데이터를 주고받을 때, Json 형식을 많이 사용한다.
Java에서 org.json 라이브러리를 이용하여 JSON 데이터를 다룰 수 있다.
이 라이브러리에서 제공하는 JSONObject, JSONArray 클래스는 JSON 데이터를 갖고 있고, JSON 형식의 문자열로 출력할 수 있습니다. 또한 JSON 문자열을 파일로 저장할 수도 있다.
이 글에서는 JSON 라이브러리 사용 방법을 소개한다.
- JSONObject 객체 생성
- HashMap으로 JSONObject 생성
- JSON 문자열로 JSONObject 객체 생성
- POJO로 JSONObject 객체 생성
- JSONArray 객체 생성
- List로 JSONArray 객체 생성
- Java에서 JSON을 파일로 저장
Json
JSON 파일은 다음과 같이 key-value 형태로 데이터를 갖고 있습니다.
{
"pageInfo": {
"pageName": "abc",
"pagePic": "http://example.com/content.jpg"
},
"posts": [
{
"post_id": "123456789012_123456789012",
"message": "Sounds cool. Can't wait to see it!",
"likesCount": "2",
}
]
}JSON 라이브러리 의존성
org.json은 Java의 JSON 라이브러리이다.
gradle 프로젝트에서 다음과 같이 build.gradle에 의존성을 추가할 수 있다.
dependencies {
...
implementation group: 'org.json', name: 'json', version: '20090211'
}JsonObject
Json 객체 : JSON에서 key-value 쌍으로 데이터를 표현하는 객체입니다.
- Json이 아닌 다른 객체(주로 String)를 Json객체로 바꿔주거나, Json객체를 새로 만드는 역할
get("key")로 값을 가져올 수 있다.
데이터 입력 : put(key, value)
toString()은 JSON 객체를 문자열 형태로 반환한다.
JSONObject jo = new JSONObject();
jo.put("name", "benjamin");
jo.put("city", "New York");
System.out.println("jo : " + jo); // System.out.println(jo.toString()); 와 동일<결과>

1. HashMap으로 JSONObject 생성
HashMap에 저장된 데이터를 JSON으로 변환할 수 있다.
다음과 같이 HashMap 객체를 JSONObject 생성자의 인자로 전달하면 된다.
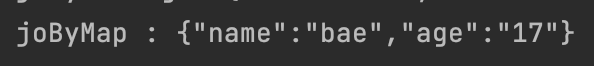
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("name", "bae");
map.put("age", "17");
JSONObject joByMap = new JSONObject(map);
System.out.println("joByMap : " + joByMap);<결과>
2. JSON 문자열로 JSONObject 객체 생성
JSON 문자열로 JSONObject 객체를 생성할 수 있습니다. 이렇게 생성된 JSONObject에 데이터를 추가할 수도 있다.
String str = "{\"read\" : true, \"book\" : \"happy\"}";
JSONObject joByString = new JSONObject(str);
System.out.println("joByString : " + joByString + ", book : " + joByString.get("book"));
Iterator<String> iter = joByString.keys();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
String key = iter.next();
System.out.print(key+ ", ");
}
System.out.println();
joByString.put("writer", "davi");
System.out.println("joByString After Add : " + joByString);<결과>

