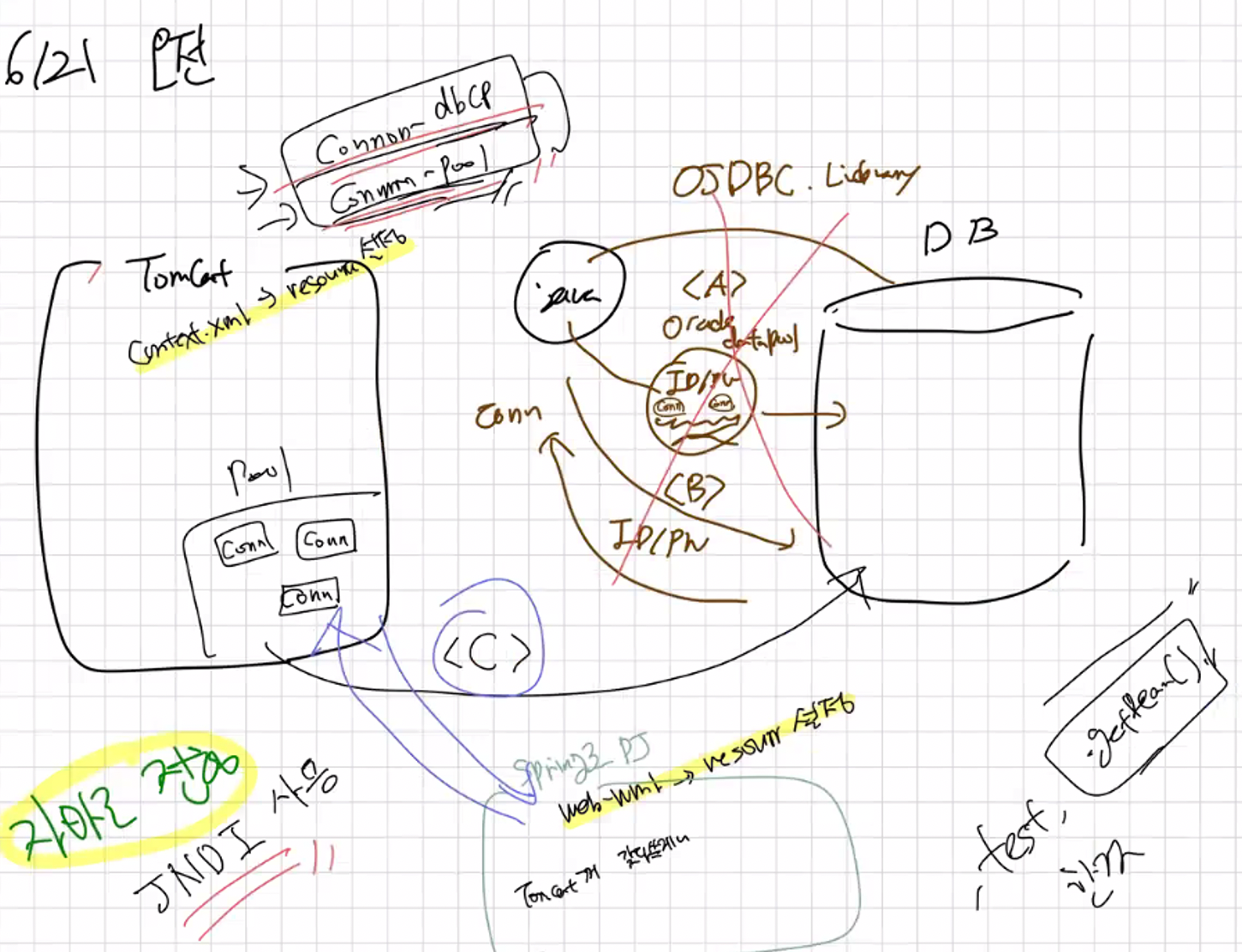
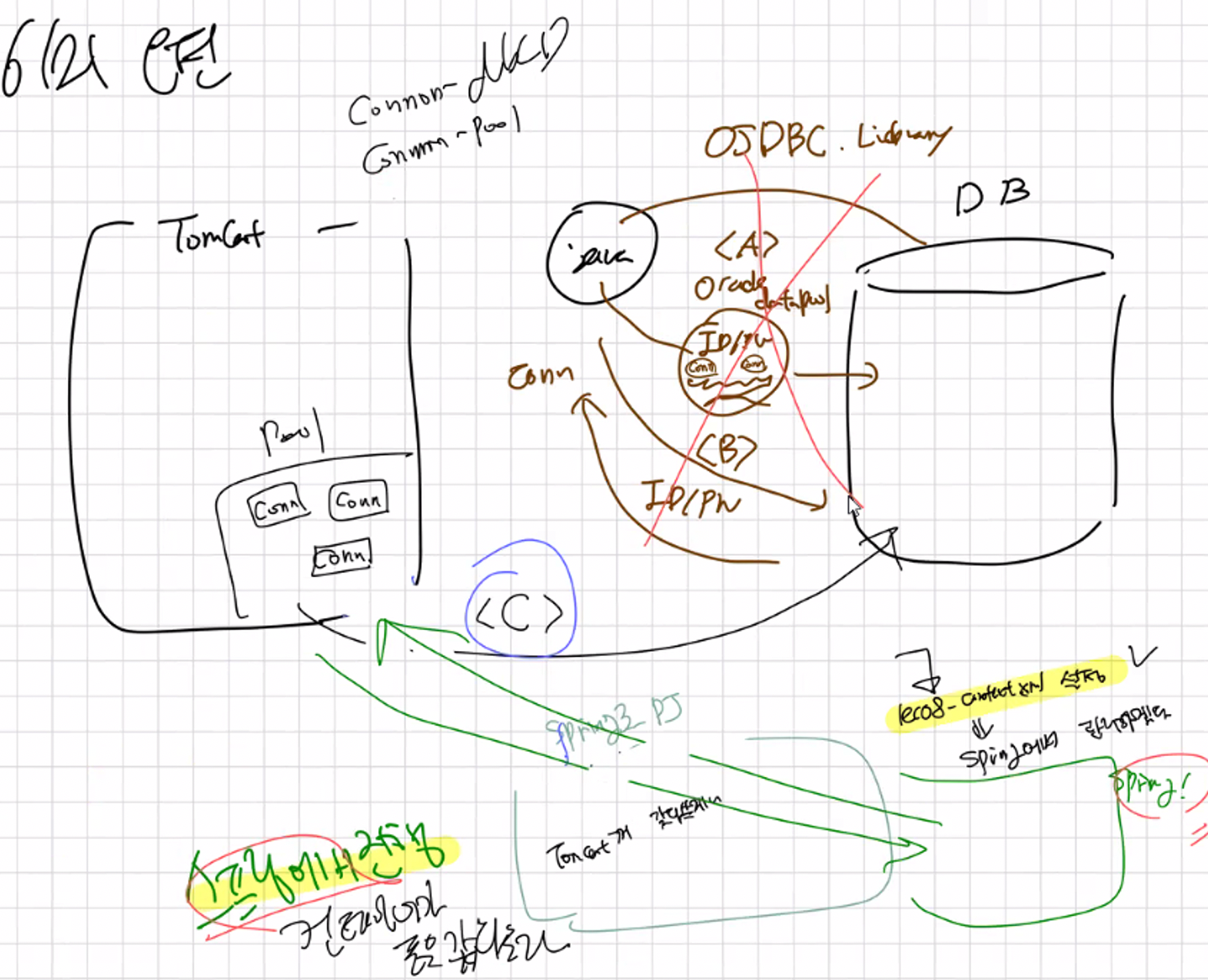
이를 Java 자체에서 호출 테스트를 했을 때 실패했습니다. ( JNDI를 통한 Call, lookup할 때 X ) => 윈도우 자체에서 환경변수 설정이 필요했습니다.
-
자바 자체에서 순수 데이터소스를 사용하는 것은 실패했지만, ( 가능합니다. )
Spring Container의 도움을 받아DataSource (=DBCP)를 사용해보겠습니다.
DataSource는, DBMS Vendor (ex. Oracle) | Tomcat | Spring 을 통해 주입받을 수 있습니다.
- 이 때, Tomcat의 DataSource를 Spring의 설정 ( servlet-context.xml )으로 받아와서 bean으로 등록하여 사용하겠습니다.
