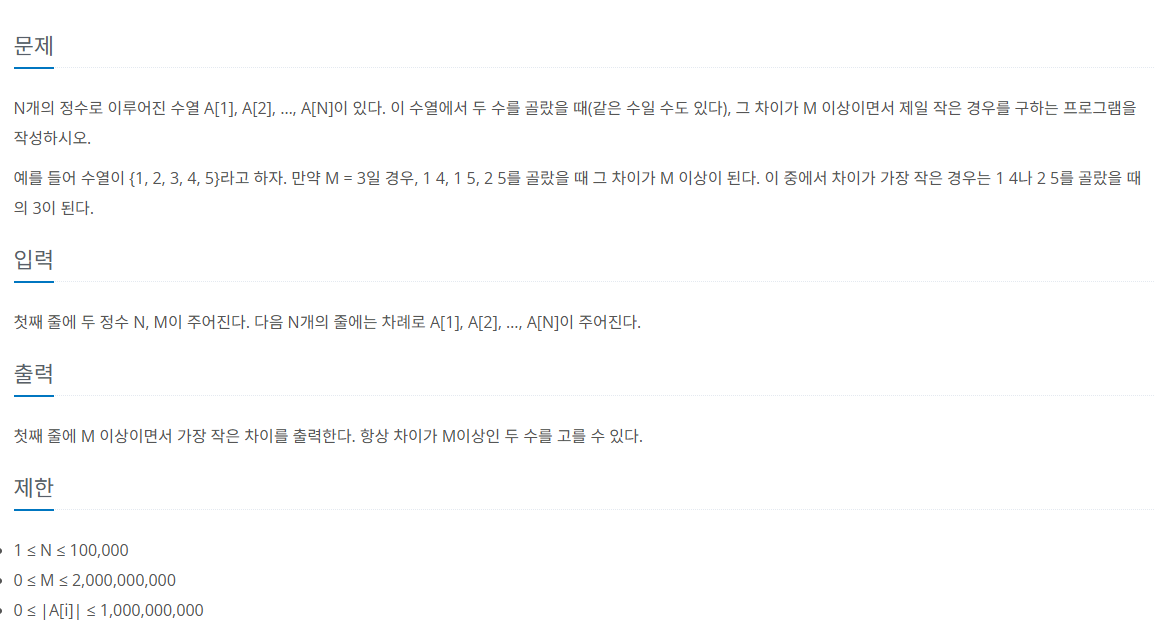
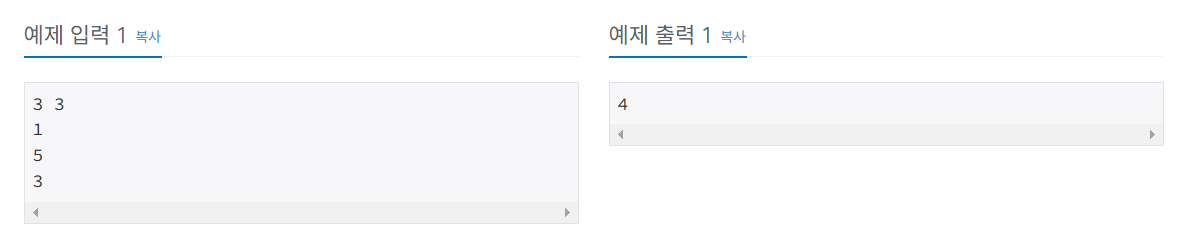
풀이
- 투 포인터 알고리즘을 사용하자
- 투 포인터 알고리즘이란 각각의 포인터를 주고 조건에 따라 인덱스를 증가시켜 원하는 값을 찾는 것 이라고 생각하면 쉽다. 비교할 두개의 인덱스 i와 j 를 선언하고 만약 두 인덱스 값의 차이가 m보다 작다면 비교할 대상의 큰 수 i인덱스를 증가 / 만약 차이가 정확히 m값과 동일하게 된다면 바로 break; / 만약 m이 두 값의 차이보다 크다면 빼주는 j번째 인덱스를 증가시킨다
- 투 포인터 알고리즘 기억하자 😎
package problem_solving.sort;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class BaekJoon_2230 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = Integer.parseInt(sc.next());
int m = Integer.parseInt(sc.next());
int [] arr = new int[n];
for(int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) {
arr[i] = Integer.parseInt(sc.next());
}
Arrays.sort(arr);
int i = 0 ;
int j = 0 ;
int answer = Integer.MAX_VALUE ;
while(i < n ) {
if( arr[i] - arr[j] < m ) {
i++;
continue;
}
if( arr[i] - arr[j] == m ) {
answer = m ;
break;
}
answer = Math.min(answer, arr[i]-arr[j]);
j++;
}
System.out.println(answer);
}
}



