런타임 데이터 영역
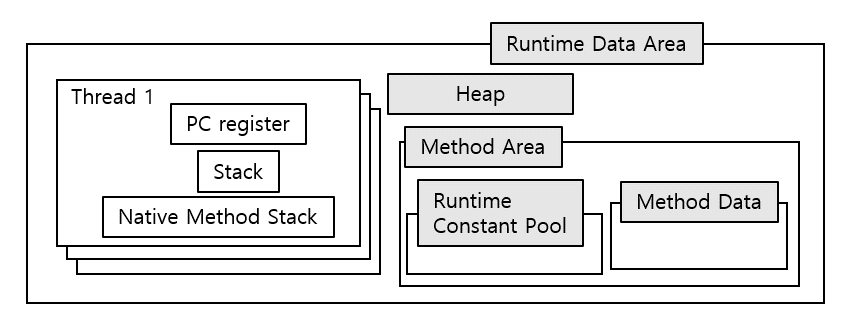
JVM이라는 프로그램이 운영체제 위에서 실행되면서 할당받는 메모리 영역이다. 런타임 데이터 영역은 5개의 영역으로 나눌 수 있다. 이 중 PC 레지스터, Stack, Native Method Stack 은 스레드마다 하나씩 생성되며, 힙(Heap), 메서드 영역(Method Area)은 모든 스레드가 공유해서 사용한다.
메서드 영역(Method Area)
메서드 영역은 보통 정적 영역이라 불린다. 프로그램 실행 중 클래스나 인터페이스를 사용하면 , JVM은 클래스 로더를 이용해 클래스와 인터페이스의 메타데이터를 메서드 영역에 저장한다. 여기서 메타 데이터는 Type Information, Runitme Constant Pool, Field Information, Method Information, Class Variable, Reference to ClassLoader , class , Reference to Class class을 가리킨다.
※Type은 클래스와 인터페이스를 통칭하는 것으로 이해하면 된다.
- 클래스 로더에 의해 Load된 모든 Type의 메타 정보를 저장하는 메모리 공간
- JVM이 시작될 때 생성
- 모든 Thread들에 공유
- GC의 대상이 됨
- 구현은 Vendor의 재량
- Sun에서는 Permenant Area로 명명하여 Generation Heap의 한 영역으로 포함
- IBM에서는 Heap 내에 별도의 구분 없이 포함
1. Type Information
- Type의 전체 이름 (패키지명 + 클래스명)
- Type의 직계 하위 클래스 전체 이름
- Type의 종류 : 클래스 / 인터페이스인지에 대한 정보
- Type의 제어자 : 접근 제어자와 그 외 제어자 정보
- 연관된 인터페이스 이름 리스트
2. Runtime Constant Pool
: 클래스 파일 포멧에서 constant_pool 테이블에 해당하는 영역이다. 각 클래스와 인터페이스의 상수뿐만 아니라 메서드와 필드에 대한 모든 래퍼런스까지 담고 있는 테이블
- Literal Constant , Type , Field, Method로의 Symbolic Reference 포함
- Contant Pool의 Entry는 index로 접근 가능
3. Field Information
: Type에서 선언된 모든 Field(Member Variable, Class Variable)의 정보이다.
- Field의 이름
- Field의 Data Type
- Field의 제어자
4. Method Information
: Type에서 선언된 모든 Method의 정보를 의미한다.
- Method의 이름
- Method의 반환 값의 Data Type OR void
- Method의 Parameter의 수와 Data Type , 선언된 순서
- Method의 제어자
- Method가 native나 abstract가 아닌 경우 추가되는 정보들
- Method의 바이트 코드
- Method Stack Frame의 Operand Stack 및 Local variable Section 크기- Exception Table
5. Class Variable
: Class에서 static으로 선언된 변수이며 모든 인스턴스에 공유되며 인스턴스가 없어도 접근 가능
- 이 변수는 Class에 속함
- Class를 사용하기 이전에 이 변수들은 미리 메모리를 할당 받아놓아야 함
- Final Class 변수는 상수로 치환되어 Constant Pool에 값을 복사
6. Reference to class 'ClassLoader'
- 하나의 Type이 다른 Type을 참조할 때 JVM은 같은 ClassLoader를 사용함
- 이런 이유로 Type의 ClassLoader정보가 필요
- User-Defined ClassLoader인 경우만 reference를 저장
- Bootstrap ClassLoader인 경우는 null
7. Referene to class 'Class' ( java.lang.class.class )
- 각 Type이 load될 때마다 java.lang.class의 인스턴스가 하나씩 생성된다.
