The Need for Security
Definition of Computer Security
The protection afforded to an automated information system in order to attain the applicable objectives of preserving the integrity, availability and confidentiality of information system resources (includes hardware, software, firmware, information/data, and telecommunications)
Principles of Security
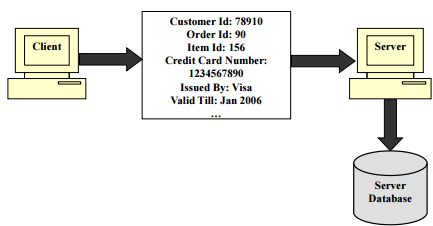
Data Transmission on the Internet
- Data travels in clear text
- Personal or confidential information is not secure
- Example: Transmission of credit card details
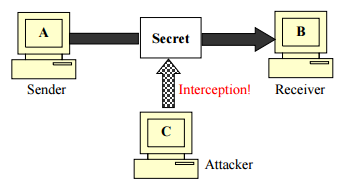
Confidentiality
- Also called as privacy
- Refers to the secrecy of information
- Only the sender and the receiver should have an access to the information
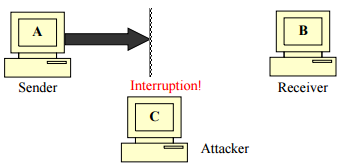
- Interception causes loss of message confidentiality
Authentication
- Identifies the sender/receiver of a message
- Required so that the communicating parties trust each other
- Answers who is who
- Fabrication is possible in absence of proper authentication mechanisms
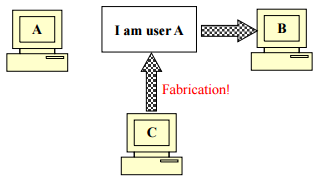 Fabrication : 위조 ( A인것처럼 )
Fabrication : 위조 ( A인것처럼 )
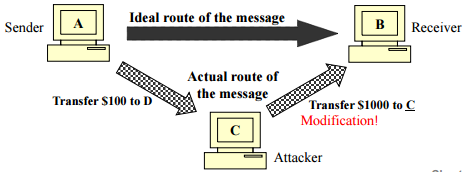
