- 데이터를 나열하고, 각 데이터를 인덱스에 대응해주고, 인덱스로 데이터를 접근할 수 있도록 구성된 데이터 구조
- 파이썬에서는 리스트 타입이 배열 기능을 제공하고 있음
배열이 왜 필요한가?
- 같은 종류의 데이터를 효율적으로 관리하기 위해 사용
- 같은 종류의 데이터를 순차적으로 저장
- 배열의 장점:
- 인덱스로 인한 빠른 접근 가능
- 배열의 단점:
- 미리 배열의 크기를 설정해줘야 하므로, 데이터를 추가하는 것이 어렵다
- 데이터를 삭제 할 경우, 뒤에 있는 데이터를 앞으로 당겨와야 하는 어려움이 있다
배열은 선형 자료구조!!
언어별로 array를 지원 or list를 지원 or 둘 다 지원
-
C
#include <stdio.h> int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) { int sampleArray[3] = {1,2,3}; int i=0; for(i;i<3;i++) { printf("%d",sampleArray[i]); } return 0; } -
Java
public Class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] sampleArray = new int[3]; for(int i=0; i<sampleArray.length; i++) { System.out.println(sampleArray[i]); } } } -
Python
sampleList = [1,2,3] print(sampleList)
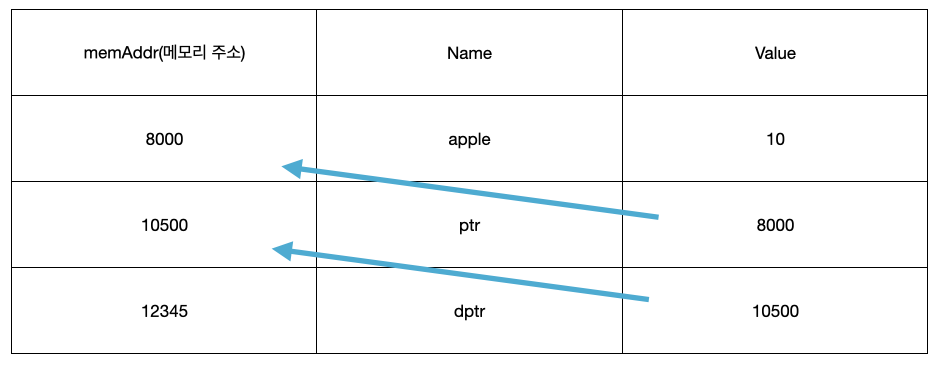
이중 포인터
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int apple = 10;
int* ptr = &apple;
int** dptr = &ptr;
setPerson(apple);
printf("%d",apple);//10;
}
void setPerson(int* ptr){
*ptr = 100;
printf("%d",apple); //100
}
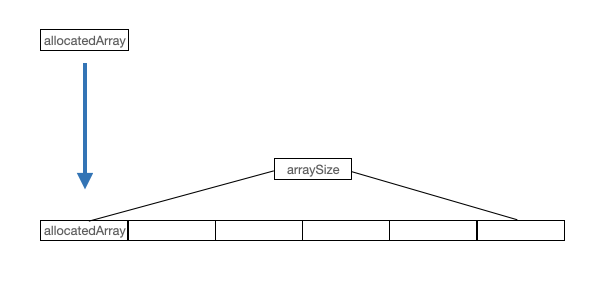
동적 배열 할당
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int arraySize = 0;
int i = 0;
scanf("%d", &arraySize);
int* allocatedArray = malloc(sizeof(int) * arraySize);
for(i; i < arraySize; i++) {
//....
}
free(allocatedArray); //중요!! 메모리 해제
return 0;
}
구조체
structure
struct 구조체이름 {
자료형 멤버이름;
};
struct Person {
int age;
char name[20];
};
struct Person tutor; //구조체는 인스턴스 생성해야 사용가능함
strcpy(tutor.name, "신치용");
tutor.age = 25;
struct Person tutee;
strcpy(tutee.name, "안녕");
tutee.age = 21;-
typedef
typedef struct _Person { //구조체 이름에 _Person으로 해서 가독성 증가 가능 int age; char name[20]; } Person; Person p1; Person tutor; -
sizeof
typedef struct _Person { int age; char gender; //man:M, woman:W double aeafef; //8 } Person; Person p1; //문제 printf("%d\n", sizeof(p1.age)); //4 printf("%d\n", sizeof(p1.gender)); //1 printf("%d\n", sizeof(p1)); //8 printf("%d\n", sizeof(struct _Person)); //8
심화.
-
이름과 나이, 주소 정보를 가진 Person구조체를 생성하고, 생성한 구조체를 이용하여 만든 인스턴스에 이름 : 둘리, 나이 : 11, 주소: 남극으로 입력한다.
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> struct _Person { char name[20]; int age; char address[30]; } Person; int main() { Person p1; //struct _Person p1; strcpy(p1.name, "둘리"); p1.age = 11; strcpy(p1.address, "남극"); printf("이름: %s\n", p1.name); printf("나이: %d\n", p1.age); printf("주소: %s\n", p1.address); return 0; } -
이제 setPerson이라는 메서드를 정의해보자. setPerson 메서드는 파라미터로 구조체 Person형식을 받는다. 그리고 setPerson 메서드는 파라미터로 들어온 구조체의 이름 항목을 "고길동"으로 바꾸고, 나이를 40으로 수정하고, 주소를 "서울시"로 변경한다. 만든 setPerson함수를 메인함수에서 호출해보고 호출한 후 처음에 만들었던 인스턴스의 이름,나이,주소 항목을 출력해보자.
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> struct Person { char name[20]; int age; char address[30]; }; void setPerson(struct Person p) { // strcpy(p->name, "고길동"); strcpy(p.name, "고길동"); p.age = 40; strcpy(p.address, "서울시"); } . p->name; int main() { struct Person p1; strcpy(p1.name, "둘리"); p1.age = 11; strcpy(p1.address, "남극"); setPerson(p1); // 함수를 호출할 때 구조체 변수 전달, 멤버가 복사됨 printf("이름: %s\n", p1.name); printf("나이: %d\n", p1.age); printf("주소: %s\n", p1.address); // 둘리, 11, 남극 인스턴스를 복사하여 파라미터로 넘겼기 때문에 원본데이터에 수정 X // 원본 데이터를 수정하기 위해선 포인터를 사용하면 됨 return 0; }

