HashSet
- Set 인터페이스에서 지원하는 구현 클래스
- 객체 그 자체를 저장한다.
- 순서가 일정하게 유지되지 않는다
- null 요소도 허용한다
- 내부적으로 HashMap을 사용한다.
- 중복을 허용하지 않는다.
중복을 허용하지 않는게 가장 큰 특징이라 할 수 있다.
중복을 걸러내는 과정
HashSet은 객체를 저장하기 전에 먼저 객체의 hashCode()메소드를 호출해서 해시 코드를 얻어낸 다음 저장되어 있는 객체들의 해시 코드와 비교한 뒤 같은 해시 코드가 있다면 다시 equals() 메소드로 두 객체를 비교해서 true가 나오면 동일한 객체로 판단해 중복 저장 하지 않는다.
문자열을 HashSet에 저장할 경우, 같은 문자열을 갖는 String객체는 동일한 객체로 간주되고 다른 문자열을 갖는 String객체는 다른 객체로 간주되는데,
그 이유는 String클래스가 hashCode()와 equals() 메소드를 재정의해서 같은 문자열일 경우 hashCode()의 리턴 값을 같게, equals()의 리턴 값은 true가 나오도록 했기 때문이다.
코드
변수 선언
HashSet<데이터타입> 변수명 = new HashSet<데이터타입>();
- HashSet : Integer형의 HashMap 데이터가 들어간다.
- HashSet : String형의 HashMap 데이터가 들어간다.
HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
HashSet<String> set2 = new HashSet<String>();값 추가
HashSet의 add(value) 메소드를 사용하여 값을 추가한다.
추가되는 값은 HashSet<데이터타입>의 맞는 데이터만 추가해준다.
public class HashSetTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Integer
HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
set.add(1);
set.add(2);
set.add(3);
set.add(1);
// String
HashSet<String> set2 = new HashSet<String>();
set2.add("a");
set2.add("b");
set2.add("c");
set2.add("a");
}
}값 삭제
HashSet의 remove(value) 메소드를 사용하면 원하는 value 값만 삭제된다.
전부 삭제하고 싶은 경우 HashSet의 clear() 메소드를 사용한다.
public class HashSetTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Integer
HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
set.remove(1);
set.clear();
// String
HashSet<String> set2 = new HashSet<String>();
set2.remove("a");
set2.clear();
}
}HashSet의 크기 구하기
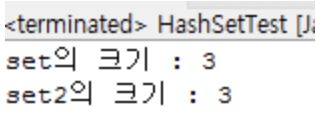
HashSet의 size() 메소드를 사용해 현재 HashSet의 크기를 구할 수 있다.
아래와 같이 중복값이 들어오면 자동으로 제거된다.
public class HashSetTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Integer
HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
set.add(1);
set.add(2);
set.add(3);
set.add(1);
System.out.println("set의 크기 : " + set.size());
// String
HashSet<String> set2 = new HashSet<String>();
set2.add("a");
set2.add("b");
set2.add("c");
set2.add("a");
System.out.println("set2의 크기 : " + set2.size());
}
}
HashSet 데이터 출력하기
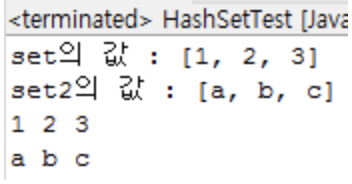
HashSet 변수를 단순히 println으로 출력을 하는 경우 [1, 2, 3], [a, b, c] 형태로 출력된다.
하나의 객체를 가져오고 싶을 경우 Iterator를 사용해서 가져올 수 있다.
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class HashSetTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Integer
HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
set.add(1);
set.add(2);
set.add(3);
set.add(1);
System.out.println("set의 값 : " + set);
// String
HashSet<String> set2 = new HashSet<String>();
set2.add("a");
set2.add("b");
set2.add("c");
set2.add("a");
System.out.println("set2의 값 : " + set2);
// Integer 출력
Iterator iter = set.iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(iter.next() + " ");
}
System.out.println("");
// String 출력
Iterator iter2 = set2.iterator();
while(iter2.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(iter2.next() + " ");
}
}
}
HashSet 검색하기
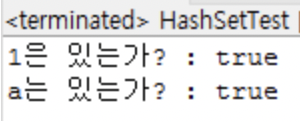
Hashet 내부의 원하는 값을 검색하는 경우 contains(value) 메소드를 사용한다.
값이 존재한다면 true, 값이 없다면 false를 return한다.
public class HashSetTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Integer
HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
set.add(1);
set.add(2);
set.add(3);
set.add(1);
System.out.println("1은 있는가? : " + set.contains(1));
// String
HashSet<String> set2 = new HashSet<String>();
set2.add("a");
set2.add("b");
set2.add("c");
set2.add("a");
System.out.println("a는 있는가? : " + set2.contains("a"));
}
}
참고
https://crazykim2.tistory.com/474
https://siahn95.tistory.com/96