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
https://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"
>
<!-- 로그출력 : log4j -->
<mvc:resources mapping="/resources/**" location="/resources/"/>
<mvc:annotation-driven/>
<context:component-scan base-package="com.lec08.dao" />
<!-- datasource -->
<bean id="MY_tomcat_ds"
class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource"
destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName"
value="oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver" />
<property name="url"
value="jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:XE" />
<property name="username"
value="it"/>
<property name="password"
value="0000" />
</bean>
-
DataSource의 XML을 보면,destroy-method=”close”가 있습니다. 이는 자동으로 자원을 close 해준다. -
따라서 이
DataSource를 DAO에서 주입받아 사용하면,finally문의 자원을 닫아주는 행위를 하지 않아도 됩니다. ( 코드 중복 제거 )
Spring DAO ( Data Access Object )
-
데이터 엑세스 계층의 코드 작성을 단순화하고 일관된 데이터 접근 방법을 제공합니다.
-
JDBC, ORM ( Mybatis, Hibernate ), JPA 등의 다양한 데이터 접근 기술을 제공합니다.
-
JdbcTemplate( JDBC를 단순히 사용 가능 )을 제공합니다. -
JPA= Java Persistence APIORM을 위한 표준 인터페이스ORM(Object Relation Mapping)- 자바 객체 = 테이블(엔티티)를 매핑해줍니다.
- DB 엔티티를 클래스와 연결,
Entity라는 형태로 고나리합니다.
JdbcTempate, MyBatis, Hibernat, Spring Data JPA 예시
- 코드 이전에, 필요 라이브러리를
pom.xml에 추가힙니다.
<!-- mapper 관련 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.annotation</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.annotation-api</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- mybatis-spring -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.4.6</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Mybatis-spring -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
<version>1.3.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<arti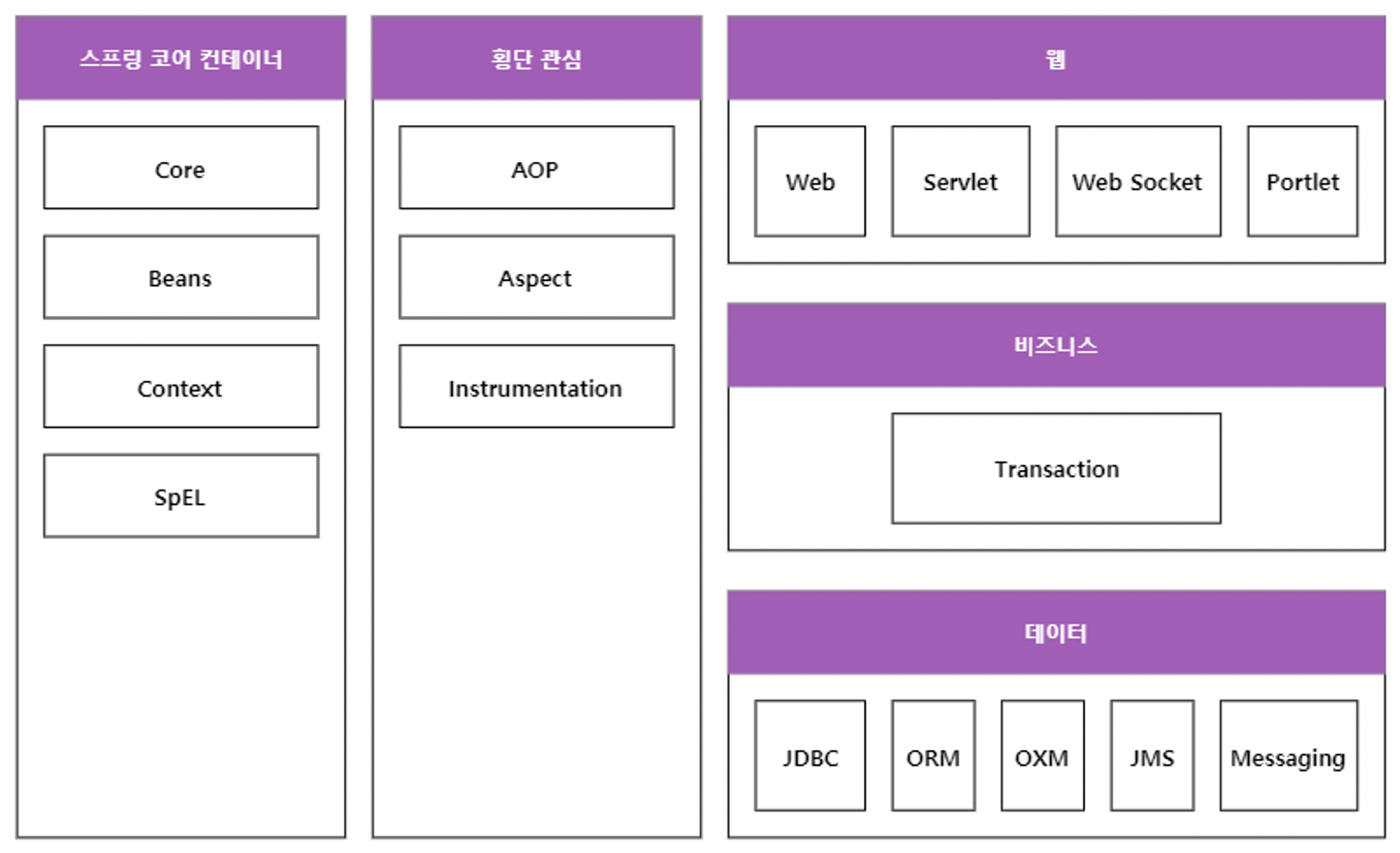
factId>spring-ibatis</artifactId>
<version>2.0.8</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.ibatis</groupId>
<artifactId>ibatis-sqlmap</artifactId>
<version>2.3.4.726</version>
</dependency>-----------------------------------------------------------------
스프링 DAO(Data Access Object)
- 데이터 액세스 계층의 코드 작성을 단순화하고 일관된 데이터 접근 방법을 제공
- JDBC, ORM(Hibernate, Mybatis, ...), JPA 등의 다양한 데이터 접근 기술 제공
- JdbcTemplate(단순) 제공
- ORM(Object Relation Mapping) : 자바객체-테이블 매핑
- JPA(Java Persistence API) : ORM을 위한 표준 인터페이스
-----------------------------------------------------------------
----------------------------------------------------------
*** JdbcTemplate
----------------------------------------------------------
public Post updatePost(Long id, Post updateParam) {
String sql = "UPDATE post SET title=?, content=?, MODIFIED_DATE=? where id=?";
template.update(sql,
updateParam.getTitle(),
