인프런, 자바(Java) 알고리즘 문제풀이
DFS, BFS 활용 - 0811. 미로의 최단거리 통로(BFS)
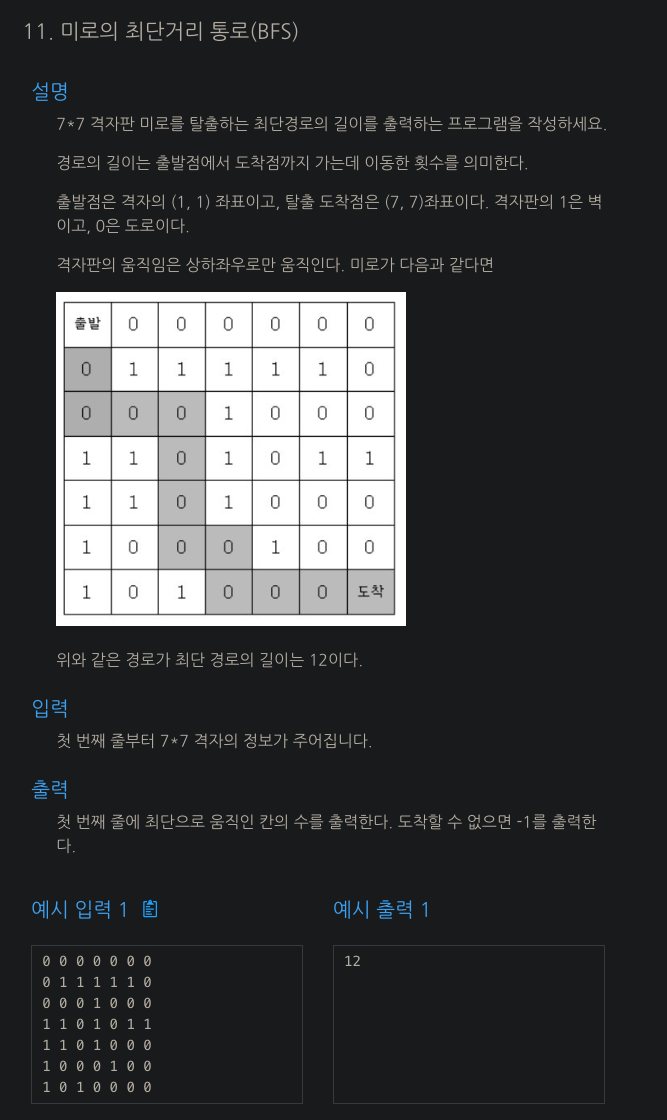
🗒️ 문제
🎈 나의 풀이
private static final int SIZE = 7;
private static int[][] maze = new int[SIZE][SIZE];
private static class Position {
int x, y;
public Position(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public boolean moveDown() {
if(x+1 < SIZE && maze[x+1][y] == 0) {
maze[x+1][y] = 1;
return true;
}
return false;
}
public boolean moveUp() {
if(x-1 >= 0 && maze[x-1][y] == 0) {
maze[x-1][y-1] = 1;
return true;
}
return false;
}
public boolean moveRight() {
if(y+1 < SIZE && maze[x][y+1] == 0) {
maze[x][y+1] = 1;
return true;
}
return false;
}
public boolean moveLeft() {
if(y-1 >= 0 && maze[x][y-1] == 0) {
maze[x][y-1] = 1;
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
private static int BFS(int x, int y) {
int answer = 0;
Queue<Position> Q = new LinkedList<>();
Q.add(new Position(0, 0));
maze[0][0] = 1;
while(!Q.isEmpty()) {
int len = Q.size();
for(int i=0; i<len; i++) {
Position p = Q.poll();
if(p.x==SIZE-1 && p.y==SIZE-1) return answer;
if(p.moveDown()) Q.add(new Position(p.x+1, p.y));
if(p.moveRight()) Q.add(new Position(p.x, p.y+1));
if(p.moveUp()) Q.add(new Position(p.x-1, p.y));
if(p.moveLeft()) Q.add(new Position(p.x, p.y-1));
}
answer++;
}
return -1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
for(int i=0; i<maze.length; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<maze.length; j++) {
maze[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
System.out.println(BFS(0, 0));
}🖍️ 강의 풀이
class Point{
public int x, y;
Point(int x, int y){
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
}
}
class Main {
static int[] dx={-1, 0, 1, 0};
static int[] dy={0, 1, 0, -1};
static int[][] board, dis;
public void BFS(int x, int y){
Queue<Point> Q=new LinkedList<>();
Q.offer(new Point(x, y));
board[x][y]=1;
while(!Q.isEmpty()){
Point tmp=Q.poll();
for(int i=0; i<4; i++){
int nx=tmp.x+dx[i];
int ny=tmp.y+dy[i];
if(nx>=1 && nx<=7 && ny>=1 && ny<=7 && board[nx][ny]==0){
board[nx][ny]=1;
Q.offer(new Point(nx, ny));
dis[nx][ny]=dis[tmp.x][tmp.y]+1;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Main T = new Main();
Scanner kb = new Scanner(System.in);
board=new int[8][8];
dis=new int[8][8];
for(int i=1; i<=7; i++){
for(int j=1; j<=7; j++){
board[i][j]=kb.nextInt();
}
}
T.BFS(1, 1);
if(dis[7][7]==0) System.out.println(-1);
else System.out.println(dis[7][7]);
}
}💬 짚어가기
해당 문제는 BFS를 이용하여 풀 수 있다. 나의 풀이에서는 Position이라는 클래스를
생성하여 현재 위치를 보관하고, 상하좌우 움직임이 가능한지를 체크할 수 있는 메소드를
두었다. 또한 동시에 해당 칸의 방문을 같이 체크하도록 하였다.
이후 시작 위치를 Queue에 보관 후, BFS를 수행하며 현재 Queue에 보관된 칸들에서
갈 수 있는 상하좌우의 칸들을 Queue에 다시 집어넣으며 탐색하는 로직이다.
목표 지점에 도착할 시 Queue를 몇 번 순회했는지(이동 횟수) 반환하여 문제를 해결한다.
강의에서는 이전 미로 탐색문제와 동일하게 dx와 dy 배열을 두고 반목문을 수행하여
상하좌우 탐방을 수행한다. 미로를 벗어나는 경우나 이미 방문한 칸을 체크하는 조건문을
확인하여 BFS를 수행하고 문제를 해결한다.
☕️ 여담으로
어.. 강의 코드에서 최단 거리를 구할 수 있는거 맞아?
처음 강의를 보았을 때 아래와 같은 의문이 들었다.
최단 거리라면 처음 목적지에 도착했을 때 탐색을 멈추고 무언가 반환해야지.
이후 탐색에서 다른 값이 들어가면 어쩌려고?
는 생각도 잠시 천천히 다시 살펴보니 이미 방문한 위치는 재방문을 하지 않는다는
사실을 떠올리며, 최초로 목적지 도달 후 이후 탐색에서는 목적지 칸을 방문할 수
없다는 사실을 깨달았다고한다...😊