Integrity
- Ensures that any changes to a message are detected
- The message from the sender to the receiver must travel without any alterations
- Changes need to be prevented, or at least, detected
- Modification causes loss of message integrity
Availability
- Resources/applications must be available to authentic users all the time
- Attackers can deny the availability
- Denial Of Service (DOS) is an example of an attack on availability
- Interruption puts the availability of resources in danger
Non-repudiation & Access Control
- Non-repudiation(거절방지) does not allow the sender of a message to refute the claim of not sending that message
- Access control specifies and controls who can access what
Security Objectives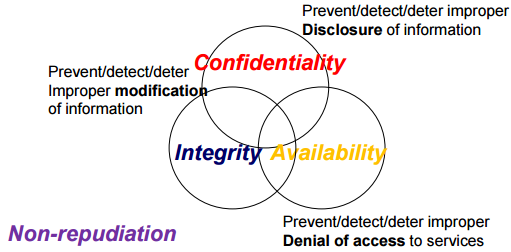
Security is PAIN;
P(Privacy, Confidentiality) A(Availability) I(Integrity) N(Non-repudiation)
Types of Attacks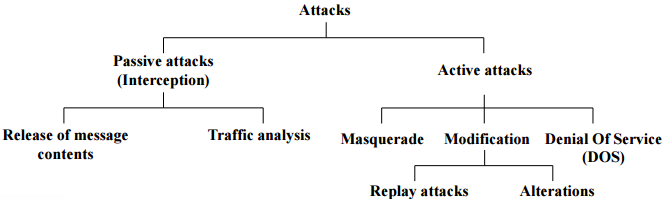
- Two types of security attacks in technical view
- Passive attacks: Observing the information from the system without affecting system resources
- Active attacks: Try to alter system resources or affect their operation
Passive Attacks
- Release of message contents
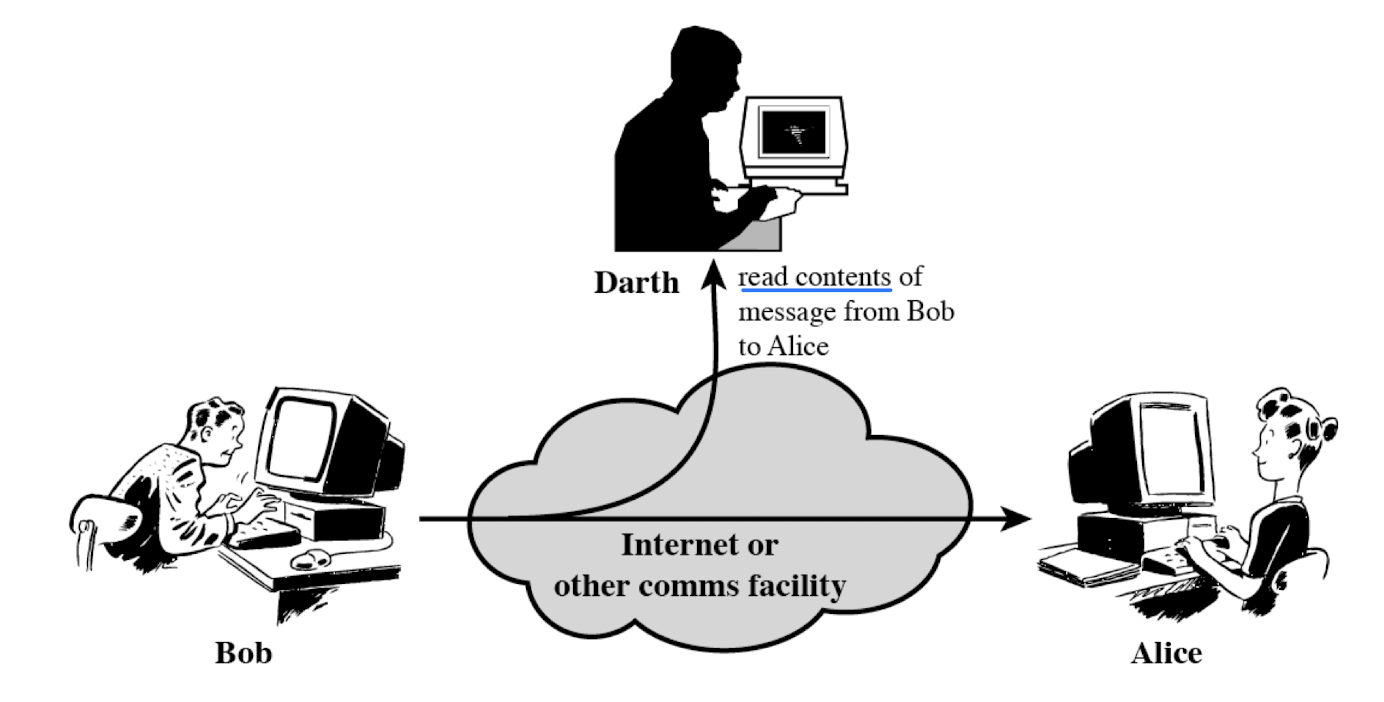
