
1. 자바 상속의 특징
상속이란 상위클래스에서 정의한 필드와 메서드를 하위클래스도 동일하게 사용할 수 있게 물려받는 것이다.
부모 클래스를 상위 클래스(슈퍼 클래스, Super Class) 또는 기반 클래스(베이스 클래스, Base Class) 로 부르며, 상속받은 자식 클래스를 하위 클래스(서브 클래스, Sub Class) 또는 파생 클래스(유도 클래스, derived Class) 라 부른다.
1.1 특징
- 다중상속을 지원하지 않는다. 즉, extends 뒤에는 단 하나의 부모클래스만 올 수 있다.
- 부모의 생성자는 상속되지 않는다.
- 자식 클래스는 부모 클래스가 가진 멤버변수와 메소드를 모두 상속받는다.
- 부모 클래스 내에서 멤버 변수 또는 메소드가 private 접근 제한자를 사용하면 멤버변수는 상속받으나 → 바로 접근이 불가능하다. 메소드는 상속되지 않는다.
- static 메서드 또는 변수도 상속이 된다.
- 동일한 이름의 변수가 부모 클래스와 자식 클래스에 둘 다 존재할 경우 부모 클래스의 변수는 가려진다.
- 상속에 대한 횟수를 제한하지 않는다.
- 최상위 클래스는 [Object] 클래스 이며, Object 클래스만이 유일하게 super class(부모 클래스)를 가질 수 없다. 즉, 모든 클래스들은 Object 클래스의 자식 클래스이다.
- 상위 클래스의 인스턴스가 먼저 생성되고, 하위 클래스의 인스턴스가 생성된다
1.2 사용 이유
Java 언어에서 상속을 하는 이유는 이미 존재하는 클래스의 메서드와 필드를 재사용할 수 있기때문이다.
즉, 새 클래스를 만들고자 하고, 구현하고자 하는 코드가 이미 다른 클래스에 존재한다면, 새로 작성할 필요없이 클래스 상속을 통해 이미 작성한 코드를 재사용할 수 있게된다.
2. super 키워드
super키워드를 사용하면 서브클래스가 수퍼클래스에 접근이 가능하다. super는 수퍼클래스의 참조변수라고 볼 수 있다.
-
부모의 기본 생성자를 호출하는 역할 (반드시 자식 생성자의 첫 줄에 위치)
-
자바는 자식 객체를 생성하면 부모 객체가 먼저 생성되고 자식 객체는 그 다음에 생성되는 구조
ex)
public class CellPhone { . . . }
public class IPhone extends CellPhone { . . . }
IPhone iPhone = new IPhone();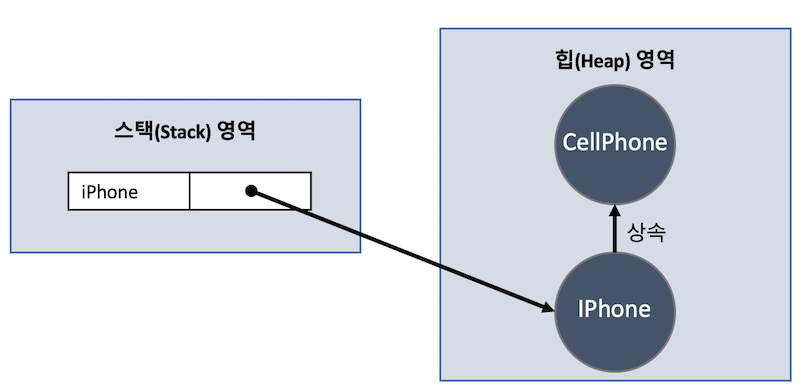
- CellPhone을 상속받는 자식 클래스 IPhone
- IPhone을 생성했을 때 내부 메모리 구조를 보면 부모 객체가 생성된 것 확인 가능
- 자식 생성자의 맨 첫 줄 자식 클래스의 생성자를 명시적으로 선언하지 않았다면 컴파일러가 자동으로 다음과 같은 기본 생성자 생성
public IPhone() {
super();
}3. 메소드 오버라이딩
super Class가 가지고있는 메서드를 서브클래스에서 새롭게 다른 로직으로 정의하고 싶을 때 사용하는 문법이다.
상속관계에 있는 클래스간에 같은 이름의 메서드를 정의하는 문법을 오버라이딩이라고 한다.
