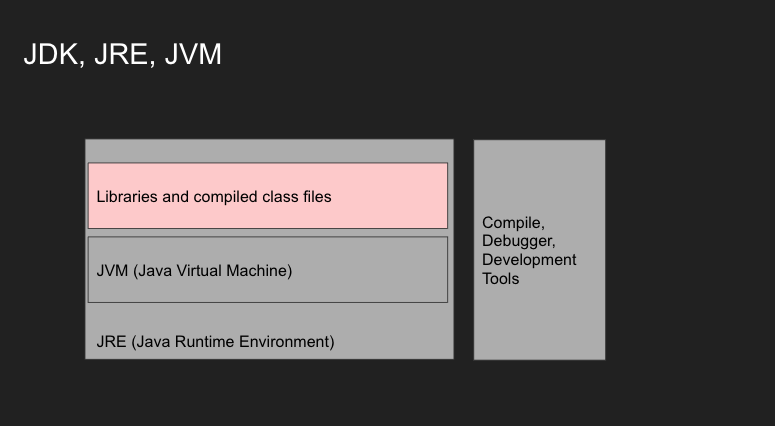
클래스와 생성자
- 클래스 : 데이터를 어떻게 관리할 것인가!
studentName[0], studentId[0], studentAge[0] → student[0].Name, student[0].Id, student[0].Age
관리적 차원에서 클래스 생성 - 생성자 : 클래스 내에서 반드시 등록되어야하는 데이터
- Class Student (Name, Age, ID)
❗️ { } 영역 조심, 파일/폴더 조심
// 하나씩 지정해서 선언
public class TestMain {
public static void main(String[] args){
String [] studentName = new String [30];
int [] studentAge = new int [30];
String [] studentId = new String[30];
studentName[0] = "abc";
studentAge[0] = 22;
studentId[0] = "abc22";
studentName[1] = "bcd";
studentAge[1] = 23;
studentId[1] = "bcd23";
studentName[2] = "cde";
studentAge[2] = 24;
studentId[2] = "cde24";
for (int i = 0; i<30 ; i++) {
System.out.println("Name : " + studentName[i]
+ " Age : " + studentAge[i]
+ " Id : " + studentId[i]);
}// Student 클래스 생성
public class TestMain {
public static void main(String[] args){
for (int i = 0; i<3; i++) {
students[i] = new Student();
}
students[0].Name = "abc";
students[0].Age = 22;
students[0].Id = "abc22";
students[1].Name = "bcd";
students[1].Age = 23;
students[1].Id = "bcd23";
students[2].Name = "cde";
students[2].Age = 24;
students[2].Id = "cde24";
*/
for (int i = 0; i<3 ; i++) {
System.out.println("Name : " + students[i].Name
+ " Age : " + students[i].Age
+ " Id : " + students[i].Id);
}
}// Student 클래스 + 생성자
public class Student {
String Name;
int Age;
String Id;
public Student(String name, int age, String id) {
Name = name;
Age = age;
Id = id;
students[0] = new Student("abe", 22, "ab322");
students[1] = new Student("bcd", 23, "ab323");
students[2] = new Student("cde", 24, "ab324");
for (int i = 0; i<3 ; i++) {
System.out.println("Name : " + students[i].Name
+ " Age : " + students[i].Age
+ " Id : " + students[i].Id);
}
}
}System.out.println("Class");
Student [] students = new Student [3];
students[0] = new Student("abe", 22, "ab322");
students[1] = new Student("bcd", 23, "ab323");
students[15] = new Student("cde", 24, "ab324");
students[1].setAge() = -999;
for (int i = 0; i<30 ; i++) {
/*
// continue 사용
if (students[i] == null) {
System.out.println("skip");
continue;
}*/
/*
// break 사용
if (students[i] == null) {
System.out.println("학생 " + i + "는 비었기에 멈춤");
break;
} */
for (int i = 0; i<3 ; i++) {
System.out.println("Name : " + students[i].Name
+ " Age : " + students[i].Age
+ " Id : " + students[i].Id);
}- 소스작업 - generator / getter / setter
@Override
public String toString() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return "클래스 안에서씀" + "Name : " + this.getName()
+ " Age : " + getAge() + " Id : " + this.getId()
+ "Special Id : " + this.getSpecialTypeId();
}- 추상클래스
- private / protected - 보안 차이
- interface
Registerable [] regi = new Registerable [6];
for (int i = 0; i<3 ; i++) {
regi [i] = students[i];
}
regi[4] = sstudent;
regi[5] = sstudent2;
for (Registerable r : regi) {
r.regist();
}
for (Registerable r : regi) {
r.drop();
}
일반학생abe등록합니다
일반학생bcd등록합니다
일반학생cde등록합니다