JDBC 인터페이스
- Connection
- Statement
- Prepared Statement
- Result Set
Driver
드라이버를 먼저 설치해야 JDBC 사용 가능! ojdbc6를 프로젝트에 임포트하고 BuildPath를 설정한다
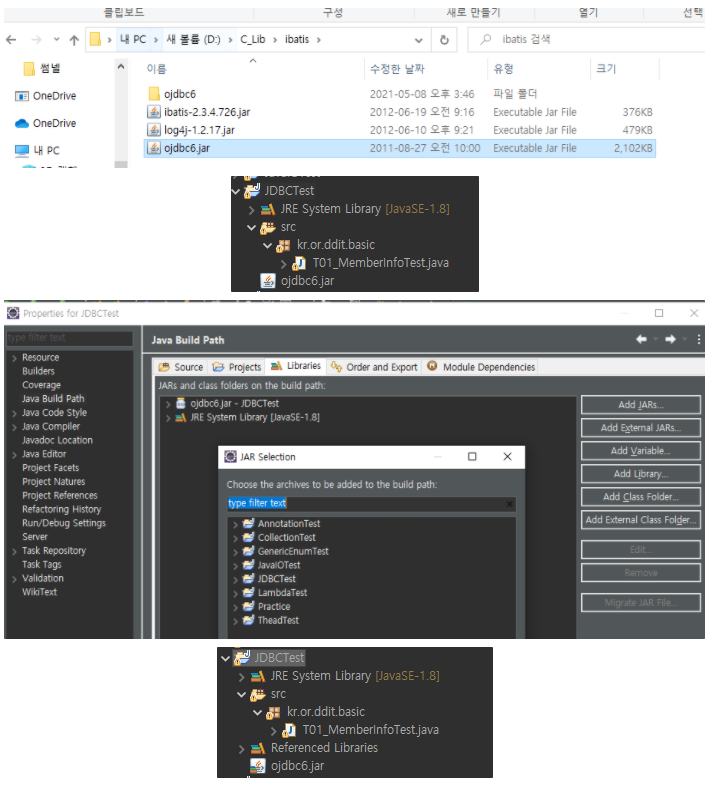
CRUD 예제
- 메인
- 이런식으로 프로그램이 실행되도록 만들거임! 중복을 제거하는 메소드가 필요하겠네~
package kr.or.ddit.basic;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Scanner;
/*
회원정보를 관리하는 프로그램을 작성하는데
아래의 메뉴를 모두 구현하시오. (CRUD기능 구현하기)
(DB의 MYMEMBER테이블을 이용하여 작업한다.)
* 자료 삭제는 회원ID를 입력 받아서 삭제한다.
예시메뉴)
----------------------
== 작업 선택 ==
1. 자료 입력 ---> insert
2. 자료 삭제 ---> delete
3. 자료 수정 ---> update
4. 전체 자료 출력 ---> select
5. 작업 끝.