3.1 특징
- 오버라이딩 어노테이션은 생략할 수도 있다.
- 메서드의 이름은 같아야 한다.
- 메서드의 매개변수가 같아야 한다.
- 메서드의 반환타입이 같아야 한다.
- JDK1.5부터 부모클래스의 반환타입을 자식클래스로 변환은 가능하다.
- 접근 제어자는 부모클래스의 메서드보다 좁은 범위로 변경할 수 없다.
- 부모클래스의 메서드보다 많은 수의 예외를 선언할 수 없다.
- 인스턴스메서드와 static메서드를 서로 변경할 수 없다.
- @Override 으로 오버라이딩이 정확하게 재정의했는지 검사할 수 있다.
- 인터페이스 또한 default 메소드를 가지며 클래스는 이를 오버라이딩할 수 있다.
4. 다이나믹 메소드 디스패치 (Dynamic Method Dispatch)
디스패치는 어떤 메소드를 호출할 것인가를 결정하여 그것을 실행하는 과정이다.
즉, 실행시킬 수 있는 다양한 메소드가 주어진다고 한다면, 받은 메세지를 기반으로 어떤 메소드를 실행할 지 결정하는것을 의미한다.
- 정적 디스패치
- 컴파일 시점에 어떤 메소드를 실행할지 결정되는 것
- 동적 디스패치
- 메소드 오버라이딩이 되어있는 경우 실행시점에 어떤 메소드를 실행할 지 결정되는 것
4.1 정적 메소드 디스패치
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AppService appService = new AppService();
appService.run();
appService.run(2);
}
}
class AppService {
void run() {
System.out.println("run 호출");
}
void run(int num) {
System.out.println("run" + num + "번 호출");
}
}
정적 타이밍(static)에 어떤 메소드를 호출할지 결정하는 과정이다. (컴파일 시점)
메소드를 오버라이딩 하거나 오버로딩 할때도 컴파일 시점에 결정된다.
4.2 동적 메소드 디스패치
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AppService appService = new subAppService();
appService.run();
AppService appService2 = new subAppService2();
appService2.run();
}
}
abstract class AppService {
abstract void run();
}
class subAppService extends AppService {
@Override void run() {
System.out.println("sub1");
}
}
class subAppService2 extends AppService {
@Override void run() {
System.out.println("sub2");
}
}-
동적타이밍(Dynamic)에 어떤 메소드를 호출해야 할지 결정하는 과정을 말한다.
-
즉 런타임 시점에 어떤 메소드를 호출해야 할지 결정되는 과정이다.
-
인터페이스 또는 추상 클래스를 선언하고, 인터페이스를 구현 및 추상클래스를 상속 받은 하위 클래스를
-
인스턴스로 생성할 때 발생한다.
4.3 더블 디스패치 - 토비의 봄 TV 정리
-
instance of를 사용하지 않는다.
-
동적 디스패치를 두 번하는 기법이다.
- Post중에 어떤 postOn메소드를 선택할지에 대한 dynamic dispatch가 1번
- sns.post(this)에서 sns에 대한 dynamic dispatch가 2번
-
파라미터는 다이나믹 디스패치의 조건이 되지 않는다.
-
자바는 싱글 디스패치 언어이다. (receiver가 1개이다.)
interface Post{
void postOn(SNS sns);
}
static class Text implements Post{
public void postOn(SNS sns){
sns.post(this);
}
}
static class Picture implements Post{
public void postOn(SNS sns){
sns.post(this);
}
}
interface SNS{
void post(Text post);
void post(Picture post);
}
static class Facebook implements SNS{
public void post(Text post){
System.out.println("text -> facebook");
}
public void post(Picture post){
System.out.println("picture -> facebook");
}
}
static class Twitter implements SNS{
public void post(Text post){
System.out.println("text -> twitter");
}
public void post(Picture post){
System.out.println("picture -> twitter");
}
}
static class GooglePlus implements SNS{
public void post(Text post){
System.out.println("text -> gplus");
}
public void post(Picture post){
System.out.println("picture -> gplus");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
List<Post> posts = Arrays.asList(new Text(), new Picture());
List<SNS> sns = Arrays.asList(new Facebook(), new Twitter(), new GooglePlus());
posts.forEach(p->sns.forEach(s.postOn(s))); }
}5. 추상 클래스
6. final 키워드
7. Object 클래스
참조
