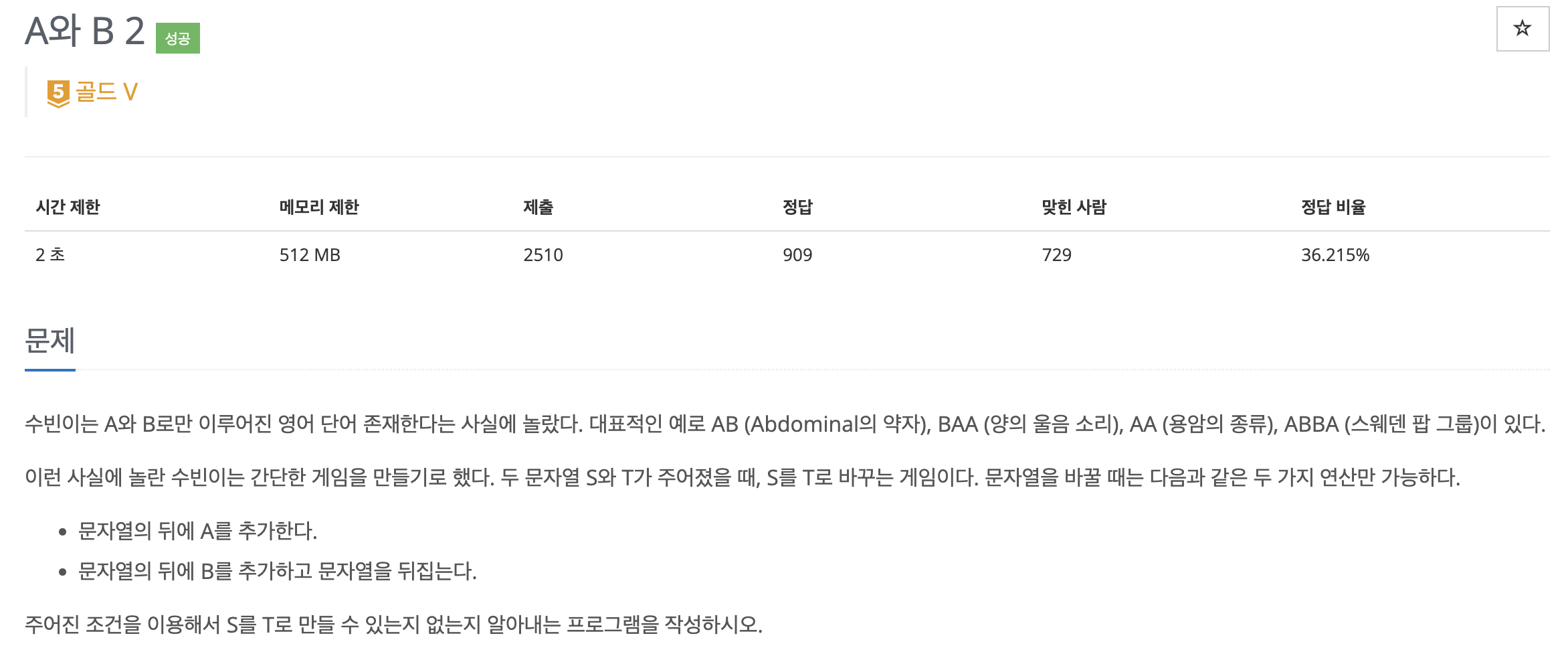
📚 Problem
📝 Solution
Key Idea
- S를 T로 바꾸는 것이 아닌 T를 S로 바꾼다
- 이전
A와 B문제와의 차이점은 B를 먼저 추가하고 문자열을 뒤집는 것인데- 이렇게되면
B・・・A와 같은 경우에 연산 2가지중 어느것을 먼저 수행해야할지 우선순위가 정해져 있지 않다- 그러므로 모든 경우의 수를 탐색하기위해
DFS를 사용한다- 문자열을 뒤집는 연산은 실제로 하지는 않고
boolean값을 이용해 판단한다DFS를 사용해 종료 조건을 문자열의 길이가 같아질때 까지로 두고head가 어딘지에 따라 문자열을 비교하여 확인한다
private static void DFS(String S, String T, boolean head) {
if (T.length() == S.length()) {
if(T.equals(S) && head || reverse(T).equals(S) && !head)
check = true;
return;
}
if (head) {
if(T.charAt(T.length() - 1) == 'A')
DFS(S, T.substring(0, T.length() - 1), true);
if(T.charAt(0) == 'B')
DFS(S, T.substring(1), false);
}
else {
if(T.charAt(0) == 'A')
DFS(S, T.substring(1), false);
if(T.charAt(T.length() - 1) == 'B')
DFS(S, T.substring(0, T.length() - 1), true);
}
}💻 Code
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Main {
private static boolean check = false;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String S = br.readLine();
String T = br.readLine();
DFS(S, T, true);
if(check)
System.out.println(1);
else
System.out.println(0);
}
private static String reverse(String T) {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(T);
return builder.reverse().toString();
}
private static void DFS(String S, String T, boolean head) {
if (T.length() == S.length()) {
if(T.equals(S) && head || reverse(T).equals(S) && !head)
check = true;
return;
}
if (head) {
if(T.charAt(T.length() - 1) == 'A')
DFS(S, T.substring(0, T.length() - 1), true);
if(T.charAt(0) == 'B')
DFS(S, T.substring(1), false);
}
else {
if(T.charAt(0) == 'A')
DFS(S, T.substring(1), false);
if(T.charAt(T.length() - 1) == 'B')
DFS(S, T.substring(0, T.length() - 1), true);
}
}
}