Math class?
java.lang 패키지에 포함된 클래스.
수학과 관련된 일련의 작업들을 처리할 수 있는 클래스.
Math 클래스의 다양한 메소드들은 전부 static으로 구현되어있으므로 따로 객체를 생성하지않고 사용가능하다.
-
abs()
인자로 넘긴 데이터의 절댓값을 반환 -
random()
0.0~1.0 사이의 임의의 double형 데이터 생성하여 반환 -
max()
전달된 데이터 중 더 큰 수를 반환
static int max(int a, int b)
static long max(long a, long b)
static double max(double a, double b)
static float max(float a, float b) -
min()
전달된 데이터 중 더 작은 수를 반환
static int min(int a, int b)
static long min(long a, long b)
static double min(double a, double b)
static float min(float a, float b) -
static long round(double a)
인수로 전달받은 실수를 소수점 첫번째 자리에서 반올림한 결과 반환 -
static double floor(double a)
전달받은 실수보다 작은 정수 중 가장 큰 정수 반환(버림) -
static double ceil(double a)
전달받은 실수보다 큰 정수 중 가장 작은 정수 반환(올림) -
static double pow(double a, double b)
a와 b에 대해서 제곱연산 수행 : a^b -
static double sqrt(double a)
전달받은 값의 제곱근에 해당하는 값 반환 -
static int subtractExact(int a, int b) -> long타입의 파라미터, 리턴타입도 가능
전달 된 인수값의 차이를 반환 : b-a
주어진 수(M)에서 소수점 n번째자리까지 나타내고싶을 때
소수점 둘째자리 혹은 소수점 셋째자리 ... 그 이하의 자리에서 반올림하려면 어떻게 해야할까?
- String.format() 사용
String.format("%x.nf", M)
x : 전체 자리수 : 소수점 앞자리 수 + 소수점(.) 한자리 + 소수점 뒷자리수 -> 전체 자리수에는 소수점도 포함!
n : 소수점 n+1의 자리를 반올림하여 소수점 n번째 자리까지 표시
소수점 앞자리의 빈자리는 공백, 뒷자리의 빈자리는 0으로 채움
예제코드
public class formatPrac {
public static void main(String[] args) {
float n = 123.123456789f;
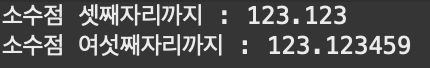
System.out.println("소수점 셋째자리까지 : " + String.format("%.3f", n));
System.out.println("소수점 여섯째자리까지 : " + String.format("%.6f", n));
}
}결과
- Math.round() 사용
M * 10^n을 한 후 round()를 적용시키고, 결과값을 다시 10^n.0으로 나누어준다.예를들어, M = 33.777 n=2일 경우
- 33.777*100 = 3377.7
- round()적용 : 3378
- 3378 / 100.0 = 33.78
예제 코드
import java.lang.Math;
public class roundPrac {
public static void main(String[] args) {
float n = 123.123456789f;
System.out.println("round() : " + Math.round(n));
System.out.println("round() 이용해 소수점 두번째 자리수까지 표현 : " + Math.round(n*100.0)/100.0);
System.out.println("round() 이용해 소수점 번째 자리수까지 표현: " + Math.round(n*10000.0) /10000.0);
}
}결과

Math.round()와 String.format()의 속도비교
예제 코드
public class formatPrac {
public static void main(String[] args) {
float n = 123.123456789f;
float roundResult;
String formatResult;
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i=0; i<10000; i++) {
formatResult = String.format("%.0f" ,n);
}
long endFormat = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(endFormat - startTime + "(ms)");
for(int i=0; i<10000; i++) {
roundResult = Math.round(n);
}
long endRound = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(endRound - endFormat + "(ms)");
}
}결과
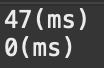
format()은 47m, round()는 0ms로 round()가 더 빠른 것을 알 수 있다.
아마 format()은 형변환이 들어가기때문에, 더 느린것같다.
대용량 계산을 수행할 경우에는 무조건 round()방식이 더 좋을것같다.

