Introduction of Firewalls
- Now everyone want to be on the Internet and to interconnect networks
- But persistent security concerns
- can’t easily secure every system in org
- Typically use a Firewall to provide perimeter defense
- Now it is a part of comprehensive security strategy
Firewall Concept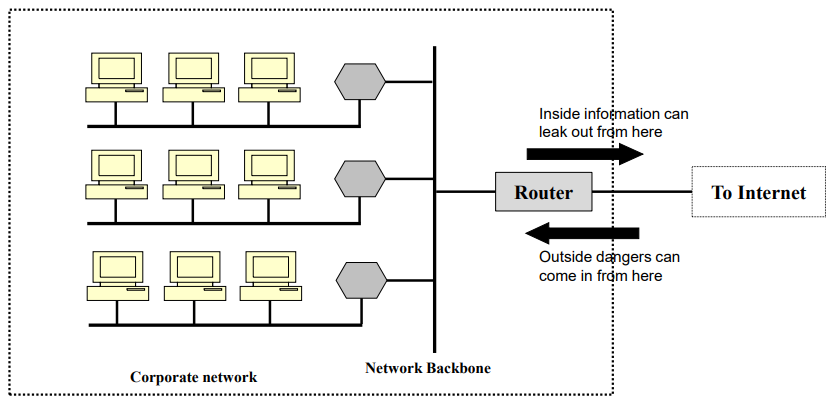
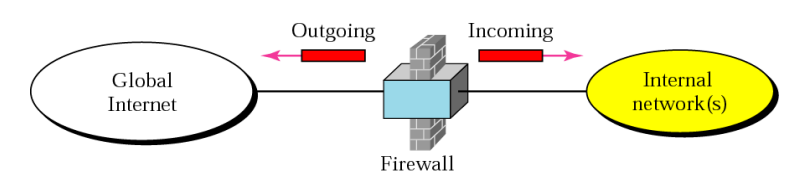
Firewall
- Special type of network router
- Controls transmission between internal and external networks
- A choke point of control and monitoring
Main Goals of Firewall
- Restrict incoming and outgoing traffic by IP address, ports, or users
- Block invalid traffic and only authorized traffic is allowed
- Hide internal network topology and services
- Protect against protocol errors
- e.g. invalid SMTP commands can be filtered
- Enable logging
- Auditing and controlling access
Types of Firewalls
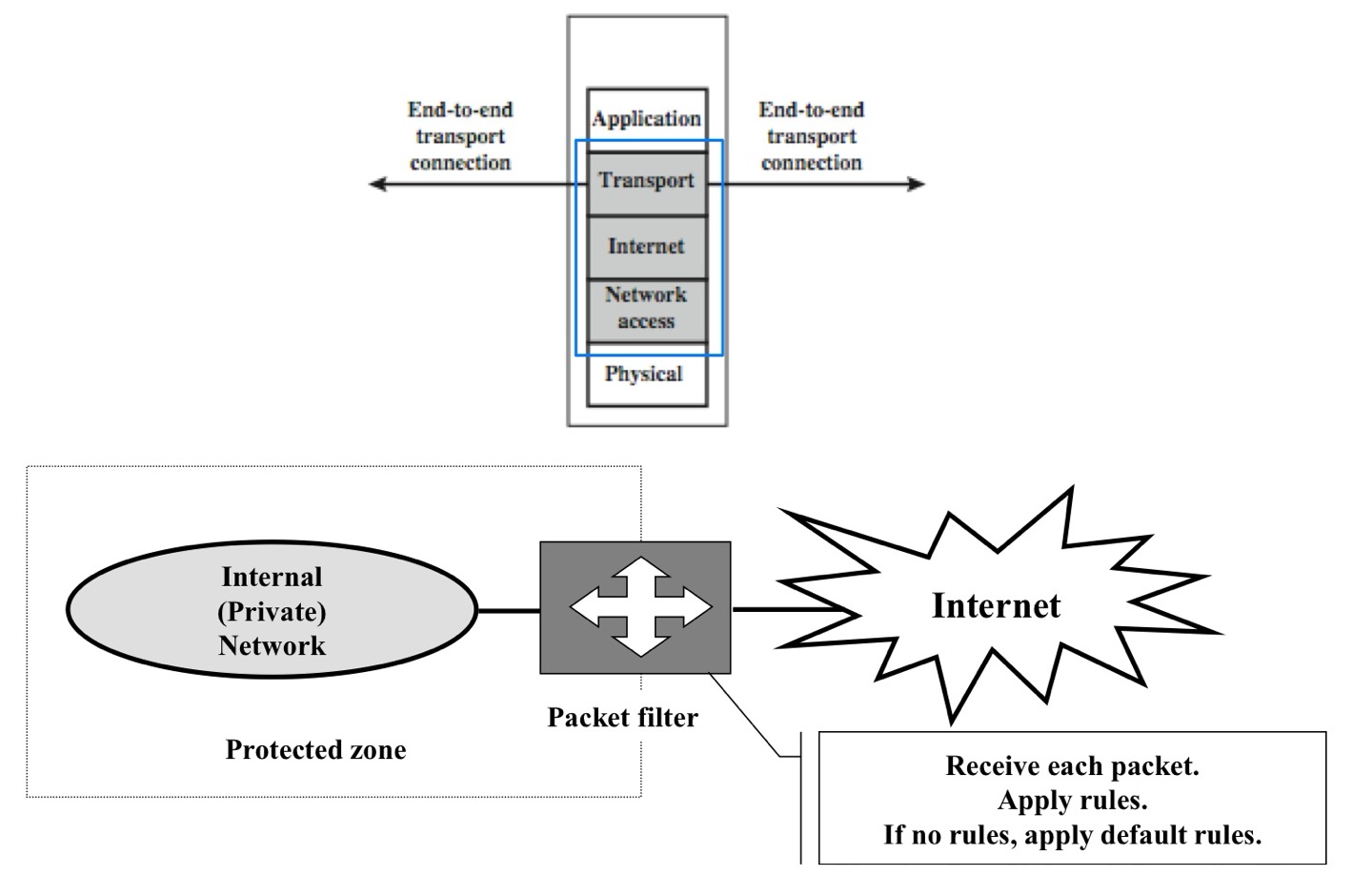
- Packet filters → network, transport layer
- Also known as screen router or screening filter
- Forward and block packets based on information in the network layer and transport layer headers, such as source and destination IP addresses, source and destination port numbers (TCP or UDP), and type of protocol (IP)
- Application gateway → application layer
- Also known as proxy server
- Forward and block packets based on the contents of the messages (i.e., at application level traffic)
Packet Filters
- Simplest, fastest firewall component → header info.만 보면되기 때문
