참조: https://techblog-history-younghunjo1.tistory.com/262
최소 신장 트리
먼저 서로소 집합 자료구조를 알고오면 좋다.
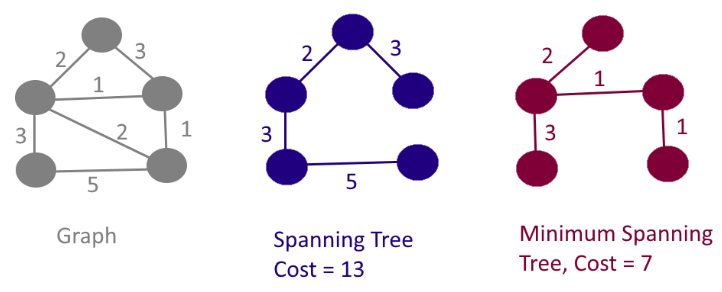
- 신장 트리란, 하나의 그래프가 있을 때 모든 노드를 포함하면서, 즉 모든 노드들 간에 서로 연결은 되어있되 사이클이 존재하지 않는 부분 그래프를 의미한다.
- 즉 최소 신장 트리란, 사이클이 없이 모든 정점이 연결되어 있는 그래프이다.
- 최소 신장 트리 알고리즘에는 크루스칼, 프림 알고리즘이 있는데 여기서는 크루스칼 알고리즘을 소개한다.
크루스칼 알고리즘
동작 과정
- 주어진 모든 간선 정보에 대해 간선 비용이 낮은 순서(오름차순)로 정렬을 수행
- 정렬된 간선 정보를 하나씩 확인하면서 현재의 간선이 노드들 간의 사이클을 발생시키는지 확인
- 만약 사이클이 발생하지 않은 경우, 최소 신장 트리에 포함시키고 사이클이 발생한 경우, 최소 신장 트리에 포함시키지 않음
- 1~3번 과정을 모든 간선 정보에 대해 반복 수행
자세한 동작 과정은 해당 자료에서 참조 가능하다.
코드
import sys
input = sys.stdin.readline
v, e = map(int,input().split())
parent = [None] * (v+1)
for i in range(1, v+1):
parent[i] = i
def FindParent(target):
if parent[target] != target:
parent[target] = FindParent(parent[target])
return parent[target]
def Union(v1, v2):
v1 = FindParent(v1)
v2 = FindParent(v2)
if parent[v1] != parent[v2]:
if v1 > v2:
parent[v1] = v2
else:
parent[v2] = v1
edges = []
totalCost = 0
for _ in range(e):
v1, v2, cost = map(int, input().split())
edges.append((cost, v1, v2))
edges.sort()
for i in range(e):
c, a, b = edges[i]
if FindParent(a) != FindParent(b):
Union(a, b)
totalCost += c
print(totalCost)