----------------------
// 회원관리 프로그램 테이블 생성 스크립트
create table mymember(
mem_id varchar2(8) not null, -- 회원ID
mem_name varchar2(100) not null, -- 이름
mem_tel varchar2(50) not null, -- 전화번호
mem_addr varchar2(128), -- 주소
reg_dt DATE DEFAULT sysdate, -- 등록일
CONSTRAINT MYMEMBER_PK PRIMARY KEY (mem_id)
);
*/
public class T01_MemberInfoTest {
private Connection conn;
private Statement stmt;
private PreparedStatement pstmt;
private ResultSet rs;
private Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
/**
* 메뉴를 출력하는 메서드
*/
public void displayMenu(){
System.out.println();
System.out.println("----------------------");
System.out.println(" === 작 업 선 택 ===");
System.out.println(" 1. 자료 입력");
System.out.println(" 2. 자료 삭제");
System.out.println(" 3. 자료 수정");
System.out.println(" 4. 전체 자료 출력");
System.out.println(" 5. 작업 끝.");
System.out.println("----------------------");
System.out.print("원하는 작업 선택 >> ");
}
/**
* 프로그램 시작메서드
*/
public void start(){
int choice;
do{
displayMenu(); //메뉴 출력
choice = scan.nextInt(); // 메뉴번호 입력받기
switch(choice){
case 1 : // 자료 입력
insertMember();
break;
case 2 : // 자료 삭제
break;
case 3 : // 자료 수정
break;
case 4 : // 전체 자료 출력
break;
case 5 : // 작업 끝
System.out.println("작업을 마칩니다.");
break;
default :
System.out.println("번호를 잘못 입력했습니다. 다시입력하세요");
}
}while(choice!=5);
}- 회원등록 메소드 만들기
// 회원을 추가하는 메서드
private void insertMember() {
boolean chk = false; //등록여부 체크
String memId ="";
do {
System.out.println();
System.out.println("추가할 회원정보를 입력하세요");
System.out.print("회원 ID : ");
memId = scan.next();
chk = checkMember();
if(chk==true) {
System.out.println("회원ID가 "+memId+"인 회원은 이미 존재합니다");
System.out.println("다시 입력하세요");
}
} while(chk==true);
System.out.println("회원이름 >> ");
String memName = scan.next();
System.out.println("회원 전화번호 >> ");
String memTel = scan.next();
scan.nextLine(); // 버퍼 비우기
System.out.println("회원주소 >> ");
String memAddr = scan.nextLine();
try {
// 1-1에서 채움
} catch (SQLException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
} finally {
}
}
private boolean checkMember() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return false;
}- util 만들기
- JDBC 드라이버를 로딩하고 Connection객체를 생성하는 메서드로 구현된 클래스
package kr.or.ddit.util;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class JDBCUtil {
// 이 static블럭은 JDBCUtil이 처음 사용되는 시점에 딱 한번만
// 실행되는 목적으로 코드를 정의하고 싶을때 사용하는 것이다.
static {
try {
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
//이게 있으면 class를 리턴, 없으면 아래 예외 발생
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 성공");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 실패");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 커션클래스가 있어야 연결이됨!
public static Connection getConnection() {
try {
return DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:xe",
"CSH99",
"java");
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("DB연결 실패");
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
// 네가지 요소 모두 닫아주는 메소드가 필요하다. 안닫으면 안돼! 나중에 호출해서 쓸거임
public static void close(Connection conn, Statement stmt, PreparedStatement pstmt, ResultSet rs) {
if(rs != null) try {rs.close();} catch(SQLException ex) {}
if(pstmt != null) try {pstmt.close();} catch(SQLException ex) {}
if(stmt != null) try {((Connection) stmt).close();} catch(SQLException ex) {}
if(conn != null) try {conn.close();} catch(SQLException ex) {}
}
}3) 커넥션 준비완료. 이제 메소드 다 만들어버리기~!
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Scanner;
import kr.or.ddit.util.JDBCUtil;
/*
회원정보를 관리하는 프로그램을 작성하는데
아래의 메뉴를 모두 구현하시오. (CRUD기능 구현하기)
(DB의 MYMEMBER테이블을 이용하여 작업한다.)
* 자료 삭제는 회원ID를 입력 받아서 삭제한다.
예시메뉴)
----------------------
== 작업 선택 ==
1. 자료 입력 ---> insert
2. 자료 삭제 ---> delete
3. 자료 수정 ---> update
4. 전체 자료 출력 ---> select
5. 작업 끝.