- Foundation of any firewall system
- Examine each IP packet (no context) and permit or deny according to rules
- Hence restrict access to services (ports)
- Most routers have packet filtering capabilities
- Possible default policies
- that not expressly permitted is prohibited → 조금 더 보수적
- that not expressly prohibited is permitted
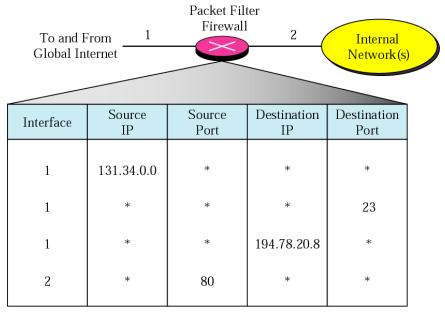
- Example of packet filter rules:
- Incoming packet from 131.34.0.0 are blocked.
- Incoming packet destined for any internal TELNET (port 23) are blocked
- Incoming packets destined for internal host 194.78.20.8 are blocked (this host for internal use)
- Outgoing packets destined for an HTTP server (port 80) are blocked. (i.e. does not want employees to browser the Internet) → Web service X
Types of Packet Filtering
- Stateless packet filtering → packet by packet
- Also known as first generation firewall
- Based on access control lists (ACL)
- Decisions are made on a per-packet basis
- Operates at either the network or transport layer
- No state information saved
- Stateful packet filtering (Session filtering) → packet들의 context를 봄
- Also known as dynamic packet filter
- Examination of packets based on current state of the network
Example of Packet Filtering
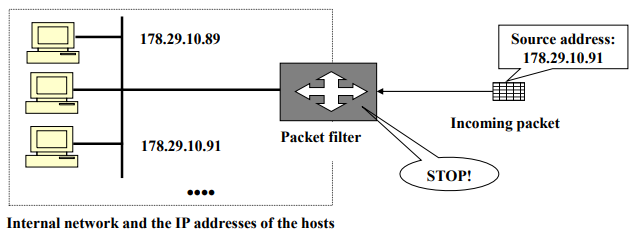
- IP address spoofing attack
- An intruder attempts to send a packet towards the internal network, with the source IP address set equal to one of the IP addresses of the internal users.
