Today I Learned
새해 첫 공부!!
뷰 바인딩
View Binding. XML 파일에 선언한 뷰 객체를 코드에서 쉽게 이용하는 방법
before 뷰바인딩
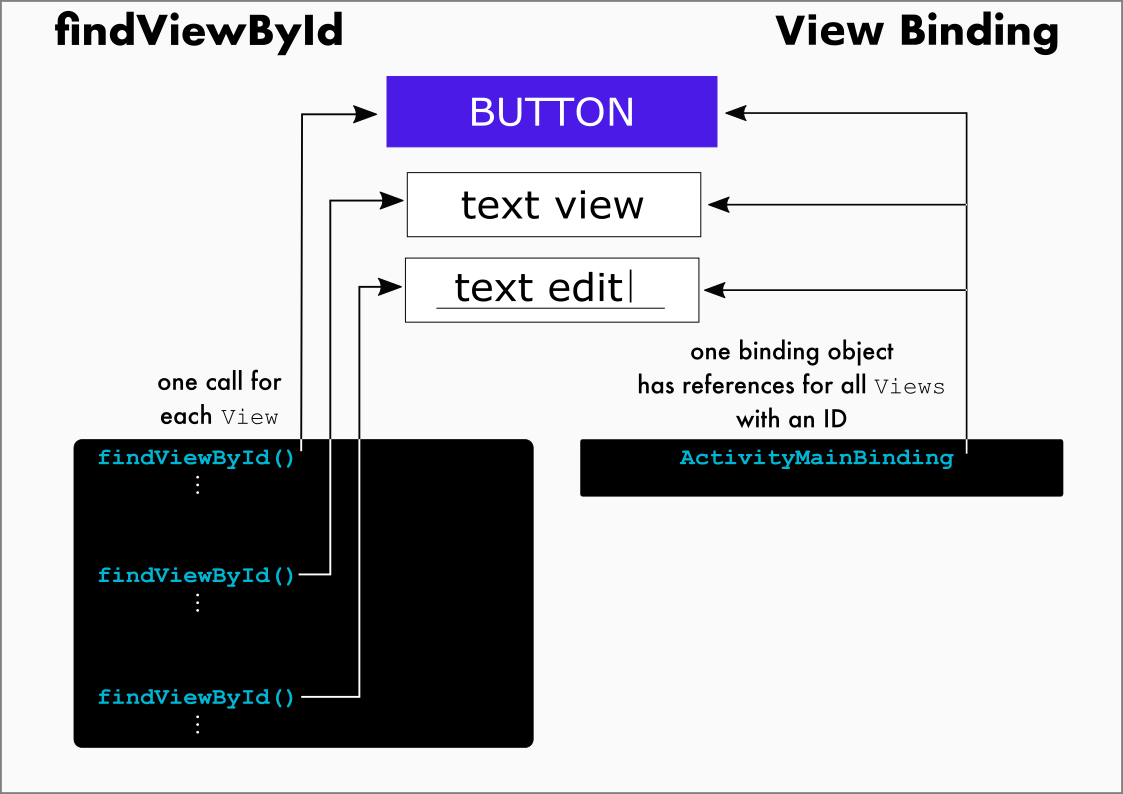
기존에는 액티비티에서 뷰의 값을 변경하려면 아래의 코드처럼 findViewById()함수로 xml의 뷰와 변수를 하나하나 연결시켜주는 번거로운 작업이 필요했다.
nameView = findViewById(R.id.name);
phoneView = findViewById(R.id.phone);
addressView = findViewById(R.id.address);
}- 이를 해결하기 위해 Butterknife라는 라이브러리를 사용하거나 kotlin synthetic 기능을 이용했으나, 아래와 같은 문제점이 있었다.
-
Null 안정성
id 오입력시 null 처리되어 NPE 발생 -
Type 안정성
imageView의 타입을 textView로 잘 못 캐스팅하면 cast exception이 발생 -
상대적으로 느린 속도
- 그래서 3.6버전에 뷰바인딩이등장해 위의 문제점을 해결하며 완전히 대체되었다.
