[Paper Introduction] BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding
Introduction
BERT, which stands for Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers, is a deep learning model developed by Google in 2018.
BERT pre-trains on unlabeled data by going through the processes named Masked Language Modeling (MLM) and Next Sentence Prediction (NSP).
Then, the obtained pre-trained parameters are fine-tuned with labeled data specific to the task, updating them accordingly.
Pre-training can be conducted in two different ways.
1. Feature-based Approaches
Training the model for a specific task from the pre-training stage, resulting in a model structure specialized for that task.
2. Fine-tuning Approaches
Minimizes the number of task-specified parameters and fine-tunes the generally pre-trained parameters to fit the task.
In this paper, pre-training of BERT is classified as a fine-tuning approach.
BERT
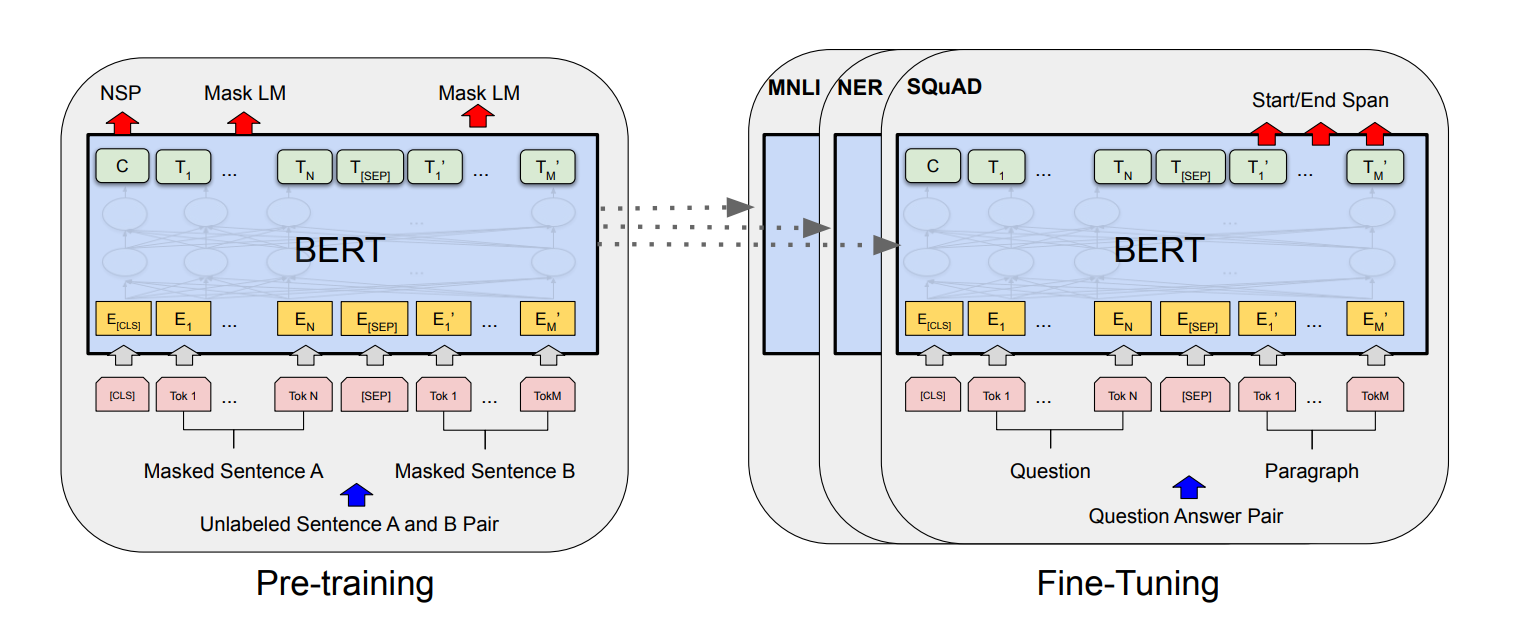
BERT goes through two phases, which are pre-training phase and fine-tuning phase. Every model starts from the same initialized model, but eventually they will become differently fine-tuned model since the parameters are updated based on the task.