----------------------
// 회원관리 프로그램 테이블 생성 스크립트
create table mymember(
mem_id varchar2(8) not null, -- 회원ID
mem_name varchar2(100) not null, -- 이름
mem_tel varchar2(50) not null, -- 전화번호
mem_addr varchar2(128), -- 주소
reg_dt DATE DEFAULT sysdate, -- 등록일
CONSTRAINT MYMEMBER_PK PRIMARY KEY (mem_id)
);
*/
public class T01_MemberInfoTest {
private Connection conn;
private Statement stmt;
private PreparedStatement pstmt;
private ResultSet rs;
private Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
/*
* 메뉴를 출력하는 메서드
*/
public void displayMenu(){
System.out.println();
System.out.println("----------------------");
System.out.println(" === 작 업 선 택 ===");
System.out.println(" 1. 자료 입력");
System.out.println(" 2. 자료 삭제");
System.out.println(" 3. 자료 수정");
System.out.println(" 4. 전체 자료 출력");
System.out.println(" 5. 작업 끝.");
System.out.println("----------------------");
System.out.print("원하는 작업 선택 >> ");
}
/**
* 프로그램 시작메서드
*/
public void start(){
int choice;
do{
displayMenu(); //메뉴 출력
choice = scan.nextInt(); // 메뉴번호 입력받기
switch(choice){
case 1 : // 자료 입력
insertMember();
break;
case 2 : // 자료 삭제
deleteMember();
break;
case 3 : // 자료 수정
updateMember();
break;
case 4 : // 전체 자료 출력
displayMemberAll();
break;
case 5 : // 작업 끝
System.out.println("작업을 마칩니다.");
break;
default :
System.out.println("번호를 잘못 입력했습니다. 다시입력하세요");
}
}while(choice!=5);
}
// 회원정보를 삭제하기 위한 메소드
private void deleteMember() {
System.out.println();
System.out.println("삭제할 회원정보를 입력하세요");
System.out.print("회원 ID : ");
String memId = scan.next();
try {
//커넥션객체 인스턴스를 통해 DB접속
conn = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
// sql작성
String sql =" delete from mymember where mem_id = ? ";
//pstmt에 sql쿼리를 넣은 변수를 매개변수로 하는 커넥션객체의 pstmt메소드 실행
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// pstmt엔 결국 sql쿼리문이 String형태로 들어간것, 다만 ?가 있는거임
//첫번째 물음표에 memId를 넣어준다는 의미이다
pstmt.setString(1, memId);
//이제 업데이트 해주자.
int cnt = pstmt.executeUpdate();
if(cnt >0) {
System.out.println(memId+"회원정보를 삭제했습니다");
}else {
System.out.println(memId+"회원정보를 삭제 실패");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtil.close(conn, stmt, pstmt, rs);
}
}
// 회원정보 수정하기 위한 메서드
private void updateMember() {
boolean chk = false; //등록여부 체크
String memId ="";
do {
System.out.println();
System.out.println("추가할 회원정보를 입력하세요");
System.out.print("회원 ID : ");
memId = scan.next();
chk = checkMember(memId);
if(chk==false) {
System.out.println("회원ID가 "+memId+"인 회원 존재하지 않습니다.");
System.out.println("다시 입력하세요");
}
} while(chk==false); //중복 없을때
System.out.println("회원이름 >> ");
String memName = scan.next();
System.out.println("회원 전화번호 >> ");
String memTel = scan.next();
scan.nextLine(); // 버퍼 비우기
System.out.println("회원주소 >> ");
String memAddr = scan.nextLine();
// 이제 업데이트를 시켜줘보자!!!
try {
conn = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
String sql = " update mymember " +
" set mem_name = ?, " +
" mem_tel = ?, " +
" mem_addr = ? " +
" where mem_id = ? " ;
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString(1, memName);
pstmt.setString(2, memTel);
pstmt.setString(3, memAddr);
pstmt.setString(4, memId);
int cnt = pstmt.executeUpdate();
if(cnt>0) {
System.out.println(memId+"회원이 정보를 수정했습니다");
}else {
System.out.println(memId+"회원의 정보 수정 실패");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtil.close(conn, stmt, pstmt, rs);
}
}
// 전체회원정보를 출력하는 메서드
private void displayMemberAll() {
System.out.println();
System.out.println("---------------------------------------");
System.out.println(" ID\t이름\t전화번호\t\t주소");
System.out.println("---------------------------------------");
try {
conn = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "select * from mymember";
stmt = conn.createStatement();
// 오직 Select만 executeQuery
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
while(rs.next()) {
String memId = rs.getString("mem_id");
String memName = rs.getString("mem_name");
String memTel = rs.getString("mem_tel");
String memAddr = rs.getString("mem_addr");
System.out.println(memId+"\t"+memName+"\t"+memTel+"\t\t"+memAddr);
}
System.out.println("---------------------------------------");
System.out.println("출력작업 끝");
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("출력작업 실패");
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtil.close(conn,stmt,pstmt,rs);
}
}
// 회원을 추가하는 메서드
private void insertMember() {
boolean chk = false; //등록여부 체크
String memId ="";
do {
System.out.println();
System.out.println("추가할 회원정보를 입력하세요");
System.out.print("회원 ID : ");
memId = scan.next();
chk = checkMember(memId);
if(chk==true) {
System.out.println("회원ID가 "+memId+"인 회원은 이미 존재합니다");
System.out.println("다시 입력하세요");
}
} while(chk==true);
System.out.println("회원이름 >> ");
String memName = scan.next();
System.out.println("회원 전화번호 >> ");
String memTel = scan.next();
scan.nextLine(); // 버퍼 비우기
System.out.println("회원주소 >> ");
String memAddr = scan.nextLine();
try {
conn = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
String sql ="insert into mymember " +
" (mem_id,MEM_NAME, mem_tel, mem_addr) " +
" values "
+" (?,?,?,?)";
//stmt는 보안에 취약해 권고되지 않는다.
