MyBatis
- MyBatis의 핵심 라이브러리 자체를 의미, MyBatis 작업과 관련한 주요 기능을 제공.
- SQL 매핑을 정의하고, 데이터베이스 작업을 실행하는 데 사용할 수 있습니다.
지금까지의 설정 상황
- Java App
mybatis-context.xml- MyBatis 자체 구동에 관련한 설정을 한다.
- MyBatis와 DB를 연결한다. ( DBCP 연동 )
- MyBatis가 보아야할 Mapper들을 등록한다.
- Spring 설정을 담당하는
servlet-context.xml과 비슷함.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!-- db.properties -->
<properties resource="oracle.properties"/>
<!-- TypeAliases -->
<typeAliases>
<typeAlias alias="userVO" type="com.lec08.dao.BoardVO"/>
</typeAliases>
<!-- DBCP -->
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${lec.driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${lec.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${lec.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${lec.userpw}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!-- mapper -->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="board-map-lec08.xml"/>
<mapper resource="user-map-lec08.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>Spring을 사용한 설정이 아닌,Mybatis자체의 설정이다.- 1) classpath (
src/main/resources)에 존재하는 db.properties를 가져옵니다.mybatis-context.xml또한 classpath의 같은 위치에 존재하기에 따로 경로를 설정해줄 필요가 없습니ㅏㄷ.
map.xml- Query 결과를
VO에 바인딩한다. ( mapper 설정 )
- Query 결과를
src/main/resources ( classpath )
log4j.xmloracle.propertiesmybatis-context.xml*-map.xml
어노테이션 기반 Mapper I/F와 *-map.xml 을 연결
이렇게 함으로써
-
App과 SQL을 분리할 수 있습니다.
-
DAO Class를 없애고, 이를 Mapper I/F로 대체 후 SQL 관련 작업은 XML로 뺄 수 있습니다.
-
Service는 이렇게 I/F화된 Mapper들을 묶어 트랜잭션 단위로 사용할 수 있습니다.
-
mapper의 id 값을 Java Mapper I/F의 FQCN(Full Qualified Class Name)으로 주어, mapper와 자바 인터페이스를 1대1 매핑할 수 있습니다.
이해를 위한, DataSource - DataSourceTransactionManager - SqlSessionFactoryBean - SqlSessionTemplate - SqlSession의 관계도 그림
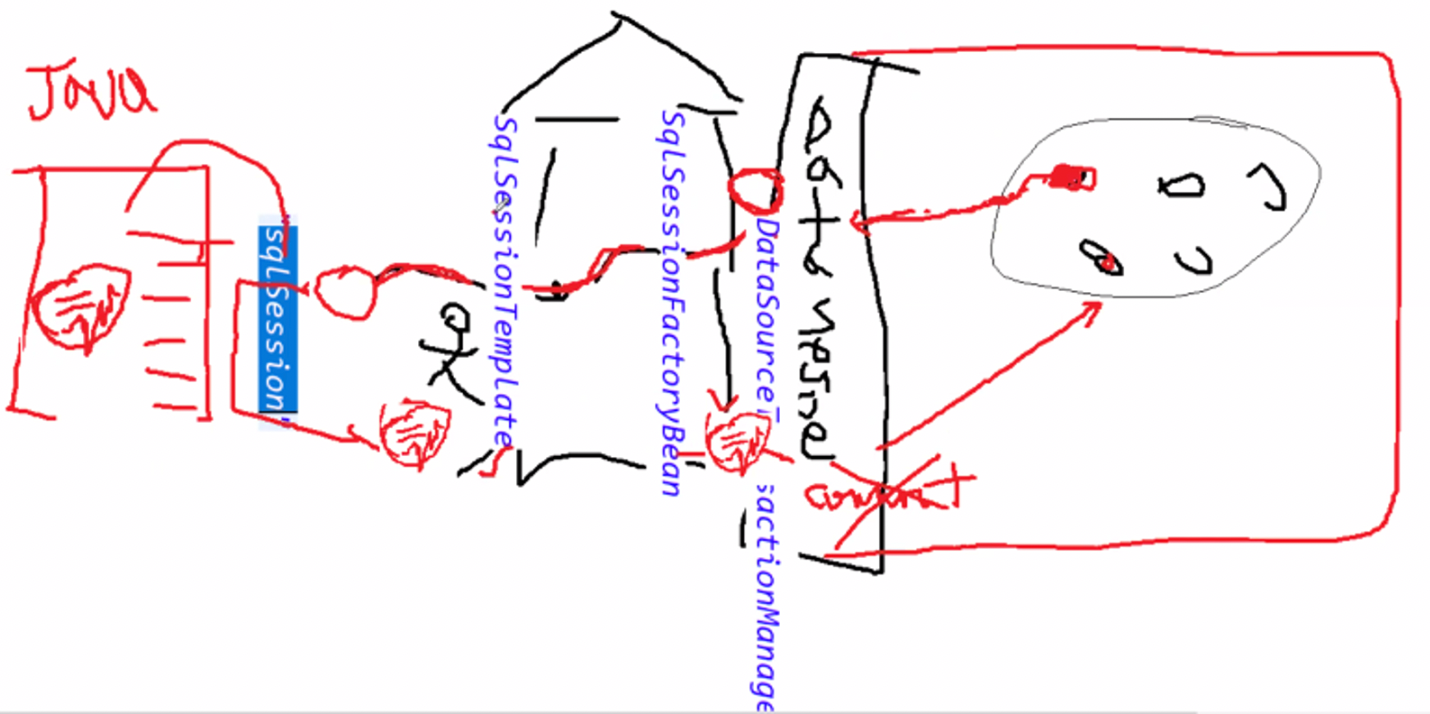
-
DataSource를 통해 DBCP에 접근할 수 있습니다. -
이 때, 이
DataSource에TransactionManager가 붙어 트랜잭션 관리를 해줍니다. -
DataSource에 MyBatis의 SqlSessionFactoryBean이 접근하여 SqlSession ( DB Connection )을 잡아옵니다.
-
SqlSessionFactory Bean 설정 XML 내용
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="myDS_CONSOL_PRINT"/>
<property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath:lec09-mappers/*-map.xml"/>
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:lec09-mappers/mybatis-context.xml"/>
</bean>
<bean id="sqlSession" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate">
<constructor-arg index="0" ref="sqlSessionFactory" />
</bean>- session의 commit과 close는 개발자가 관리해주어야 합니다.
트랜잭션 매니저를 통한 트랜잭션 관리 설정
-
트랜잭션 적용은 모두 AOP를 통해 진행합니다.
-
어노테이션 기반으로 설정할 수도 있고, XML기반으로 설정할 수도 있습니다.
1) 어노테이션 기반 설정
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="txManager"/>
-
@Transactional이 붙은 클래스와 메서드를 대상으로 트랜잭션 커밋/롤백을 진행해줍니다. -
여기서
tx는spring-tx의존성의 설정이라 생각하면 됩니다.
2) XML 기반 설정
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="txManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="*" rollback-for="Exception"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="cut" expression="execution(* com.lec09..*Impl.*(..))"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="cut" />
</aop:config>3) 스프링 부트에서는 @Configuration 을 통해 DataSource 빈 설정, 트랜잭션 설정을 해줄 수 있습니다.