- getClass, forClass, isInterface 등의 메서드가 호출 될 때 이 Reference를 통해 값을 반환
힙(Heap)
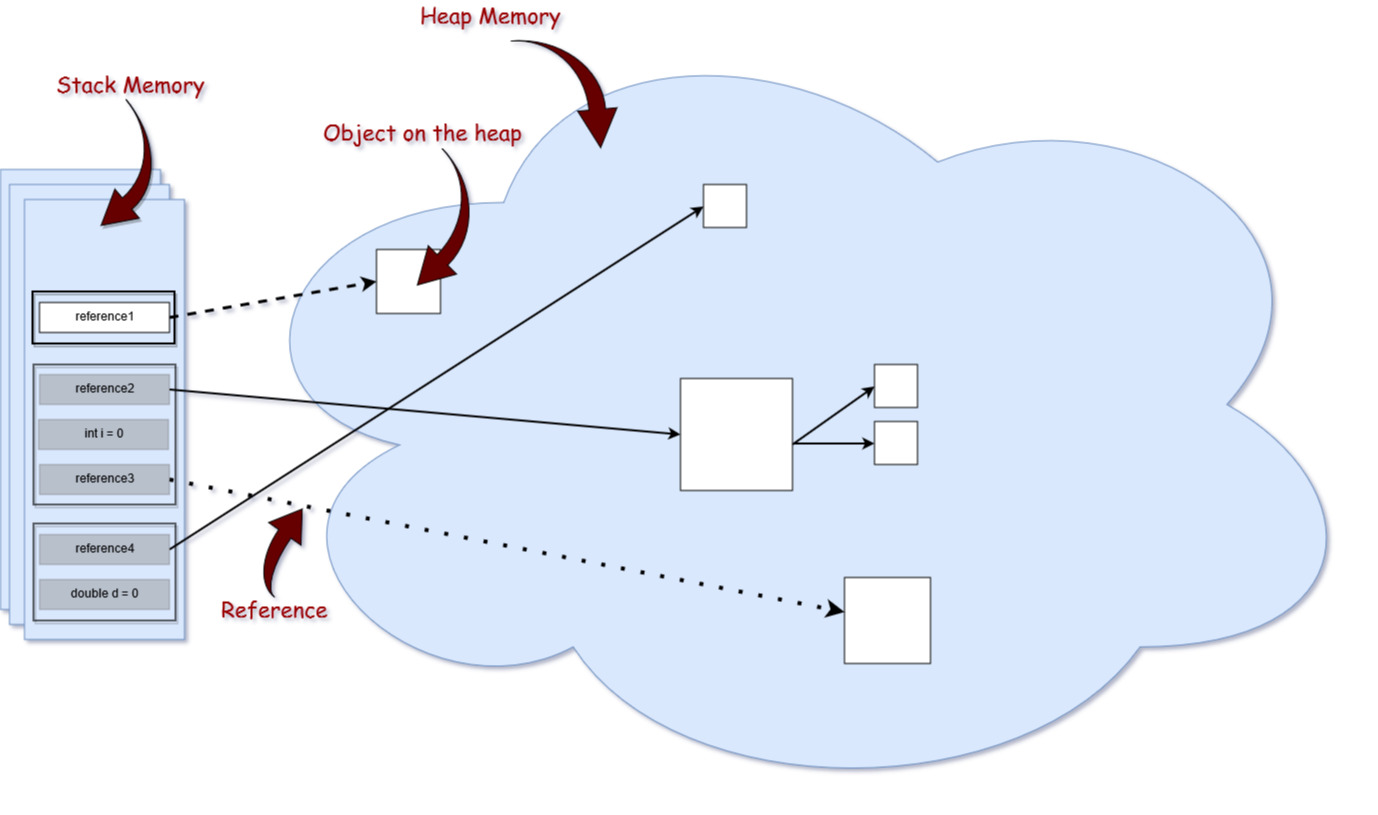
힙은 문자열에 대한 정보를 가진 String Pool뿐만 아니라 실제 데이터를 가진 인스턴스, 배열 등이 저장이 된다. 그리고 힙은 모든 쓰레드간 공유된다. 그렇기 때문에 멀티 스레드 환경에 객체에 접근할 때는 동기화에 주의해야한다. 그리고 JVM에는 메모리를 할당하는 instruction은 있지만, 메모리를 해제(free)하는 instruction은 없다. 따라서 JVM은 Garbage Collector를 이용해 힙을 관리한다.