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString(1, memId);
pstmt.setString(2, memName);
pstmt.setString(3, memTel);
pstmt.setString(4, memAddr);
// insert할거니까 update
int cnt = pstmt.executeUpdate();
// insert시 업데이트 된 레코드의 수를 cnt에 넣기
if(cnt>0) {
System.out.println(memId+"회원 추가 작업 성공");
}else {
System.out.println(memId+"회원 추가 작업 실패");
}
} catch (SQLException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 커넥션을 해제해 주지 않으면 오라클 서버에서 메모리를 소비하고 있는 채로 유지되게 된다
JDBCUtil.close(conn, stmt, pstmt, rs);
}
}
// 회원 아이디를 이용하여 회원이 존재하는지 알려주는 메소드
// @param memId
// @return true : 회원이 존재함, false : 회원이 존재하지 않음
private boolean checkMember(String memId) {
boolean chk = false; //회원 존재여부 체크
try {
conn = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "select count(*) as cnt from mymember "
+ " where mem_id = ? ";
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString(1, memId);
rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
int cnt=0;
//레코드를 한줄씩 이동.
while(rs.next()) {
//cnt = rs.getInt(columnIndex);
cnt = rs.getInt("CNT");
}
if(cnt>0) { //중복이 존재한다
chk=true;
}
} catch (SQLException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JDBCUtil.close(conn, stmt, pstmt, rs);
}
return chk;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
T01_MemberInfoTest memObj = new T01_MemberInfoTest();
memObj.start();
}
}ExecuteQuery
-
수행결과로 ResultSet 객체의 값을 반환합니다.
-
SELECT 구문을 수행할 때 사용되는 함수입니다.
ExecuteUpdate
-
수행결과로 Int 타입의 값을 반환합니다.
-
SELECT 구문을 제외한 다른 구문을 수행할 때 사용되는 함수입니다.
Properies
- 외부의 properties파일을 읽어와 Properties 객체로 처리하기
- Map과 비교해서 key와 value가 String만 가능하다는 차이가 있다
- key와 value가 있고 중간에 이퀄(=)이 들어간다
url=jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:xe
password=java
driver=oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver
username=CSH99
greeting=HelloJDBC드라이버를 로딩하고 Connection객체를 이용하여 DB정보 가져오기
이제 DB설정 정보는 프로퍼티에서 모두 제어 가능! 유지보수 편해진다
db.properties
url:jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:xe
password:java
driver:oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver
username:CSH99
JDBCUtil2
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Properties;
public class JDBCUtil2 {
static Properties prop;
static {
prop = new Properties();
try {
// 파일읽기를 수행할 FileInputStream객체 생성
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("res/db.properties");
// Properties객체로 파일내용 읽기
// 파일내용을 읽어와 key와value값으로 분류한 후 Properties객체에 담아준다.
