지금까지는 소켓을 생성해서 별 다른 조작 없이 바로 사용함
(기본적으로 설정되어 있는 소켓의 특성을 그대로 받아들이겠다는 의미가 됨)
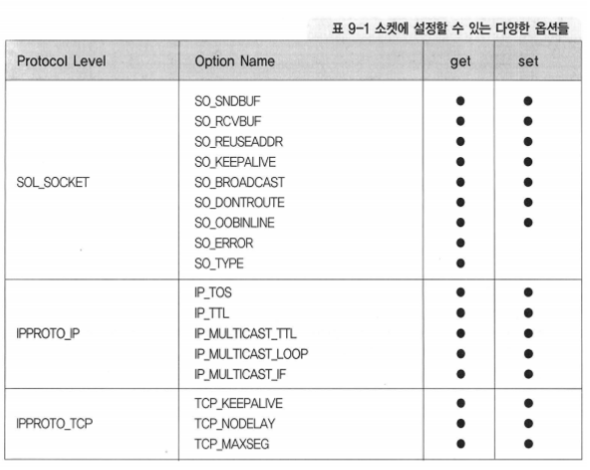
소켓의 특성을 변경하는 옵션의 종류들은 계층별로 분류됨
[Protocol Level]
- SOL_SOCKET : 소켓에 대한 가장 일반적인 옵션들
- IPPROTO_IP : IP 프로토콜에 관련된 사항
- IPPROTO_TCP : TCP 프로토콜에 관련된 사항
대부분의 옵션은 설정 상태를 참조해 볼 수도 변경할 수도 있지만 일부 옵션은 참조만 가능하거나, 설정 상태를 변경하는 것만 가능하기도 함
[설정 상태 정보를 가져오는 함수]
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
int getsockopt(int sock, int level, int optname, void* optval, socklen_t* optlen);
// 성공 시 0, 실패 시 -1 리턴
// sock : 설정 상태를 확인해 보고 싶은 소켓의 파일 디스크립터를 인자로 전달함
// level : 확인할 옵션의 프로토콜 레벨을 인자로 전달함
// optname : 확인할 옵션의 이름을 전달함
// optval : 확인 결과를 저장할 버퍼를 가리키는 포인터를 전달함
// optlen : optval 포인터가 가리키는 버퍼의 크기를 전달함
// 함수의 호출이 완료되면, 전달된 포인터가 가리키는 변수에는 버퍼에 저장된 확인 결과의 길이가 바이트 단위로 저장됨[옵션을 변경하는 함수]
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
int setsockopt(int sock, int level, int optname, const void* optval, socklen_t optlen);
// 성공 시 0, 실패 시 -1 리턴
// sock : 설정 상태를 변경하고자 하는 소켓의 파일 디스크립터를 인자로 전달함
// level : 변경할 오션의 프로토콜 레벨을 인자로 전달함
// optname : 변경할 옵션의 이름을 전달함
// optval : 변경할 옵션의 값을 저장한 버퍼의 포인터를 전달함
// optlen : 전달하는 옵션의 바이트 단위 길이를 전달함[소켓을 생성하고 나서 타입 정보를 얻어내기]
- 프로토콜 레벨 : SOL_SOCKET
- 확인할 옵션의 이름 : SO_TYPE
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
void error_handling(char* message);
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
int tcp_sock, udp_sock;
int sock_type = -1;
socklen_t optlen;
int state;
optlen = sizeof(sock_type);
tcp_sock = socket(PF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
udp_sock = socket(PF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);
printf("SOCK_STREAM : %d \n", SOCK_STREAM);
printf("SOCK_DGRAM : %d \n", SOCK_DGRAM);
state = getsockopt(tcp_sock, SOL_SOCKET, SO_TYPE, &sock_type, &optlen);
if(state)
error_handling("getsocket() error!");
printf("첫 번째 소켓의 타입은 %d \n", sock_type);
state = getsockopt(udp_sock, SOL_SOCKET, SO_TYPE, &sock_type, &optlen);
if(state)
error_handling("getsocket() error!");
printf("두 번째 소켓의 타입은 %d \n", sock_type);
return 0;
}
void error_handling(char* message)
{
fputs(message, stderr);
fputc('\n', stderr);
exit(1);
}[실행 결과]
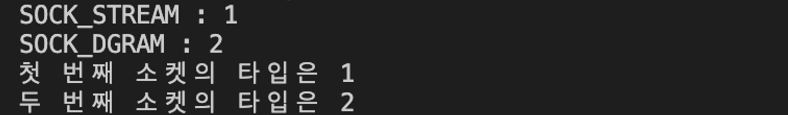
SO_TYPE 옵션은 상태 확인만 가능하고 변경은 불가능함
→ 즉, 소켓의 타입은 소켓 생성 시에 결정되면 변경할 수 없음
[소켓 생성 시 만들어지는 버퍼의 크기 확인하기]
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
void error_handling(char* message);
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
int sock;
int snd_buf;
int rcv_buf;
int state;
socklen_t len;
sock = socket(PF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
len = sizeof(snd_buf);
state = getsockopt(sock, SOL_SOCKET, SO_SNDBUF, &snd_buf, &len);
if(state)
error_handling("getsockopt() error");
len = sizeof(rcv_buf);
state = getsockopt(sock, SOL_SOCKET, SO_RCVBUF, &rcv_buf, &len);
if(state)
error_handling("getsockopt() error");
printf("데이터 입력을 위한 소켓의 버퍼 크기 : %d \n", rcv_buf);
printf("데이터 출력을 위한 소켓의 버퍼 크기 : %d \n", snd_buf);
return 0;
}
void error_handling(char* message)
{
fputs(message, stderr);
fputc('\n', stderr);
exit(1);
}[실행 결과]


