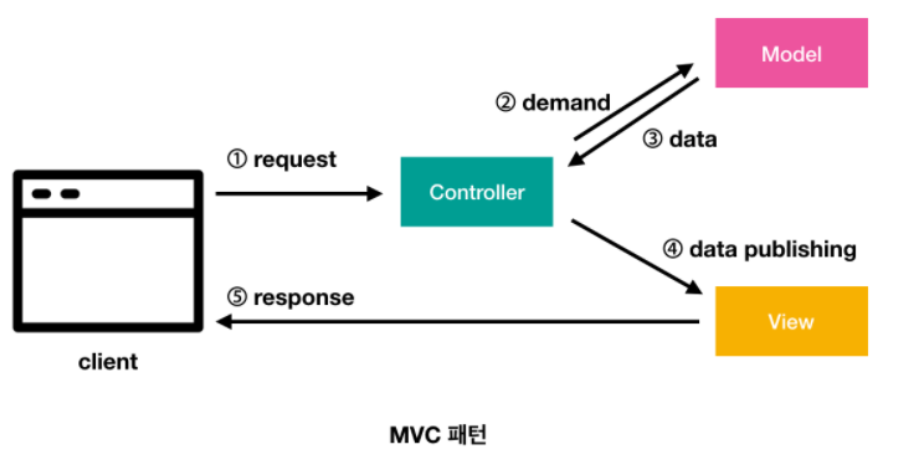
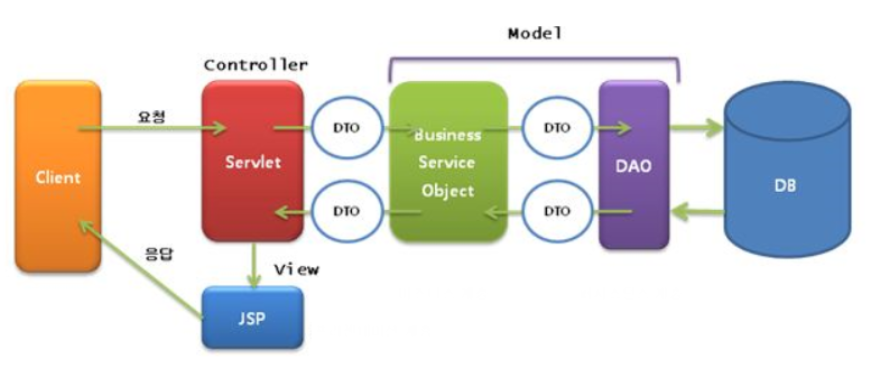
- M(Model) : 사용자가 원하는 데이터나 정보를 제공
- V(View) : 보여지는 화면
- C(Controller) : 사용자의 요청을 처리하고, 그 요청에 따른 전체적인 흐름을 제어
1. Model
- 애플리케이션의 정보, 데이터를 나타냄
- 이러한 data 정보들의 가공을 책임지는 컴포넌트
2 View
- input 텍스트, 체크박스 항목 등과 같은 사용자 인터페이스 요소를 나타냄. 다시 말해 데이터 및 객체의 입력, 그리고 보여주는 출력을 담당
- 데이터를 기반으로 사용자들이 볼 수 있는 화면
3. Controller
- 데이터와 사용자 인터페이스 요소들을 잇는 다리 역할을 함
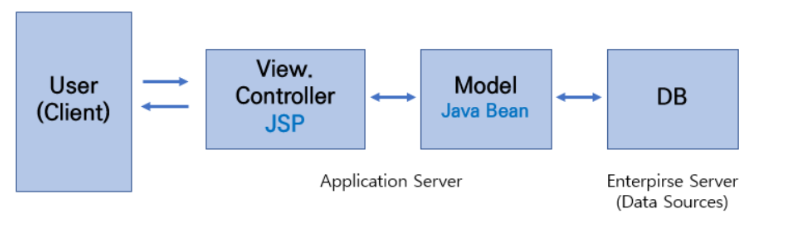
4. MVC1
- MVC1 패턴의 경우 View와 Controller를 모두 JSP가 담당하는 형태를 가짐
- 즉, JSP 하나로 유저의 요청을 받고 응답을 처리하므로 구현 난이도는 쉽다
- 단순한 프로젝트에는 괜찮겠지만 내용이 복잡하고 거대해질수록 이 패턴은 힘을 잃음
- 즉, 유지보수에 문제가 발생
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%
int num = 0;
String num_ = request.getParameter("num");
if(num_ != null && !num_.equals("")) {
num = Integer.parseInt(num_);
}
%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<% if(num%2 != 0) {%>
홀수입니다.