- Traffic analysis
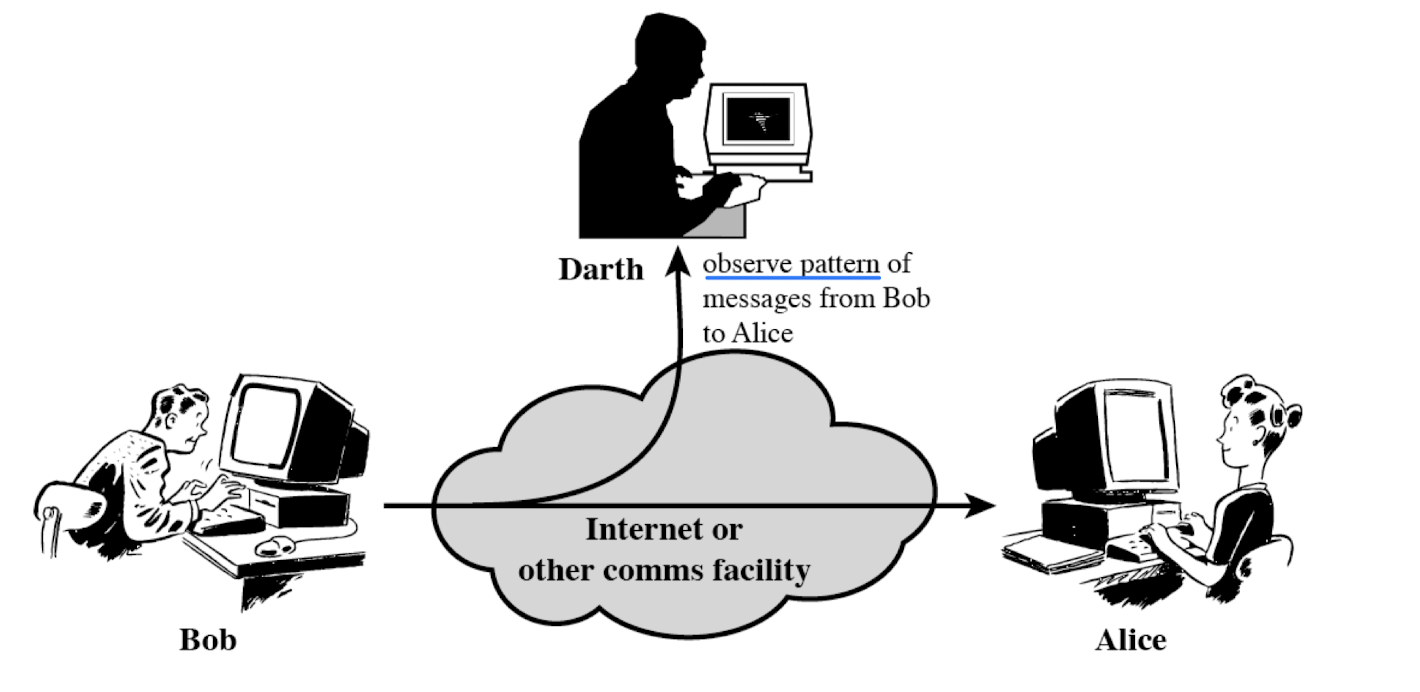
- Difficult to detect (after they occurred)
→ because they do not involve any change of the data - Thus, they should be prevented rather than be detected
Active Attacks
- Creating illegitimate messages
- Masquerade (who) → 위장, 가장
- One entity pretends to be a different entity
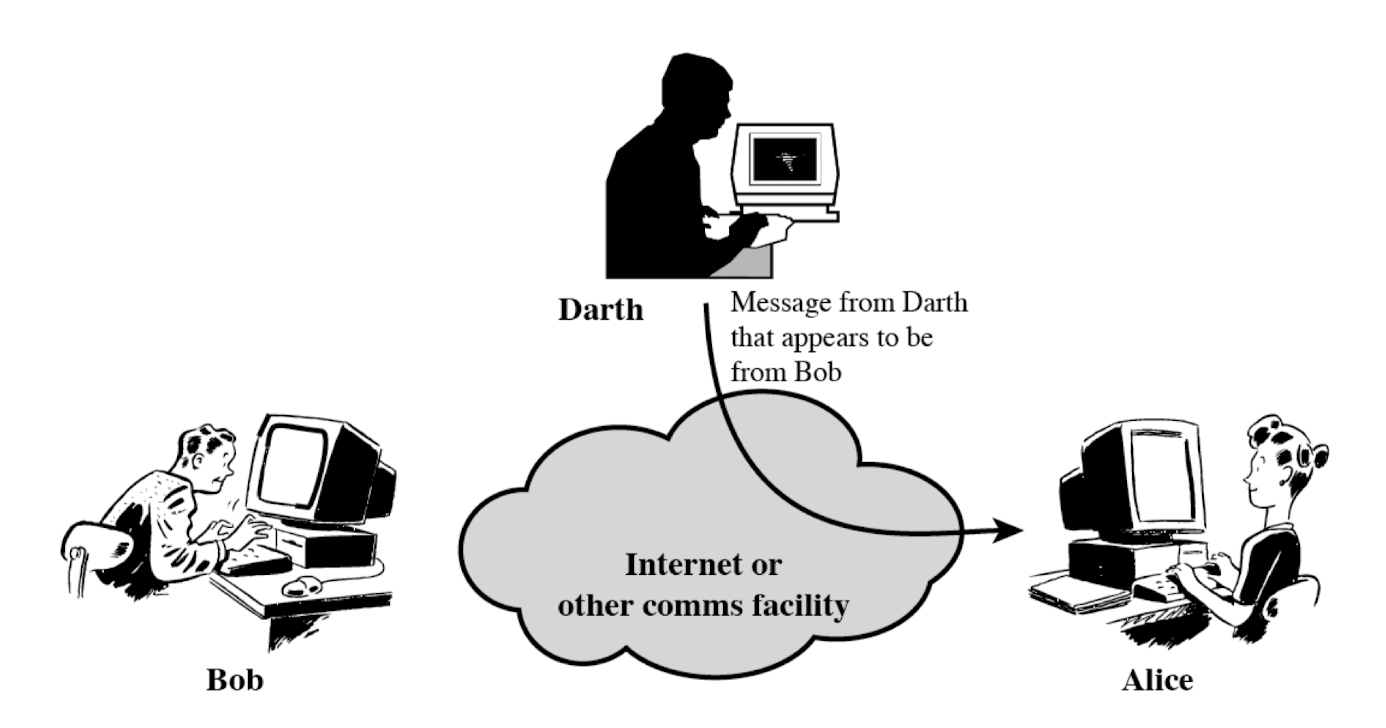
- One entity pretends to be a different entity
- Replay (when)
- A message is captured and retransmitted later
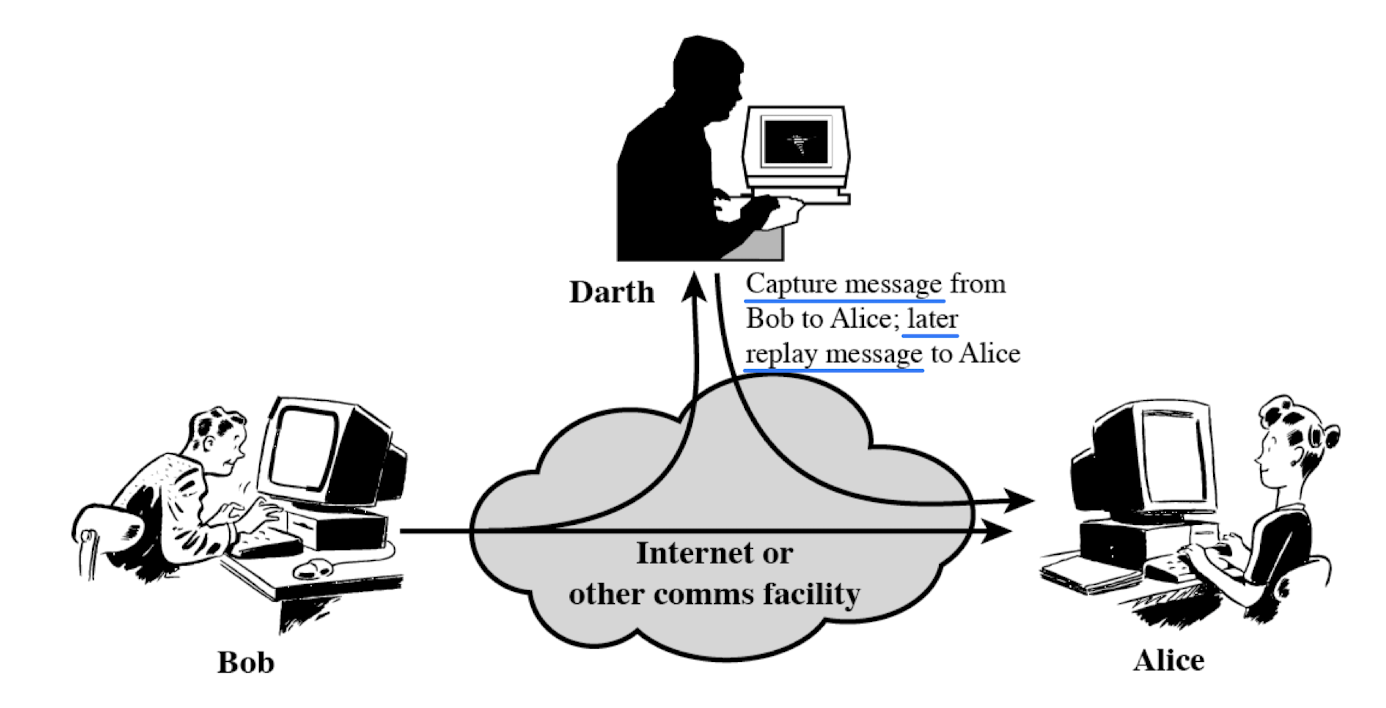
- A message is captured and retransmitted later
