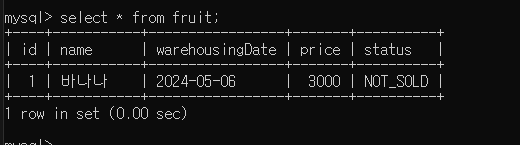
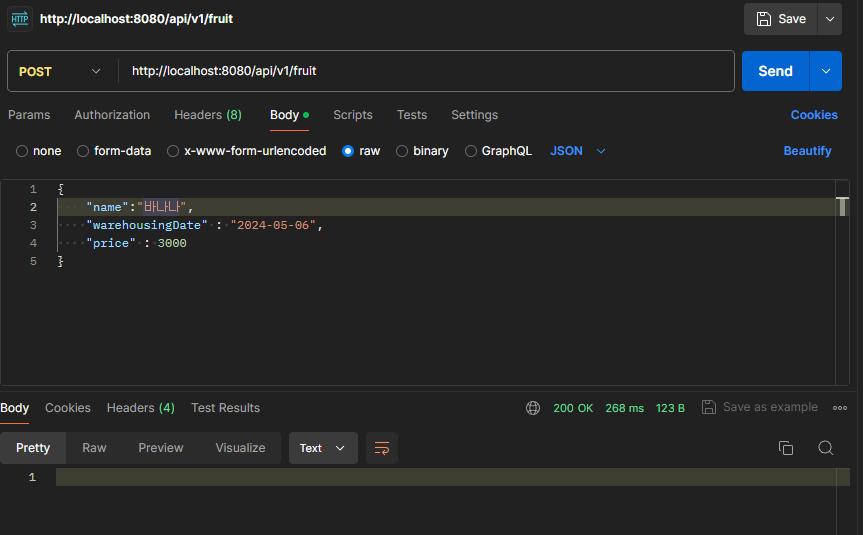
1. API Spec
- HTTP Method : POST
- HTTP Path : /api/vi/fruit
- HTTP Request Body
{ "name" : String, "warehousingDate" : LocalDate, "price" : Long } - 응답 : 성공시 상태 코드 200
createDTO
package com.group.libraryapp.practice;
import java.time.LocalDate;
public class FruitCreateRequest {
private long id;
private String name;
private LocalDate warehousingDate;
private Long price;
public long getId() {
return id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public LocalDate getWarehousingDate() {
return warehousingDate;
}
public long getPrice() {
return price;
}
}
Controller
package com.group.libraryapp.practice;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController
public class FruitController {
private final JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public FruitController(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
}
@PostMapping("/api/v1/fruit")
public void saveFruit(@RequestBody FruitCreateRequest request) {
String sql = "INSERT INTO fruit (name, warehousingDate, price) VALUES (?, ?, ?)";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql, request.getName(), request.getWarehousingDate(), request.getPrice()
);
}
API에서 int 대신 long을 사용한 이유
- 1) int 보다는 long이 더 많은 값을 저장할 수 있다.
- int
- 저장 공간: 32 bit
- 값의 범위 : -2147483648 ~ 2147483647
- long
- 저장 공간: 64 bit
- 값의 범위: -9223372036854775808 ~ 9223372036854775807
- 2) long 대신 Long 쓰는 이유
long은 primitive type으로, 값이 없을 경우 0으로 초기화된다.
따라서, id가 없어서 0으로 세팅이 된 것인지, 아니면 실제 값이 0인지 데이터만 보고 판별할 수 없다. 반면 Long은 wrapper type으로, 값이 없을 경우 null로 초기화 된다. 따라서 값이 0이라면, id가 0으로 저장됐음을 알 수 았다.
