인프런, 자바(Java) 알고리즘 문제풀이
Recursive, Tree, Graph - 0707. 이진 트리 레벨 탐색(BFS)
🗒️ 문제
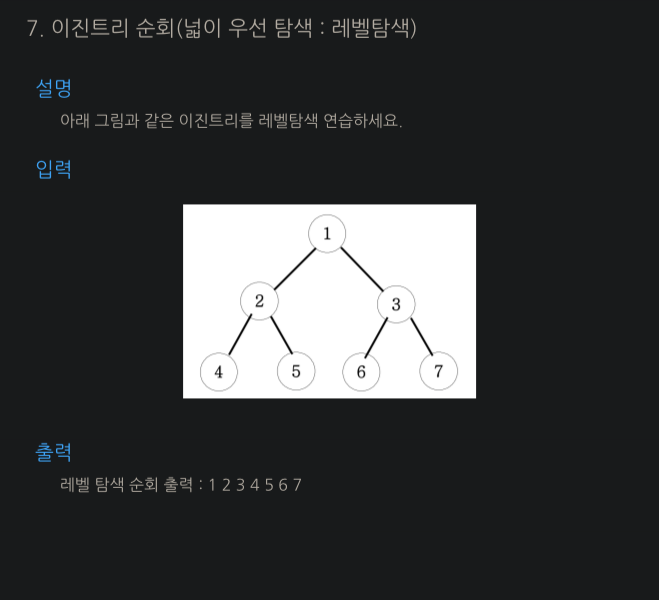
🎈 나의 풀이
private static class Node {
int data;
Node rt;
Node lt;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
rt = lt = null;
}
}
private static void BFS(Node node) {
Queue<Node> Q = new LinkedList<>();
Q.offer(node);
while(!Q.isEmpty()) {
int len = Q.size();
for(int i=0; i<len; i++) {
Node n = Q.poll();
System.out.print(n.data + " ");
if(n.lt != null) Q.add(n.lt);
if(n.lt != null) Q.add(n.rt);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node root = new Node(1);
root.lt = new Node(2);
root.rt = new Node(3);
root.lt.lt = new Node(4);
root.lt.rt = new Node(5);
root.rt.lt = new Node(6);
root.rt.rt = new Node(7);
BFS(root);
}🖍️ 강의 풀이
class Node{
int data;
Node lt, rt;
public Node(int val) {
data=val;
lt=rt=null;
}
}
public class Main{
Node root;
public void BFS(Node root){
Queue<Node> Q=new LinkedList<>();
Q.add(root);
int L=0;
while(!Q.isEmpty()){
int len = Q.size();
System.out.print(L+" : ");
for(int i=0; i<len; i++){
Node cur = Q.poll();
System.out.print(cur.data+" ");
if(cur.lt!=null) Q.add(cur.lt);
if(cur.rt!=null) Q.add(cur.rt);
}
L++;
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Main tree=new Main();
tree.root=new Node(1);
tree.root.lt=new Node(2);
tree.root.rt=new Node(3);
tree.root.lt.lt=new Node(4);
tree.root.lt.rt=new Node(5);
tree.root.rt.lt=new Node(6);
tree.root.rt.rt=new Node(7);
tree.BFS(tree.root);
}
} 💬 짚어가기
BFS란?
해당 문제는 BFS(Breadth-First Search) : 너비 우선 탐색 알고리즘의 예시이다.
이는 그래프 탐색 방식의 하나로, 그래프 탐색이란 하나의 정점으로부터 시작하여 차례로
모든 정점들을 한 번씩 방문하는 것이다.
그 중 BFS는 루트 노드(혹은 임의의 노드)에서 시작해서 인접한 노드(같은 레벨의 노드)를
먼저 탐색하는 방법이다. 이렇게 시작 정점으로부터 가까운 정점을 먼저 방문하게 되고, 멀리 있는
정점을 나중에 방문하게 된다.
트리를 넓게 탐색하며, 두 노드 사이의 최단 경로 혹은 임의의 경로를 찾을 때 이용한다.
BFS 구현하기
BFS는 DFS와 달리 재귀적으로 동작하지 않는다. 방문한 노드들을 차례로 저장한 후 꺼낼 수
있는 자료 구조인 큐(Queue)를 사용한다. 즉, 선입선출(FIFO) 원칙으로 탐색한다.
이를 코드로 구현하면 아래와 같다.
private static void BFS(Node node) {
Queue<Node> Q = new LinkedList<>();
Q.offer(node);
while(!Q.isEmpty()) {
int len = Q.size();
for(int i=0; i<len; i++) {
Node n = Q.poll();
System.out.print(n.data + " ");
if(n.lt != null) Q.add(n.lt);
if(n.lt != null) Q.add(n.rt);
}
System.out.println();
}
}코드를 살펴보면 큐에 노드가 존재하는 동안 동작하며, while 반복문을 시작할 때 큐의 사이즈를
보관하여 다음 for문을 처음 보관한 큐의 사이즈 만큼 돌도록 한다.
(반복문을 돌며 추가되는 노드 이전까지 큐를 순회하며, 추가된 노드들은 그 다음 while문을 돌 때
확인 할 수 있게된다.)
for문을 돌 때 큐에서 하나의 노드를 poll()하게 되고, 다음 해당 노드가 자식 노드를 가지고
있는 경우에 자식 노드들을 큐에 보관하도록 한다.
이렇게 구성함으로 트리의 상위 레벨부터 시작하여 동 레벨의 노드들을 순차적으로 탐색할 수 있게된다.