- Alteration(Modification) of messages (what)
- A message is captured, modified, and transmitted
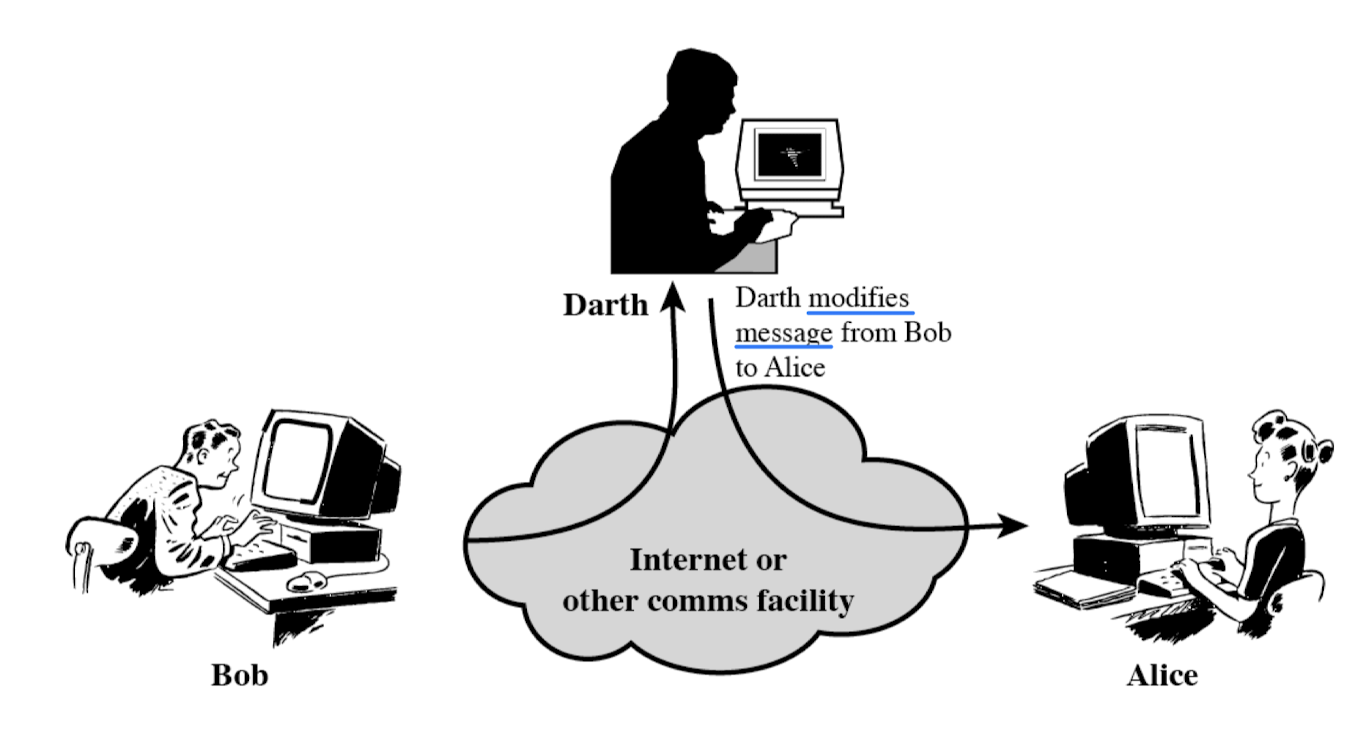
- A message is captured, modified, and transmitted
- Masquerade (who) → 위장, 가장
- Making system facilities unavailable
- Denial of service
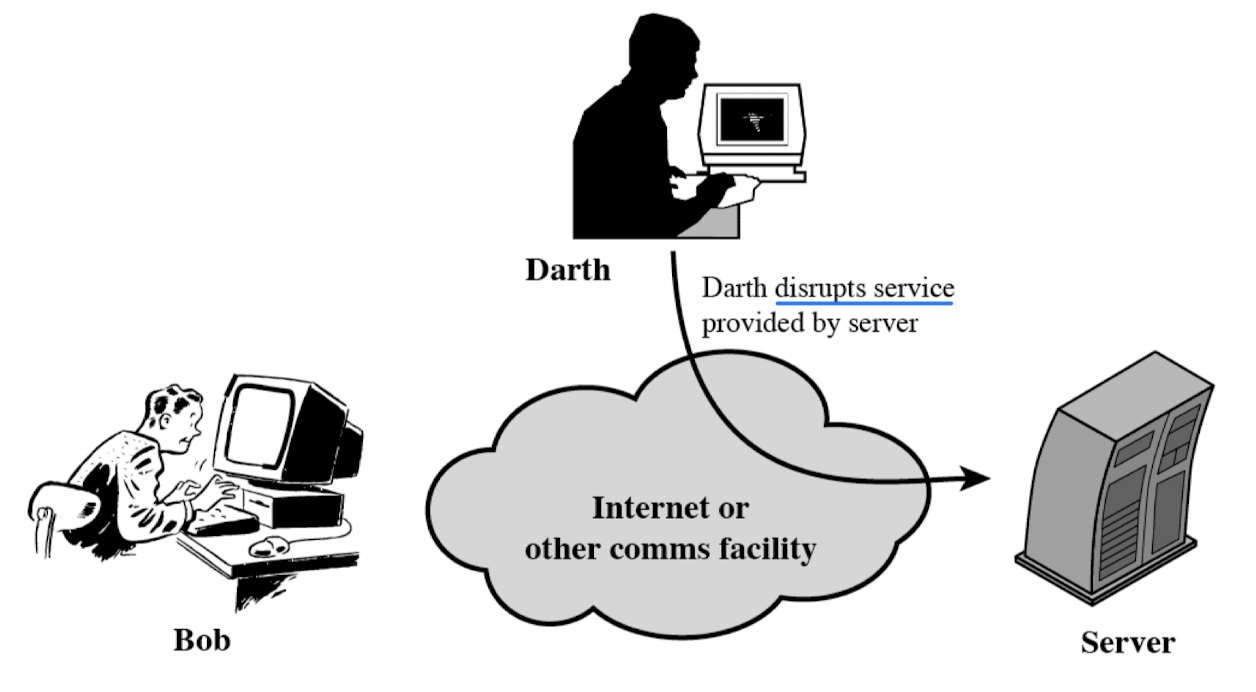
- Denial of service
- Denying legitimate messages
- Repudiation
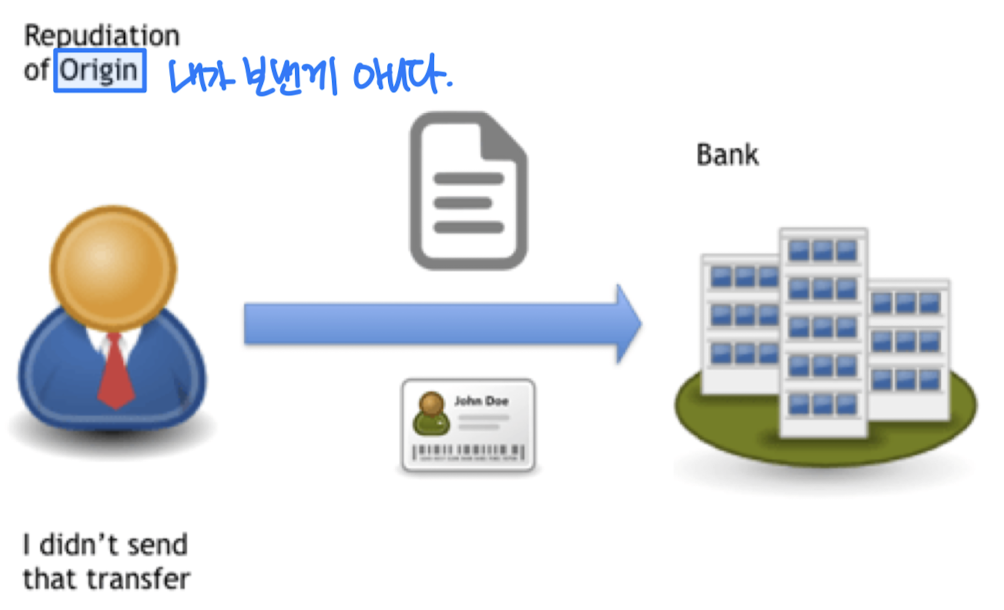
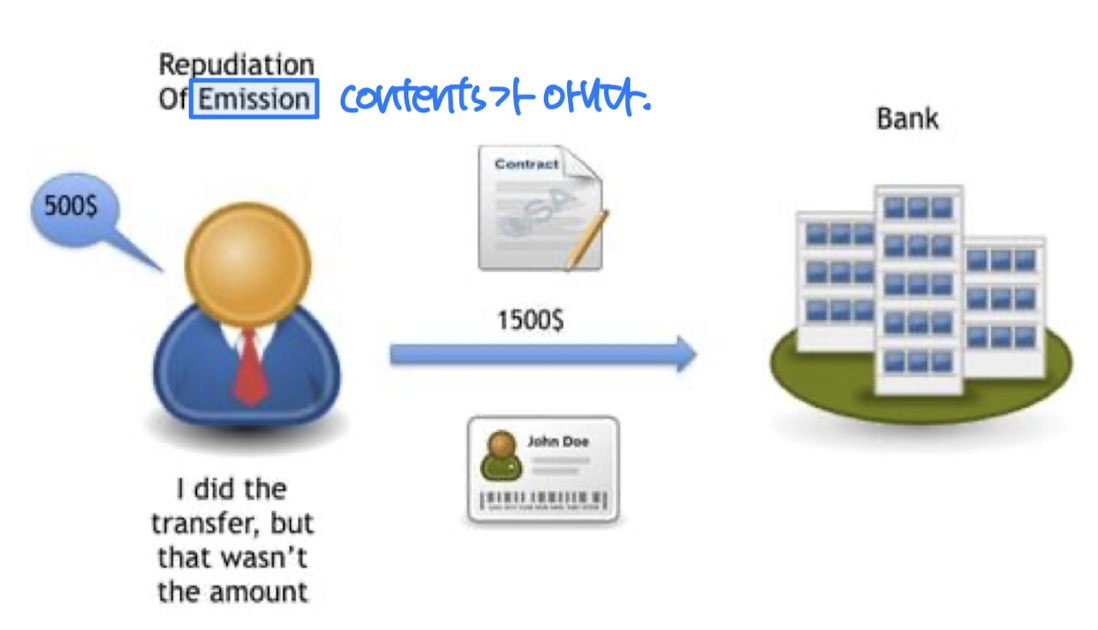
- Repudiation
- Difficult to prevent
→ because of new vulnerabilities - So, the goal is to detect active attacks and to recover as soon as possible.