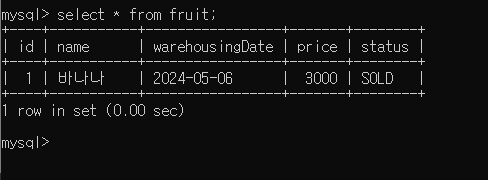
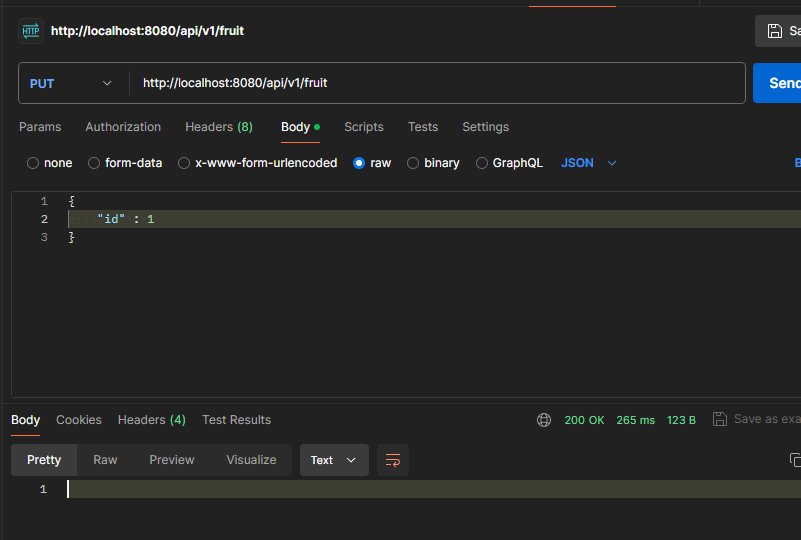
2. API Spec
- HTTP Method : PUT
- HTTP Path : /api/v1/fruit
- HTTP Request Body
{ "id" : long } - 응답 : 성공시 상태 코드 200
@PutMapping("/api/v1/fruit")
public void updateFruit(@RequestBody FruitCreateRequest request) {
String readSql = "SELECT * FROM fruit WHERE id = ?";
boolean isFruitNotExist = jdbcTemplate.query(readSql, (rs, rowNum) -> 0, request.getId()).isEmpty();
if (isFruitNotExist) {
throw new IllegalStateException();
}
String sql = "UPDATE fruit SET status = 'SOLD' WHERE id = ?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql, request.getId());
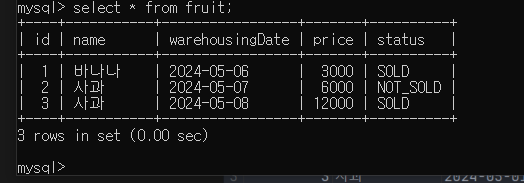
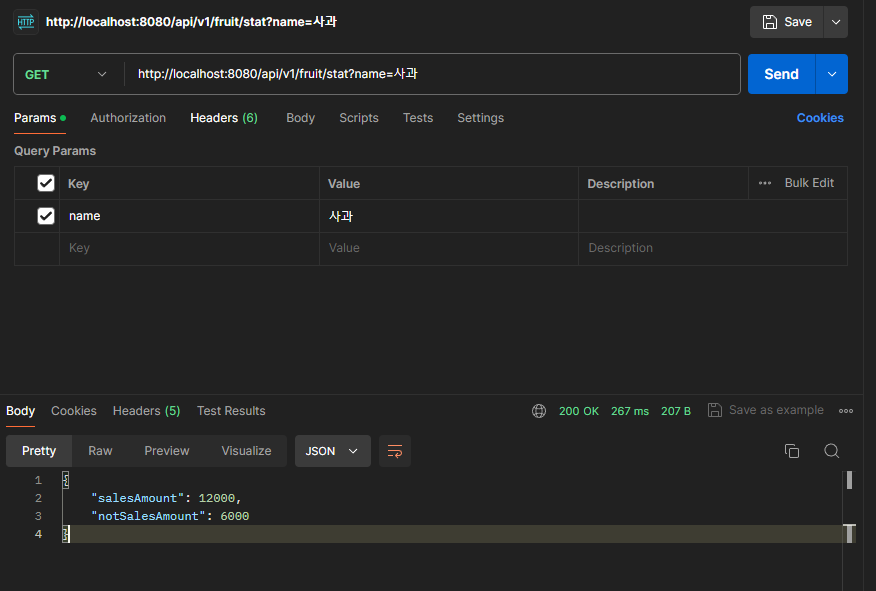
}3. API Spec
- HTTP Method : GET
- HTTP Path : /api/vi/fruit/stat
- Query : name=과일이름
- HTTP Response Body
{
"salesAmount" : long
"notSalseAmout" : long
}
@GetMapping("/api/v1/fruit/stat")
public FruitTotalPriceResponse getAmountInfo(@RequestParam String name) {
String sqlForSold = "SELECT SUM(price) FROM fruit WHERE name = ? AND status = 'SOLD'";
String sqlForNotSold = "SELECT SUM(price) FROM fruit WHERE name = ? AND status = 'NOT_SOLD'";
int salesAmount = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sqlForSold, Integer.class, name);
int notSalesAmount = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sqlForNotSold, Integer.class, name);
return new FruitTotalPriceResponse(salesAmount, notSalesAmount);
}