prop.load(fis);
}catch(IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
try {
Class.forName(prop.getProperty("driver"));
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 성공");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 실패");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static Connection getConnection() {
try {
return DriverManager.getConnection(
prop.getProperty("url"),
prop.getProperty("username"),
prop.getProperty("password"));
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("DB연결 실패");
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
public static void close(Connection conn, Statement stmt, PreparedStatement pstmt, ResultSet rs) {
if(rs != null) try {rs.close();} catch(SQLException ex) {}
if(pstmt != null) try {pstmt.close();} catch(SQLException ex) {}
if(stmt != null) try {stmt.close();} catch(SQLException ex) {}
if(conn != null) try {conn.close();} catch(SQLException ex) {}
}
}ResourceBundle
- 확장자가 properties인 파일 정보를 읽어와 key값과 value값을 분리한 정보를 갖는 객체
- 읽어올 파일은 ‘key값 = value값’ 형태로 되어 있어야 한다
출력해보기
package kr.or.ddit.basic;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Locale;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
public class T03_ResourceBundleTest {
// ResourceBundle객체
public static void main(String[] args) {
//ResourceBundle객체생성
//파일을 지정할때는 '파일명'만 지정하고 확장자는 지정하지 않는다
//이유:확장자는 항상 properties이기 때문
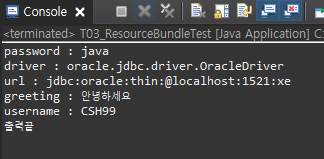
ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("db");
Enumeration<String> keys = bundle.getKeys();
while(keys.hasMoreElements()) {
String key = keys.nextElement();
String value = bundle.getString(key);
System.out.println(key+" : "+value);
}
System.out.println("출력끝");
}
}
JDBCUtil3
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class JDBCUtil3 {
static ResourceBundle bundle;
static {
//처음에 한번만 실행
bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("db");
try {
Class.forName(bundle.getString("driver"));
//이게 있으면 class를 리턴, 없으면 아래 예외 발생
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 성공");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 실패");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static Connection getConnection() {
try {
return DriverManager.getConnection(
bundle.getString("url"),
bundle.getString("username"),
bundle.getString("password"));
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("DB연결 실패");
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
public static void close(Connection conn, Statement stmt, PreparedStatement pstmt, ResultSet rs) {
if(rs != null) try {rs.close();} catch(SQLException ex) {}
if(pstmt != null) try {pstmt.close();} catch(SQLException ex) {}
if(stmt != null) try {stmt.close();} catch(SQLException ex) {}
if(conn != null) try {conn.close();} catch(SQLException ex) {}
}
}- 이러고 이전 CRUD예제를 JDBCUtil2로 바꿔서 실행해보면 똑같이 실행된다!
conn = JDBCUtil3.getConnection();Properties와 ResourceBundle의 차이점은?
⇒ 국제화! : 나라별로 메세지를 만들어 세팅해 Location에 맞춰 Resoruce를 첨부하면 프로그램 메세지들이 나라마다 나오게 할 수 있는거! 즉 같은말을 여러나라 언어로 만든 뒤 위치에따라 적절한 메세지 파일을 띄우게 하는 기능을 ResourceBundle은 갖고있다~
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Locale;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
public class T03_ResourceBundleTest {
// ResourceBundle객체
public static void main(String[] args) {
//ResourceBundle객체생성
//파일을 지정할때는 '파일명'만 지정하고 확장자는 지정하지 않는다
//이유:확장자는 항상 properties이기 때문
ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("db",Locale.JAPAN);
Enumeration<String> keys = bundle.getKeys();
while(keys.hasMoreElements()) {
String key = keys.nextElement();
String value = bundle.getString(key);
System.out.println(key+" : "+value);
}
System.out.println("출력끝");
}
}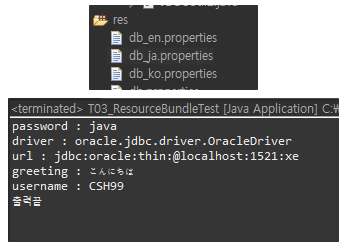
Locale에 해당하는 국가의 언어가 쓰여진 프로퍼티 파일이 실행된다.