-
모든 Object 타입(Integer, String, ArrayList, ...)은 heap 영역에 생성된다.
-
Heap 영역에 있는 오브젝트들을 가리키는 레퍼런스 변수가 stack 에 올라가게 된다.
-
힙 구성 방식이나 가비지 컬렉션 방법 등은 JVM 벤더의 재량이다.
Garbage Collection
A garbage collector is not strictly required by the Java virtual machine specification. The specification only requires that an implementation manage its own heap in some manner. For example, an implementation could simply have a fixed amount of heap space available and throw an OutOfMemory exception when that space fills up.
-Inside Java Virtual Machine -
GC에 대한 내용은 따로 포스팅하겠습니다.
Object Representation , Array Representation
이 또한 vendor에 따라 구현 방식이 다릅니다.
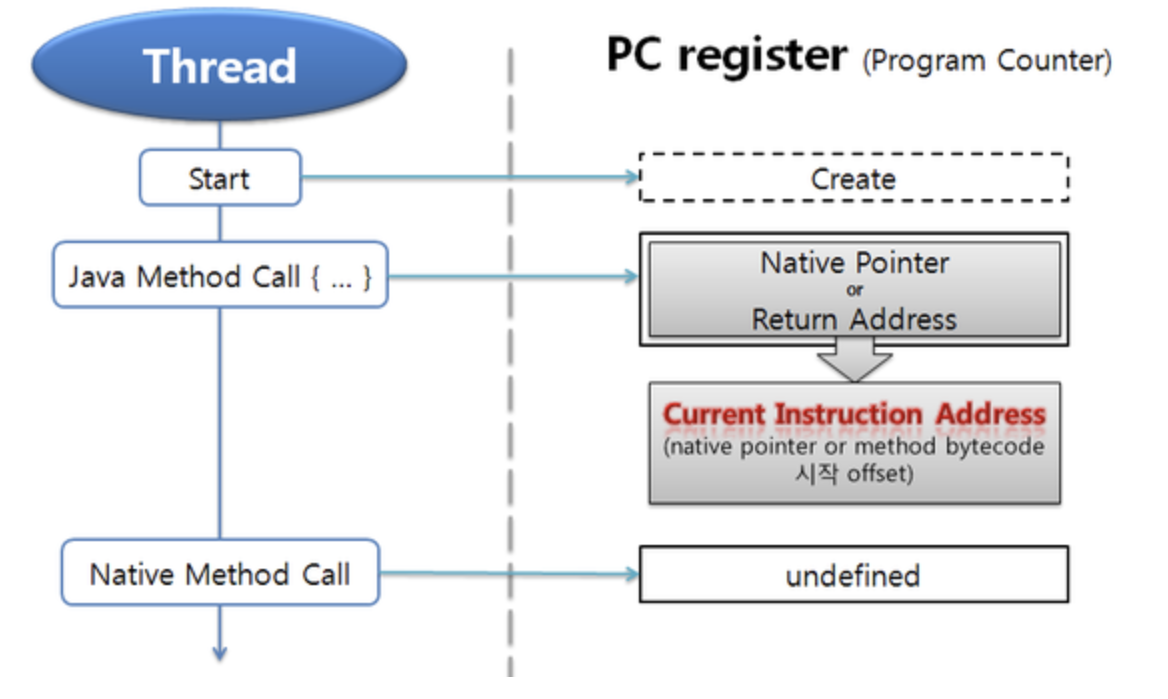
PC 레지스터
PC(Program Counter) 레지스터는 각 스레드마다 하나씩 존재하며 스레드가 시작될 때 생성된다. PC 레지스터는 현재 수행 중인 JVM 명령의 주소를 갖는다.
