이 글은 깡샘의 안드로이드 프로그래밍을 보며 글을 작성하였습니다
안드로이드 파일구조
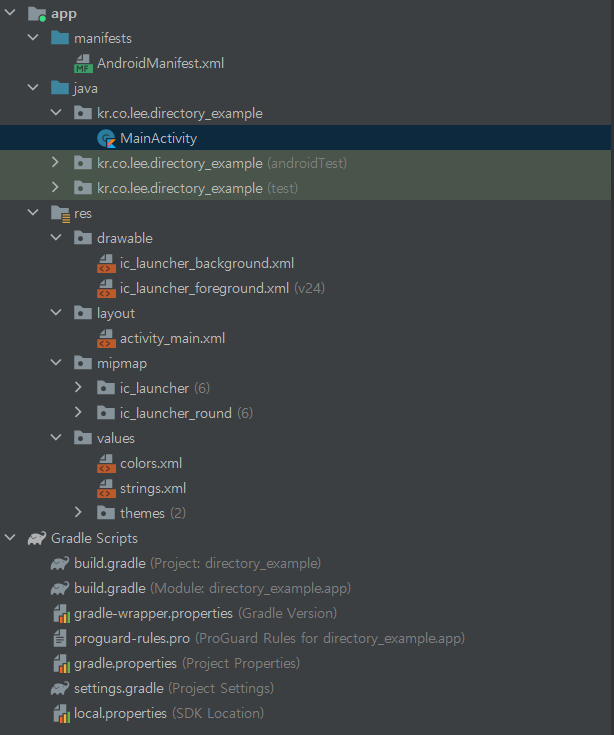
안드로이드 프로젝트의 기본적인 폴더 구조
R.java의 이해
안드로이드 앱에서는 많은 리소스 파일을 이용하는데, 모든 리소스 파일은 res 폴더 하위에 있어야 합니다. res 하위의 폴더는 이름이 지정되어 있으며, 개발자가 임의로 이름을 추가할 수 없습니다
이렇게 개발하다 보면 수많은 리소스가 만들어 지는데, 코드 영역에서 이를 식별할 방법이 필요합니다. 이를 도와주기 위한게 R.java 입니다.
R.java 파일은 툴이 자동으로 만들어주고, 이 파일은 단순하게 int형 변수만 선언되어 있습니다. 개발자가 res 밑에 하나의 리소스 파일을 추가하면 해당 파일명으로 된 int형 변수가 자동으로 추가됩니다. 그리고 자바코드에서 이 변수로 리소스를 지칭해서 사용하는 구조입니다.
res 폴더의 종류
- res/drawable : 리로스 중 이미지 파일을 저장하기 위한 폴더
- res/layout : 리로스 중 UI 구성을 위한 레이아웃 XML 파일을 위한 폴더
- res/mipmap : 리소스 중 앱의 아이콘 이미지를 위한 폴더
- res/values : 리소스 중 문자열 값 등을 위한 폴더(색상, 테마 - 스타일 등)
위처럼 처음 생기는 폴더에 말고도 res/menu(메뉴), res/anim(애니메이션), res/raw(오디오 등의 리소스파일) 등 많은 종류의 리소스 폴더가 있습니다
R.java의 주의사항
- R.java에서 각각의 리소스를 내부 클래스명인 string, drawable, layout등으로 구분하고 있기기에 res 밑에 임의의 폴더를 생성하면 안됩니다.
- 리소스 파일명도 자바 명명규칙을 위배할 수 없습니다. 또한, 리소스 파일명에 대문자를 사용할 수 없습니다.
그레이들(gradle) 파일
앱을 개발할 때 테스트를 진행하거나 개발이 완료된 후 배포하려면 빌드작업이 필요합니다. 이러한 빌드 작업을 그레이들이라는 도구를 이용합니다. 정리하자면 그레이들은 안드로이드의 빌드 도구 정도로 이해하면 됩니다.

안드로이드 스튜디오에서는 앱이 모듈 단위이며, 여러 모듈을 묶어서 관리하기 위한 개념이 프로젝트 개념입니다. 위 사진의 프로젝트 build.gradle은 프로젝트를 전체 프로젝트를 위한 설정, 모듈 build.gradle은 각 모듈을 위한 설정입니다.
settings.gradle
include ':app'위의 소스는 settings.gradle 파일의 소스인데, 이 파일은 그레이들에 모듈을 포함하여 그레이들이 모듈을 관리하고 빌드하게 설정하는 파일입니다. 위 예시에서는, app 이라는 이름의 모듈 하나만 추가된 예입니다.
프로젝트 수준의 gradle
gradle scripts 영역에서 괄호안에 Project라고 적힌 build.gradle인데, 이 파일은 모든 모듈을 위한 최상위 설정을 목적으로 합니다.