- This attack can be defeated by discarding all the packets that arrive at the incoming side of the firewall, with the source address equal to one of the internal addresses
- Dynamic packet filter → Statefull
- Allow incoming TCP packets only if they are responses to the outgoing TCP packets that have gone through out network
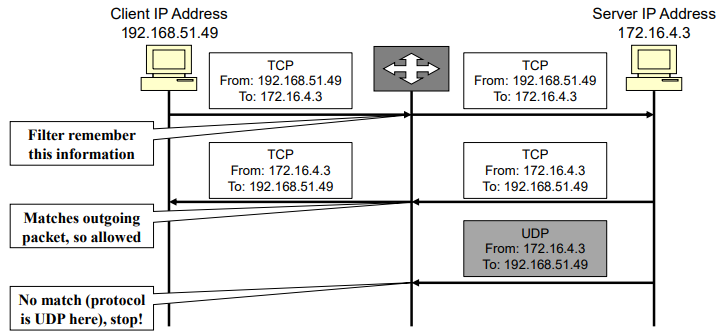
- Allow incoming TCP packets only if they are responses to the outgoing TCP packets that have gone through out network
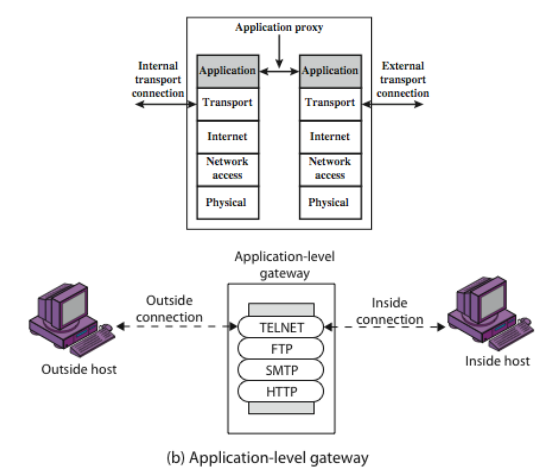
Application Level Gateway
- Have application specific gateway / proxy
- Has full access to protocol
- User requests service from proxy
- Proxy validates request as legal
- Then actions request and returns result to user
- Can log / audit traffic at application level
- Need separate proxies for each service
- Circuit-gateway operation
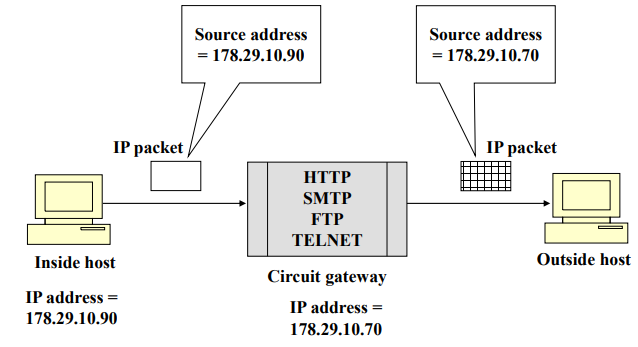 → 각각 TCP Session을 맺고 forwarding
→ 각각 TCP Session을 맺고 forwarding
→ 뭐가 좋을지 한번 생각해보기
- Application-level gateway tend to be more secure than packet filters since we simply detect whether a user is allowed to work with a TCP/IP application or not (not examine every packets)
- It is easy to log and audit traffic at application level, but requires additional overhead (overhead: illusion there is one set of connections)
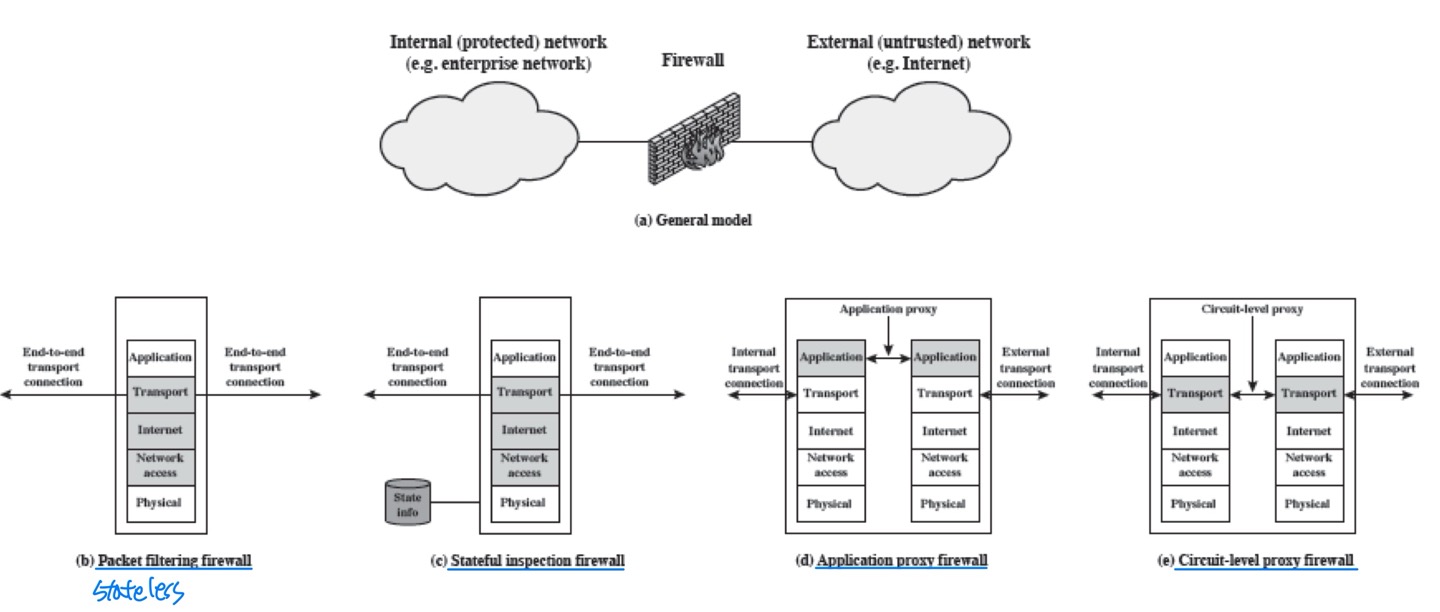
Bastion Host
- Serves as a platform for Application level gateway / Circuit gateway
- Only the services that the network administrator considers essential such as Telnet, DNS, and FTP are installed on the bastion host.