JVM은 Stack-Base 방식으로 작동 하는데, JVM은 CPU에 직접 Instruction을 수행하지 않고 Stack에서 Operand를 뽑아내 이를 별도의 메모리 공간에 저장하는 방식을 취한다.
- 자바 메서드를 실행할 때는 현재 수행중인 Instruction의 주소를 포함한다.
- Native 메서드를 실행할 때는 undefined 상태로 아무것도 할당 되지 않는다.
JVM Stack
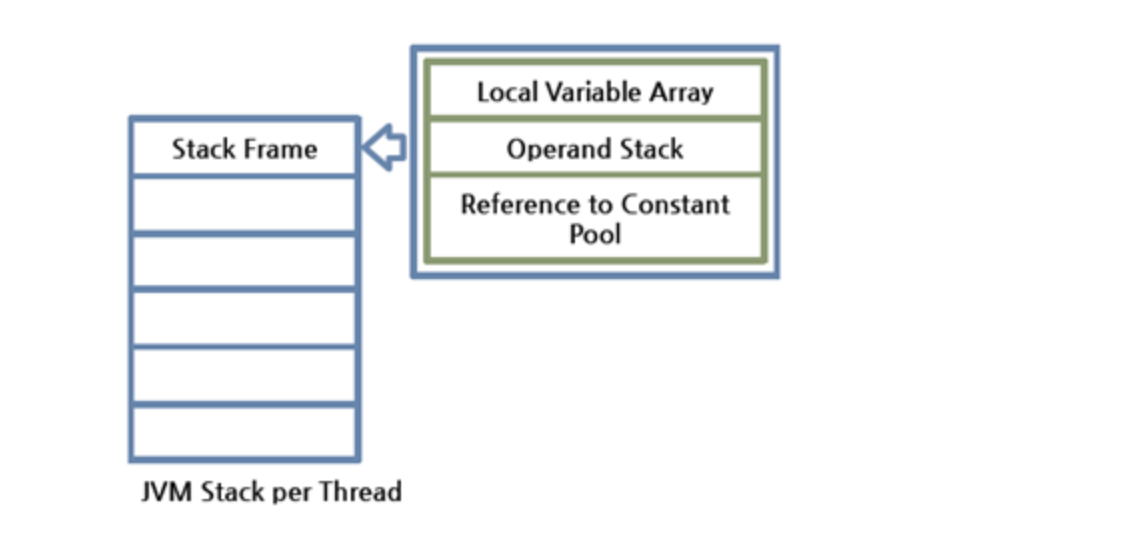
자바 스택은 스레드별로 1개만 존재하고, 스택 프레임(Stack Frame)이라는 구조체를 저장하는 스택이다. 스택 프레임은 메서드가 호출될 때마다 생성된다. 메서드 실행이 끝나면 스택 프레임은 pop되어 스택에서 제거된다.
-
여기서 스택 프레임이란 메소드 상태 정보를 저장하고 있으며, Local Variables Array ,Operand Stack, Frame Data를 갖는다.
-
Frame Data는 Constant Pool Reference, 이전 스택 프레임에 대한 정보, 현재 메서드가 속한 클래스/객체에 대한 참조 등의 정보를 갖는다.
-
쓰레드가 허락된 스택 용량보다 많은 계산을 필요로 하면 StackOverflowError가 발생합니다.
-
실행 중인 쓰레드의 스택을 확장할 만큼 충분한 메모리가 없거나, 새로 생성될 쓰레드에게 메모리가 부족해 스택을 할당할 수 없는 경우 OutOfMemoryError가 발생합니다.
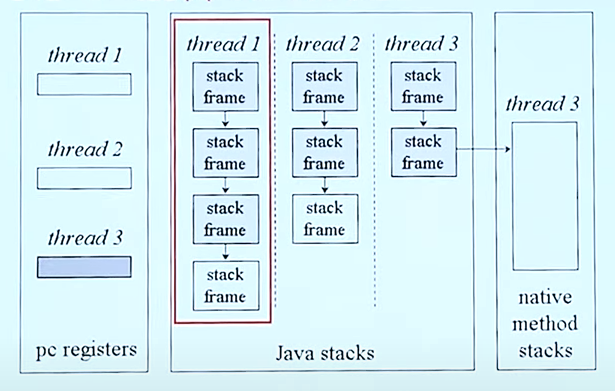
위에 그림에서 thread1을 보면 가장 위에 있는 stack frame이 main method, 그 밑에 있는 stack frame은 main method에서 호출한 메서드에 해당한다. 그 밑에는 그 메서드에서 호출한 또 다른 메서드에 해당한다.