// Top-level build file where you can add configuration options common to all sub-projects/modules.
buildscript {
ext.kotlin_version = "1.5.10"
repositories {
google()
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
classpath "com.android.tools.build:gradle:4.2.2"
classpath "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-gradle-plugin:$kotlin_version"
// NOTE: Do not place your application dependencies here; they belong
// in the individual module build.gradle files
}
}
allprojects {
repositories {
google()
mavenCentral()
jcenter() // Warning: this repository is going to shut down soon
}
}
task clean(type: Delete) {
delete rootProject.buildDir
}프로젝트 수준의 build.gradle 파일의 소스입니다.
대부분 모듈 수준의 build.gradle 파일 설정이 자주 이러어지며, 프로젝트 수준의 그레이들 파일 설정은 빈번하지 않습니다. 설정된다면 위의 코드에서 dependencies 부분에 라이브러리를 추가하는 정도입니다.
모듈 수준의 gradle
plugins {
id 'com.android.application'
id 'kotlin-android'
}
android {
compileSdkVersion 30
buildToolsVersion "30.0.3"
defaultConfig {
applicationId "kr.co.lee.directory_example"
minSdkVersion 23
targetSdkVersion 30
versionCode 1
versionName "1.0"
testInstrumentationRunner "androidx.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"
}
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled false
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android-optimize.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro'
}
}
compileOptions {
sourceCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
targetCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
}
kotlinOptions {
jvmTarget = '1.8'
}
}
dependencies {
implementation "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib:$kotlin_version"
implementation 'androidx.core:core-ktx:1.6.0'
implementation 'androidx.appcompat:appcompat:1.3.1'
implementation 'com.google.android.material:material:1.4.0'
implementation 'androidx.constraintlayout:constraintlayout:2.1.1'
testImplementation 'junit:junit:4.+'
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test.ext:junit:1.1.3'
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test.espresso:espresso-core:3.4.0'
}모듈 수준의 build.gradle 파일의 소스입니다.
- compileSdkVersion : 빌드 시 이용되는 툴 버전 정보
- applicationId : 액의 식별자 정보를 설정하는 곳으로, 액의 식별자 이므로 세상에서 유밀무이해야 합니다. 왜냐하면 Play Store에 올릴 때 같은 식별자 Id로 등록된 앱이 있다면 등록되지 않습니다. 또한, 이 식별자 값으로 다른 앱이 사용자 스마트폰에 설치되어 있다면 자신이 만든 앱은 설치되지 않습니다.
- midSdkVersion : 개발자가 이 앱을 몇 버전의 스마트폰까지 지원할 것인지에 대한 설정입니다. 위의 예시에서는 23인데, 23버전 하위 스마트폰에서는 설치되지 않습니다. 즉 앱이 지원하는 최소의 버전을 명시하는 것입니다.
- targetSdkVersion : 개발 시 이용하고 있는 라이브러리 버전입니다. 대부분은 개발 시점의 최신 버전을 지정하여 사용합니다.
- versionCode : 앱의 버전 정보입니다. 앱들은 수시로 버전이 업데이트 되므로 앱을 서비스하는 도중 앱이 업데이트 되면, 이 정보를 변경해 다시 구글 Play Store에 등록합니다.
- dependencies : 외부 라이브러리를 이용 시 그레이들 파일의 dependencies에 등록해야 합니다. 그래야 그레이들이 빌드 때 참조할 수 있어서 정상적으로 빌드됩니다.
AndroidManifes.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="kr.co.lee.directory_example">
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/Theme.Directory_example">
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>위의 소스는 AndroidManifest.xml의 소스입니다
AndroidManifest.xml은 앱의 메인 환경 파일입니다. 앱이 스마트폰에서 동작할 때도 이 파일에 정의된 대로 동작합니다.
-
manifes 태그안의 package : 앱의 식별자 정보입니다. 그레이들 파일에 설정된 applicationId의 값과 같습니다.
-
application 태그 : 앱의 구성요소를 등록하기 위한 태그입니다. 안드로이드 컴포넌트 클래스(생명주기를 시스템이 관리)들은 AndroidManifest.xml에 등록해야 하며, 이 태크의 하위 태그로 등록합니다.
- android:icon : 앱의 아이콘 이미지 설정
- android:label : 앱의 이름을 명시
-
activity 태그 : 액티비티 컴포넌트를 등록하기 위한 태그입니다. 안드로이드 컴포넌트에 해당하는 activity, service, content provider(태그는 provider), broadcast receiver(태그는 receiver)가 이와 같이 추가됩니다. 액티비티는 name 속성을 생략할 수 없습니다.