Input / Output
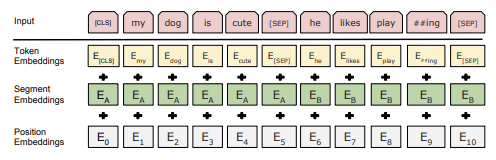
BERT gets three different embedding as input.
Token Embedding has a similar structure with word embedding. In the figure, you can check special tokens named [CLS] and [SEP]. [CLS] token is appended at the beginning of the input, and is used in the final hidden state of classification. [SEP] token is used when separating the sentences.
Segment Embedding is needed when handling BERT's downstream tasks. Tasks like QA or NLI, accepts sentence pair as an input, and it is essential to distinguish between the sentences. Segment embedding indicates whether each sentence belongs to sentce A or B.
Position embedding is used to represent the positional information of each word token which are missed due to the characteristic of Transformer's structure.
These three types of embeddings are summed together to form the final input.
Pre-training
BERT train the model bidirectionally by two unsupervised tasks.
1. Masked Language Model
If traditional approaches like left-to-right or right-to-left is used, when an input sentence is provided, the model indirectly references the word it is trying to predict.
In a multi-layer structure, the output of previous layer contains information about all tokens in the sentence, so indirect reference causes a problem which makes predicting the target word possible.
In the paper, 15% of tokens were maksed, however, since there is no [MASK] token in actual fine-tuning, an inconsistency takes place beteween pre-training and fine-tuning. To solve this problem, an author substituted the 15% of tokens.
- 80%: substituted with [MASK] token
- 10%: substituted with random token
- 10%: no substitution
The model is trained to predict the original tokens using cross-entropy loss by utilizing such substitution strategy.
2. Next Sentence Prediction
If only MLM is applied, the model can learn relationships between tokens, but cannot learn the relationships between sentences. Therefore, NSP is used to train masked language model regarding text-pair representation.
Sentence A and B become the input of the model as follows:
- 50% : Provide sentence B, which is the correct sentence, after sentence A (→ IsNext)
- 50% : Provide a random sentence after sentence A (→ NotNext)
This allows the model to learn whether the two sentences are connected or not based on the provided data.
Fine-tuning
After pre-training, BERT possesses information on general language representations, such as relationships between tokens and relationships between sentences.
Fine-tuning is conducted by training the pre-trained model with labeld data for a specific task, which eventually updates the pre-trained parameters.
Fine-tuning phase can be completed in relatively less time compared to pre-training phase.
Conclusion
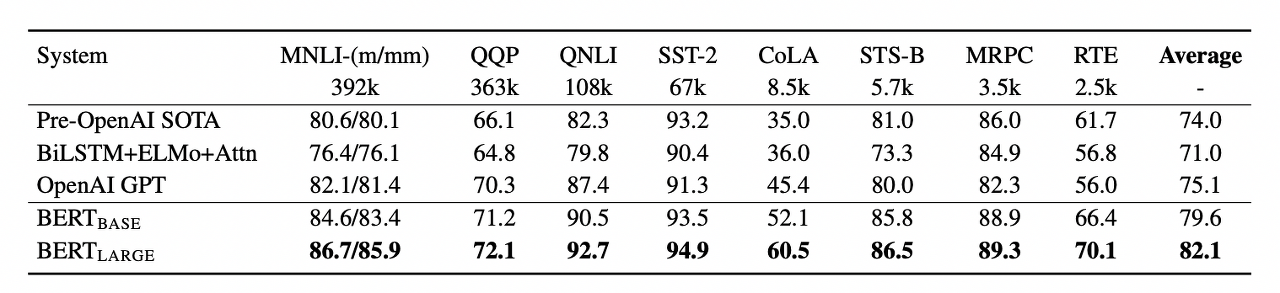
BERT trains the model bidirectionally using large-scaled unlabeled data, and gets the parameter value.
These parameter values are then updated with labeled data for the specific task.
With an approach of pre-training → fine-tuning, BERT has demonstrated outstanding performance across 11 different NLP tasks.