Local variables array
0부터 시작하는 인덱스를 가진 배열이다. 0은 메서드가 속한 클래스 인스턴스의 this 레퍼런스이고, 1부터는 메서드에 전달된 파라미터들이 저장되며, 메서드 파라미터 이후에는 메서드의 지역 변수들이 저장된다.
다음과 같은 자바 코드가 있을 때,
class Test {
public int hello(int a, double b, String c) {
return 0;
}
}프레임의 로컬 변수 배열은 다음과 같이 만들어진다.

- reference는 heap의 레퍼런스를 의미한다.
- primitive 타입은 그냥 프레임에 저장한다.
- 그래서 int, double이 Integer, Double 보다 조금 빠르다. - double, long은 두 칸씩 차지한다.
Operand Stack
메서드 내 계산을 위헌 실제 작업 공간이다. 각 메서드는 피연산자 스택과 지역 변수 배열 사이에서 데이터를 교환하고, 다른 메서드 호출 결과를 추가하거나(push) 꺼낸다(pop). 피연산자 스택 공간이 얼마나 필요한지는 컴파일할 때 결정할 수 있으므로, 피연산자 스택의 크기도 컴파일 시에 결정된다.
예를 들어 다음과 같이 4+3을 계산하는 자바 코드가 있을 때,
package main;
class Main {
public int test() {
int a = 4;
int b = 3;
return a + b;
}
}컴파일한 다음 javap로 바이트 코드를 확인해 보면 다음과 같다.
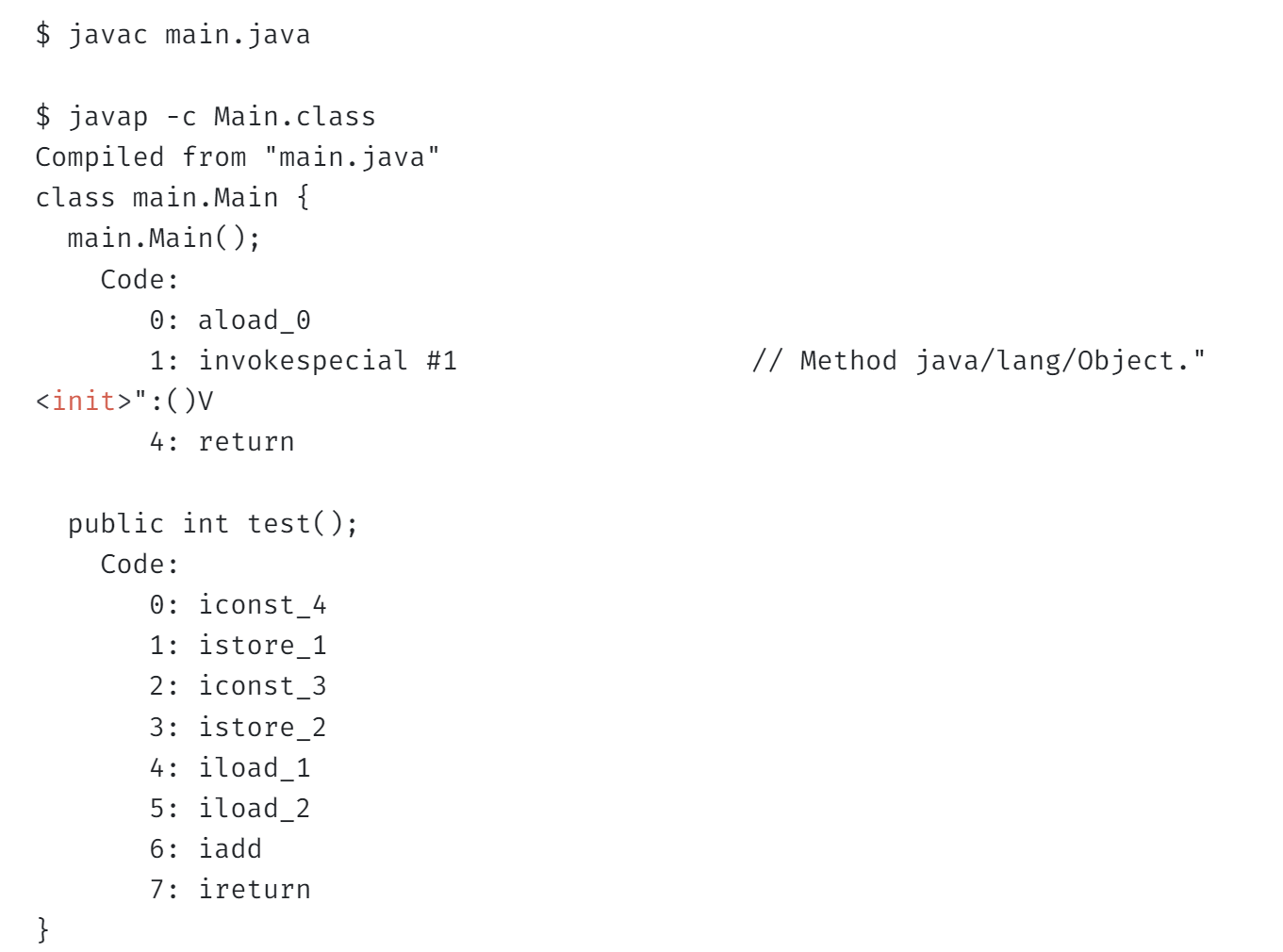
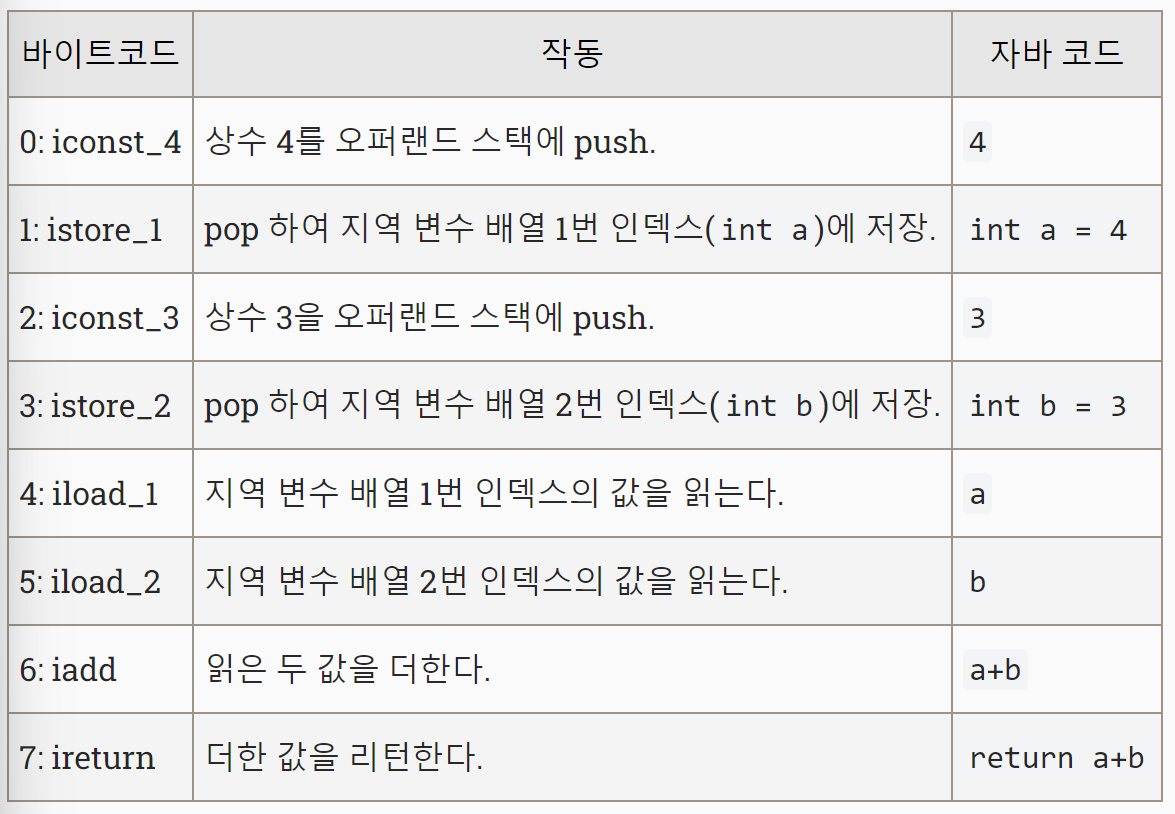
test() 메서드에 바이트 코드를 살펴보자.