사용방법
- 아래와 같이 버튼과 텍스트뷰에 id를 선언한 xml이 있다.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/visibleBtn"
android:text="Button1" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/targetView"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="hello"
android:background="#FF0000"
android:textColor="#FFFFFF"/>
</LinearLayout>- 먼저, build.gradle.kts 파일의 android 안에 buildFeature 안에 아래와 같이 선언한다.
android {
buildFeatures {
viewBinding = true
}
}-
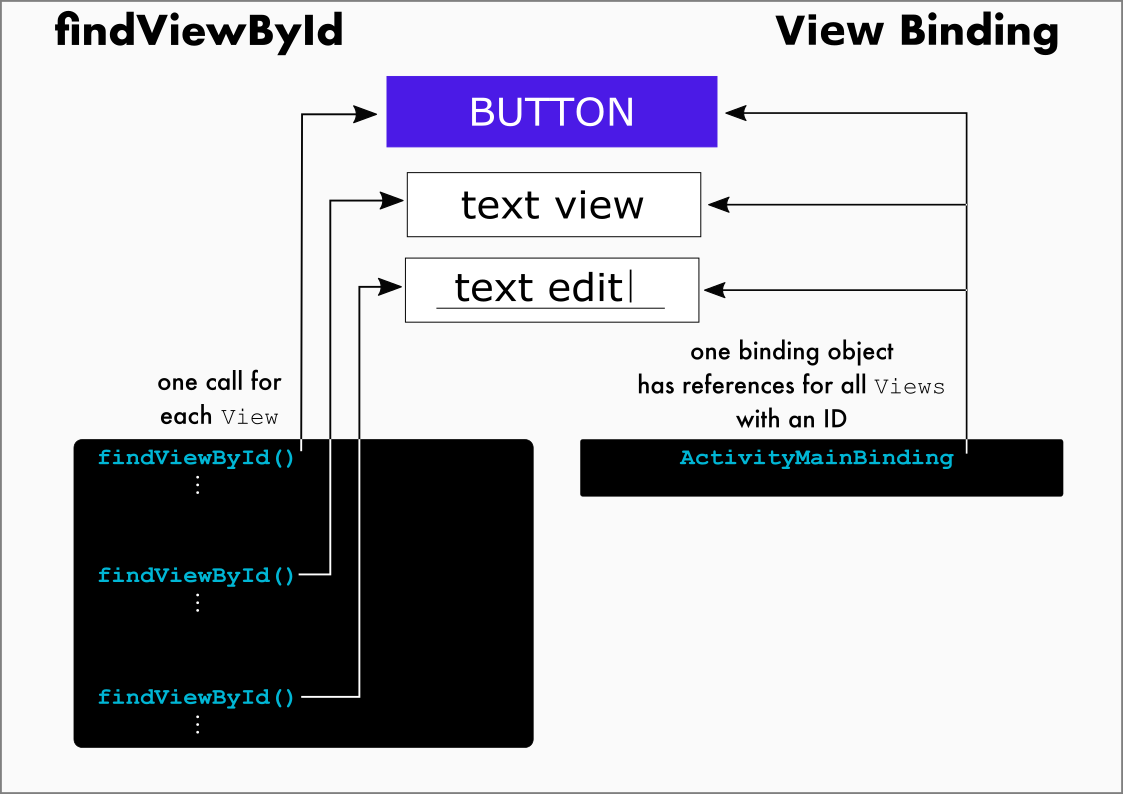
그 결과, 레이아웃 XML 파일에 등록된 뷰 객체를 포함하는 클래스가 자동으로 만들어진다. 즉, 직접 findViewById()를 호출하지 않아도 구현한 클래스가 자동으로 생성되므로 이 클래스를 이용해 뷰를 사용하면 된다.
-
자동으로 만들어지는 클래스의 이름은 레이아웃 XML 파일명을 따른다.
activity_main.xml --> ActivityMainBinding
item_main.xml --> ItemMainBinding
XXXActivity --> ActivityXXXBinding
첫문자를 대문자로 하고, _(언더바)를 제외한 뒤의 단어를 대문자로 만든 뒤 Binding 추가.
- android:id="@+id/visibleBtn"로 id를 등록한 버튼을 바인딩 객체의 visibleBtn 프로퍼티로 접근해 사용이 가능하다.
// in Activity Code..
// 바인딩 객체 획득
val binding = Practice1Binding.inflate(layoutInflater)
// 액티비티 화면 출력
setContentView(binding.root)
binding.visibleBtn.setOnClickListener {
binding.targetView.visibility = View.VISIBLE
}
뷰바인딩 미사용 XML
build.gradle에 뷰바인딩을 이용한다고 선언하면 모든 레이아웃 XML 하나당 바인딩 클래스가 자동으로 생성하는데, 바인딩 클래스가 필요없는 XML은 아래와 같이 제외할 수 있다.
- XML 파일의 루트 태그에 아래와 같이 속성을 추가하면 된다.
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
tools:viewBindingIgnore="true"
//...