3. POJO로 JSONObject 객체 생성
POJO(Plain Old Java Object)는 아래 예제의 Customer 클래스와 같이, 단순히 get, set 메소드들만 있는 자바 클래스를 의미한다.
JSONObject는 POJO 객체를 인자로 받으며, 여기서 key와 value를 추출하여 JSON 데이터로 추가한다.
public class JsonExample4 {
public static class Customer {
private String name;
private String city;
Customer(String name, String city) {
this.name = name;
this.city = city;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
public String getCity() {
return city;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
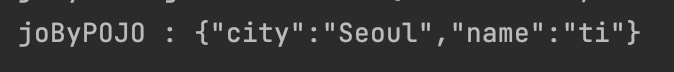
public static void main(String[] args) throws JSONException {
Customer customer = new Customer("Jone", "Seoul");
JSONObject jo = new JSONObject(customer);
System.out.println(jo);
}
}<결과>
JSONArray
JSON은 key-value 형태로 데이터를 갖고 있는데, 여기서 value는 아래와 같이 Array 타입이 될 수 있다.
"friends":["Harry","Sam"]
다음 예제와 같이 JSONArray에 put(value)로 0개 이상의 데이터를 배열에 추가할 수 있다.
그리고 JSONArray는 JSONObject의 value가 되도록 다시 추가할 수 있다.
JSONArray ja = new JSONArray();
ja.put("harry");
ja.put("Sam");
JSONObject jo = new JSONObject();
jo.put("feeling", "sad");
jo.put("age", 17);
jo.put("names", ja);
System.out.println(jo);
반대로, JSONArray안에 JSONObject를 넣을수도 있다.
JSONObject jo1 = new JSONObject();
jo1.put("test1", "testValue1");
JSONObject jo2 = new JSONObject();
jo2.put("test2", "testValue2");
JSONArray jaByJSONObject = new JSONArray();
jaByJSONObject.put(jo1);
jaByJSONObject.put(jo2);
System.out.println("jaByJSONObject : " + jaByJSONObject);
1. List로 JSONArray 객체 생성
JSONArray 생성자는 인자로 List를 받고, List의 모든 데이터를 JSONArray에 추가한다.
List<String> namesList = new ArrayList<>();
namesList.add("Jam");
namesList.add("Miky");
JSONArray jaByList = new JSONArray(namesList);
JSONObject joByList = new JSONObject();
joByList.put("feeling", "soso");
joByList.put("age", 20);
joByList.put("names", jaByList);
System.out.println(joByList);<결과>

JSON을 파일로 저장
Java의 JSON 객체들이 갖고 있는 데이터를 JSON 형식의 문자열로 변환하고 파일로 저장하는 예제이다.
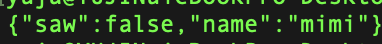
JSONObject jo = new JSONObject();
jo.put("saw", false);
jo.put("name", "mimi");
String strOfJo = jo.toString();
File jsonFile = new File("${경로}");
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(jsonFile));
bw.write(strOfJo);
bw.close();파일을 저장한 경로에 가서 해당 파일을 보면 잘 저장된 것을 볼 수 있다.
<결과>
json 파싱(parsing)하기
JsonParser 사용
JsonParser를 사용하기 위해서는 아래 라이브러리를 의존해야한다.
implementation 'com.googlecode.json-simple:json-simple:1.1.1'
그럼 이후 JsonParser를 사용하여 다음과 같이 파싱할 수 있다.
참고로, 이전에
org.json을 의존해서 사용하고있었다면, json-simple을 사용하는 코드에서 org.json을 import해서 사용 할 경우(ex. JSONObject, JSONArray... 등의 사용을 위해) 빌드 에러가 발생한다.
그러므로 JsonParser를 사용해야하는 경우, JSONObject.. 이런것도 json-simple으로 사용을 통일하라. (import org.json.JSONObject;코드를 지우라는 의미)
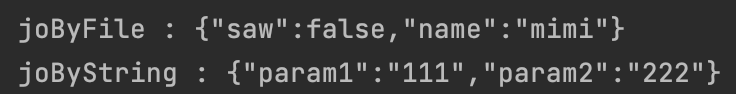
// File(.json) To Json
Reader reader = new FileReader("${경로}");
JSONParser jsonParser = new JSONParser();
Object obj = jsonParser.parse(reader); // 우선, file을 Object로 만들기
JSONObject joByFile = (JSONObject) obj;
System.out.println("joByFile : " + joByFile);
// Json 형태의 String To Json
String jsonData = "{\"param1\":\"111\",\"param2\":\"222\"}";
JSONParser parser = new JSONParser();
Object o = parser.parse(jsonData);
JSONObject joByString = (JSONObject) o;
System.out.println("joByString : " + joByString);(reader의 경로는 'JSON을 파일로 저장'의 예시에서 만들었던 경로를 사용했습니다)
<결과>