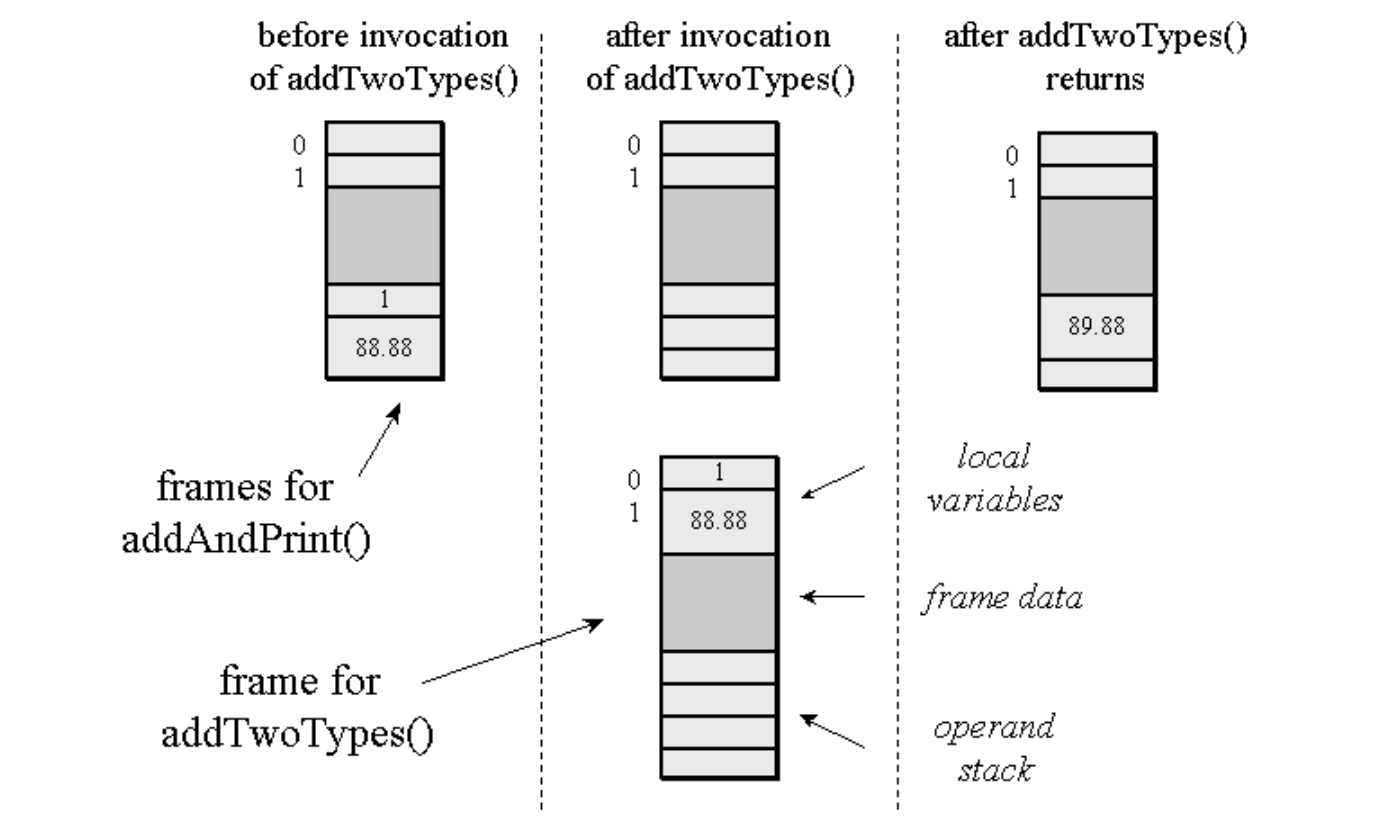
Frame Data
the Java stack frame includes data to support constant pool resolution, normal method return, and exception dispatch. This data is stored in the frame data portion of the Java stack frame.