- Each proxy module is a very small software package specially designed for network security.
- Each proxy is independent of other proxies. Thus, if there is a problem with one proxy, it can be uninstalled without affecting others.
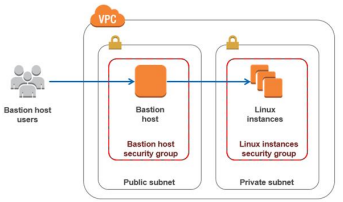
Personal Firewalls
- Controls traffic between PC/workstation and Internet or enterprise network
- A software module on personal computer or in home/office to DSL/cable/ISP router
- Typically much less complex than other firewall types
- Primary role to deny unauthorized remote access to the computer
- Monitor outgoing activity for malware
→ OS 제공 개인 방화벽
Demilitarized Zone Networks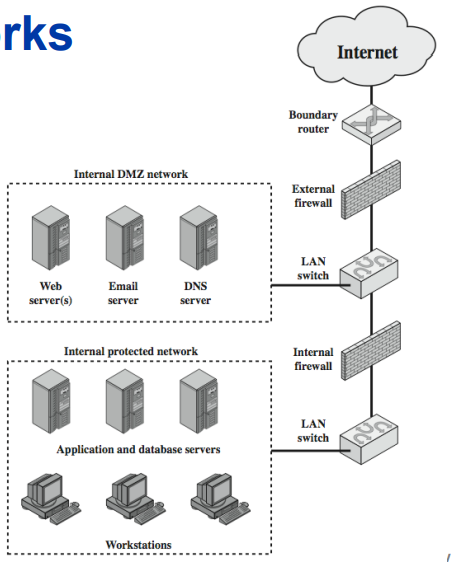
- DMZ (Demilitarized Zone)
- Firewall configuration that allows an organization to securely host its public servers and also protect its internal network at the same time.
- a network for public access service / servers (e.g. mail server, web server)
- Firewall configuration that allows an organization to securely host its public servers and also protect its internal network at the same time.
- DMZ is simply a network segment that is located between the protected and the unprotected networks.
- Usually with less restricted rules (e.g. less restricted access control rules)
- Another firewall features is provision of DMZ
- Not every firewall come with DMZ.
- many low-end router/firewall does not have DMZ.
- DMZ provides high flexibility for security rule / policy
- Not every firewall come with DMZ.
Distributed Firewalls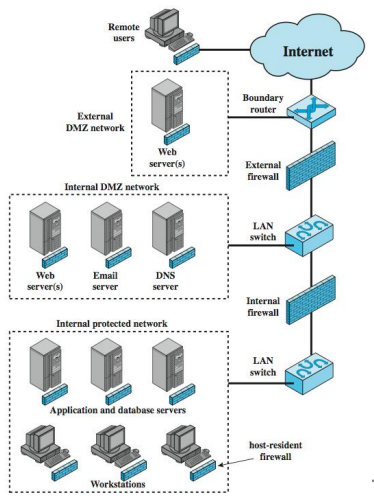
HGU 전산전자공학부 고윤민 교수님의 24-2 컴퓨터 보안 수업을 듣고 작성한 포스트이며, 첨부한 모든 사진은 교수님 수업 PPT의 사진 원본에 필기를 한 수정본입니다.