<%} else {%>
짝수입니다
<%}%>
</body>
</html><%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%
int num = 0;
String num_ = request.getParameter("num");
if(num_ != null && !num_.equals("")) {
num = Integer.parseInt(num_);
}
String result ="";
if(num%2 != 0) {
result ="홀수";
} else {
result ="짝수";
}
%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<%=result %>
</body>
</html><%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<%=request.getAttribute("result")%>입니다.
</body>
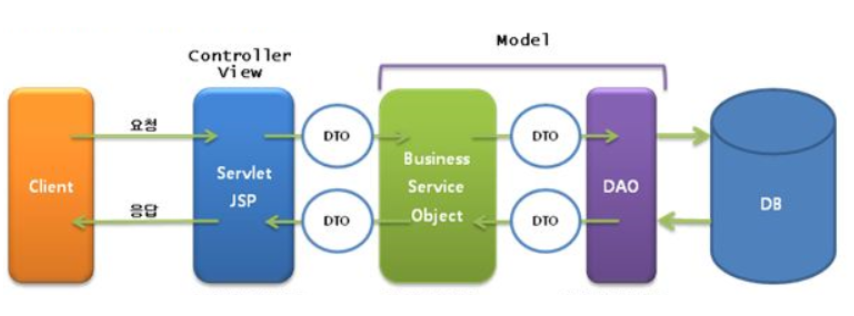
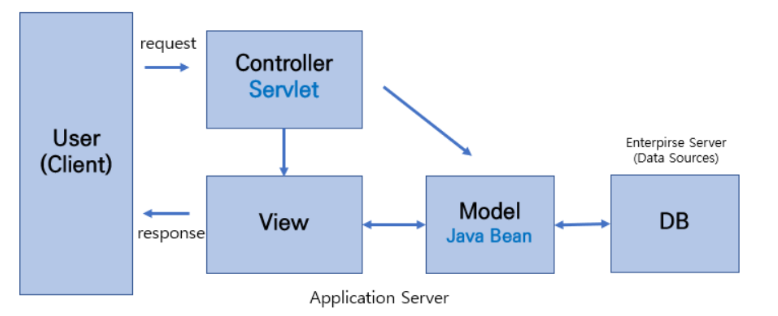
</html>5. MVC2
- MVC2 패턴은 널리 표준으로 사용되는 패턴
- 요청을 하나의 컨트롤러(Servlet)가 먼저 받는다
- 즉 MVC1과는 다르게 Controller, view가 분리되어 있음
- 따라서 역할이 분리되어 MVC1 패턴에서 단전을 보완할 수 있음
- 그러므로 개발자는 M, V, C 중에서 수정해야 할 부분이 있다면, 그것만 꺼내어 수정하면 됨
- 따라서 유지 보수에 있어서도 큰 이점이 있음
package com.kh.web.servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
import jakarta.servlet.RequestDispatcher;
import jakarta.servlet.ServletException;
import jakarta.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@WebServlet("/mvc2")
public class mvcServelt extends HttpServlet{
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
int num = 0;
String num_ = req.getParameter("num");
if(num_ != null && !num_.equals("")) {
num = Integer.parseInt(num_);
}
String result ="";
if(num%2 != 0) {
result ="홀수";
} else {
result ="짝수";
}
req.setAttribute("result", result);
// RequestDispatcher : 요청을 보내주는 인터페이스
RequestDispatcher dispatcher = req.getRequestDispatcher("mvc2.jsp");
dispatcher.forward(req, resp);
}
}