Whenever the Java virtual machine encounters any of the instructions that refer to an entry in the constant pool, it uses the frame data's pointer to the constant pool to access that information. As mentioned earlier, references to types, fields, and methods in the constant pool are initially symbolic. When the virtual machine looks up a constant pool entry that refers to a class, interface, field, or method, that reference may still be symbolic. If so, the virtual machine must resolve the reference at that time.
- int, long ,float or String 뿐만 아니라 class, 배열의 값, 필드 , 메소드를 호출하기 위해 많은 명령어가 Constant Pool에서 값들을 참조한다. 이 때 frame data's pointer to Constant pool을 이용하여 값들에 접근한다.
the frame data must assist the virtual machine in processing a normal or abrupt method completion.
- 뿐만 아니라 frame data는 메서드의 종료와 관련된 정보 또한 포함하고 있다.
Possible Implementations of the Java Stack
class Example3c {
public static void addAndPrint() {
double result = addTwoTypes(1, 88.88);
System.out.println(result);
}
public static double addTwoTypes(int i, double d) {
return i + d;
}}
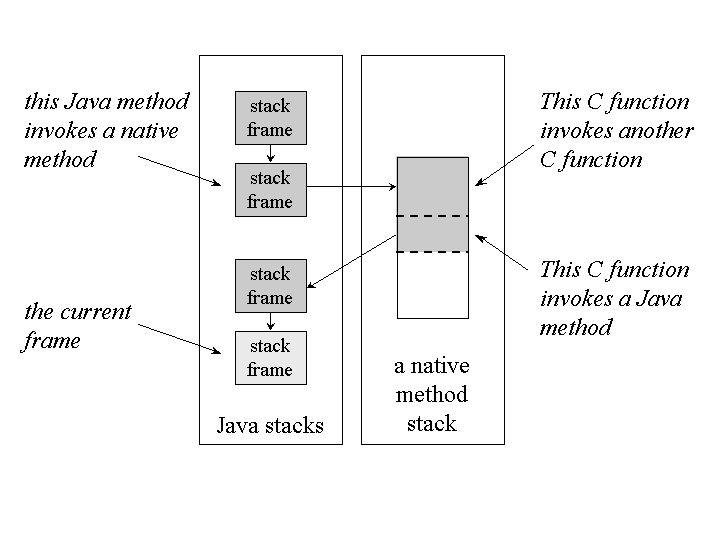
Native Method Stack
자바 외의 언어로 작성된 네이티브 코드를 위한 스택이다. 즉, JNI(Java Native Interface)를 통해 호출하는 C/C++ 등의 코드를 수행하기 위한 스택으로, 언어에 맞게 C 스택이나 C++ 스택이 생성된다.
When a thread invokes a Java method, the virtual machine creates a new frame and pushes it onto the Java stack. When a thread invokes a native method, however, that thread leaves the Java stack behind. Instead of pushing a new frame onto the thread's Java stack, the Java virtual machine will simply dynamically link to and directly invoke the native method.
If an implementation's native method interface uses a C-linkage model, then the native method stacks are C stacks. When a C program invokes a C function, the stack operates in a certain way. The arguments to the function are pushed onto the stack in a certain order. The return value is passed back to the invoking function in a certain way. This would be the behavior of the of native method stacks in that implementation.
- 자바 메서드가 호출 될 때는 스택 프레임이 스택에 추가 되지만, native 메서드가 호출 될 때는 새로운 스택 프레임이 추가 되는 것이 아니라, 동적으로 native 메서드를 연결한다.
- native method interface가 C 일 때는 C스택이 생성된다.
출처
Inside the Java Virtual Machine by Bill Venners
JVM D2 자료
JVM 스택관련
JVM - 김한도
https://tecoble.techcourse.co.kr/post/2021-08-09-jvm-memory/
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UzaGOXKVhwU