updateParam.getContent(),
updateParam.getModifiedDate(),
id);
}
----------------------------------------------------------
*** JPA
----------------------------------------------------------
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
//slect * from user where uname = ?
List<User> findByName(String name);
}
----------------------------------------------------------
*** ORM(Mybatis)
----------------------------------------------------------
package com.lec09.orm;
public class MemberVO {
private int id;
private String name;
private String email;
private Date regdate;
// getters and setters
}
package com.lec09.orm.mapper;
public interface MemberMapper {
void myMethodName__insert(MemberVO mvo);
}
'MemberMapper.xml'
<mapper namespace="com.lec09.mapper.MemberMapper">
<insert id="myMethodName__insert" parameterType="com.lec09.orm.MemberVO">
INSERT INTO member (name, email) VALUES (#{name}, #{email})
</insert>
</mapper>
@Service
public class MemberServiceImpl {
@Autowired
private MemberMapper memberMapper;
public void addMember(MemberVO prmVO) {
memberMapper.myMethodName__insert(prmVO);
}
}
----------------------------------------------------------
*** ORM(Hibernate)
----------------------------------------------------------
@Data
@Table(name = "Member")
@Entity
public class Board implements java.io.Serializable {
@Id
@Column(name = "seq")
@GenenratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private int seq;
@Column(name = "title", nullable = false)
private String title;
public Board() {}
public Board(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
}
hibernate-board-mapper.xml
@Temporal(TemporalType.TIME)
private Date playTime;
@Temporal(TemporalType.DATE)
private Date added;
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name="com.lec09.orm.BoardVO" table="board">
<meta attribute="class-description">
Represents a single playable track in the music database.
@author Jum Elliott (with help from Hibernate)
</meta>
<id name="seq" type="int" column="seq">
<meta attribute="scope-set">protected</meta>
<generataor class="native">
</id>
<property name="title" type="string" not-null="true"/>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
public class ServiceImpl {
SessionFactory sessionFactory = HibernateUtil5.getSessionFactory();
SessionFactory session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction tx = null;
public void svcMethodd() {
try {
tx = session.beginTransaction();
// 쿼리 작성
tx.commit();
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
if (tx != null) tx.rollback();
} finally {
session.close();
}
sessionFactory.close();
}
}
----------------------------------------------------------Property & Classpath