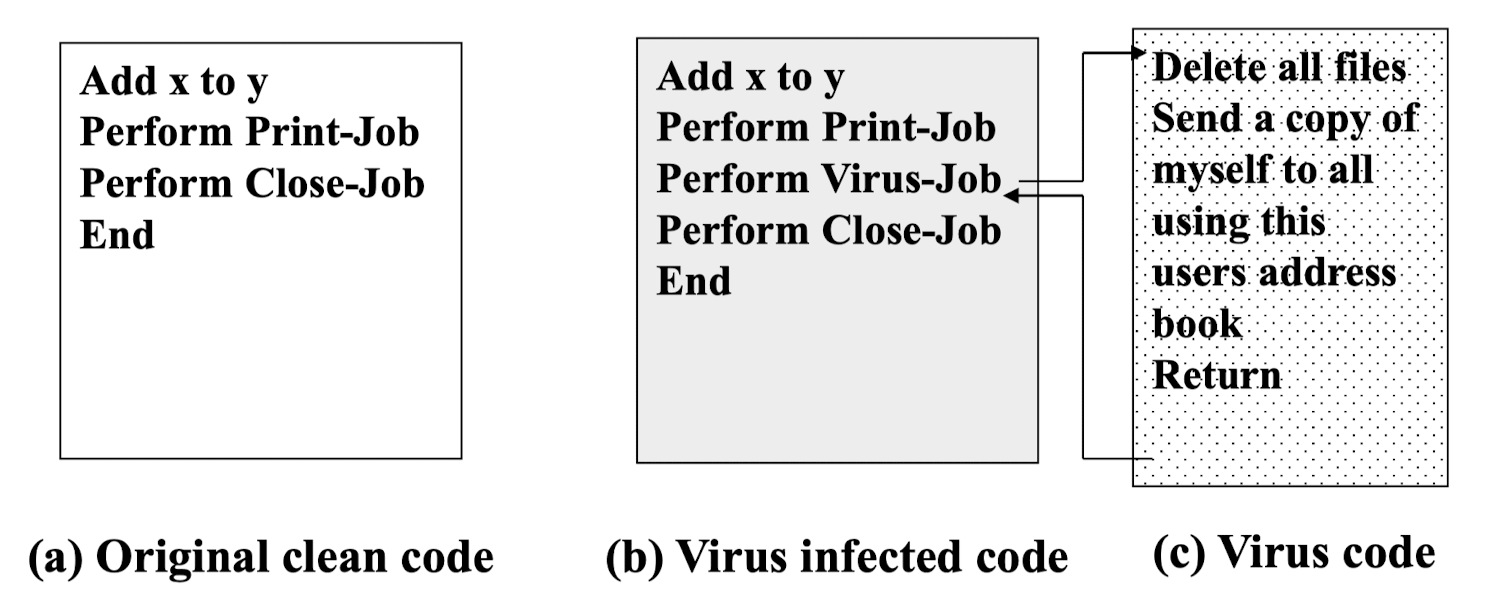
Virus
- Program that causes damage to other programs/applications/data
- Contains malicious code
- Propagates as it damages
Worm
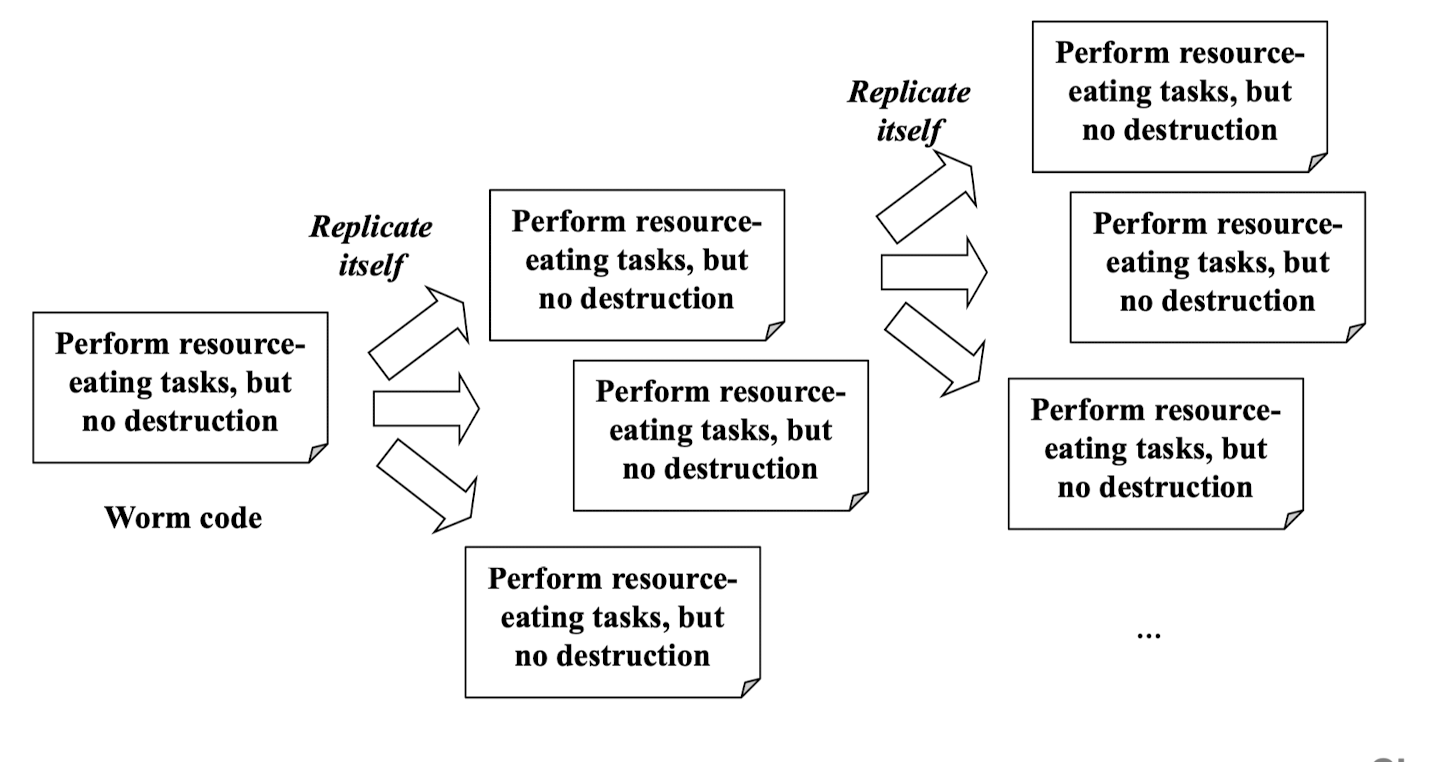
- Propagates as it damages
- Does not damage a program/data
- Consumes resources(traffic), and brings system to a halt
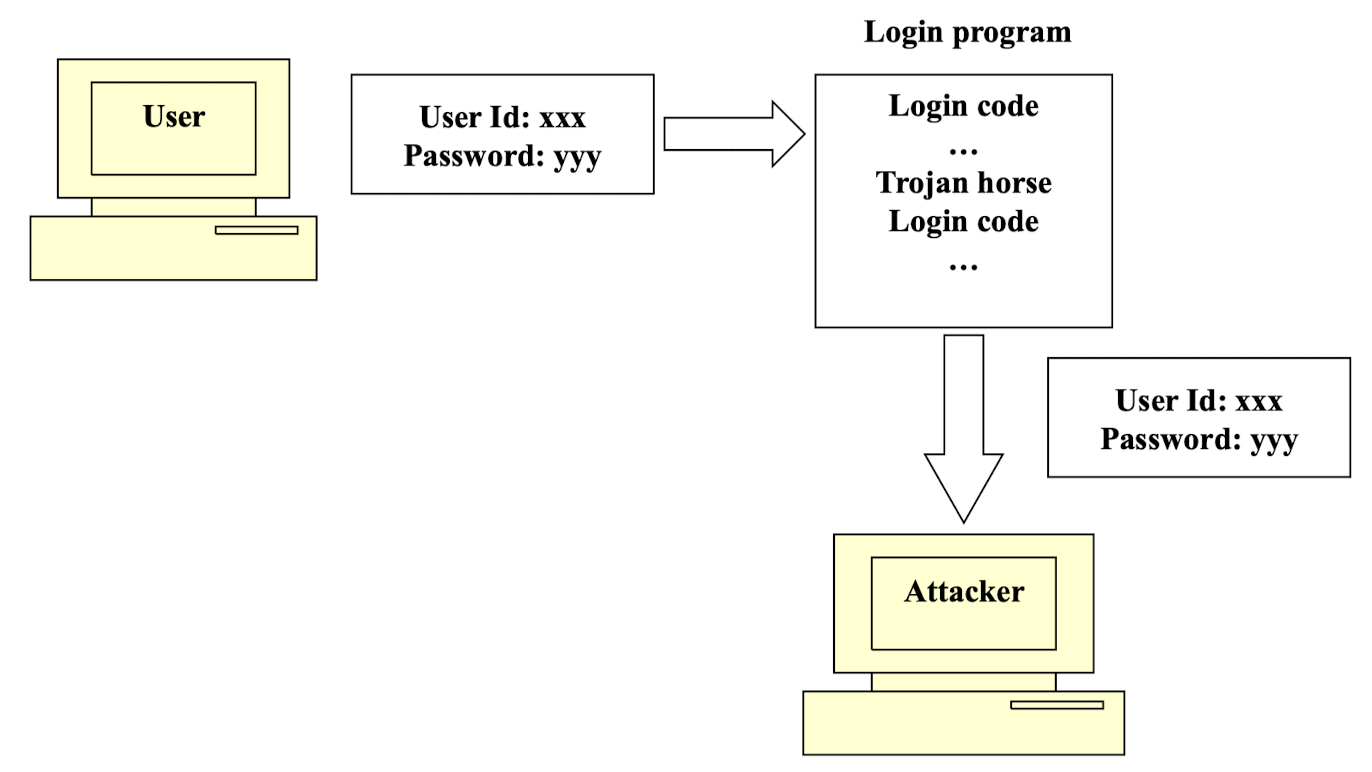
Trojan Horse
- Silently observes user actions and captures confidential information
- Uses captured information for its use
- Example: Capturing user id and password
HGU 전산전자공학부 고윤민 교수님의 24-2 컴퓨터 보안 수업을 듣고 작성한 포스트이며, 첨부한 모든 사진은 교수님 수업 PPT의 사진 원본에 필기를 한 수정본입니다.

