모든 내용의 출처는 엘리스
00
스코프(scope): 코드가 현재 실행되는 환경, 맥락을 의미하는 단어
실행 컨텍스트(execute context)에 포함되는 것: 스코프 체인, this 포인터, variable objects
01
this
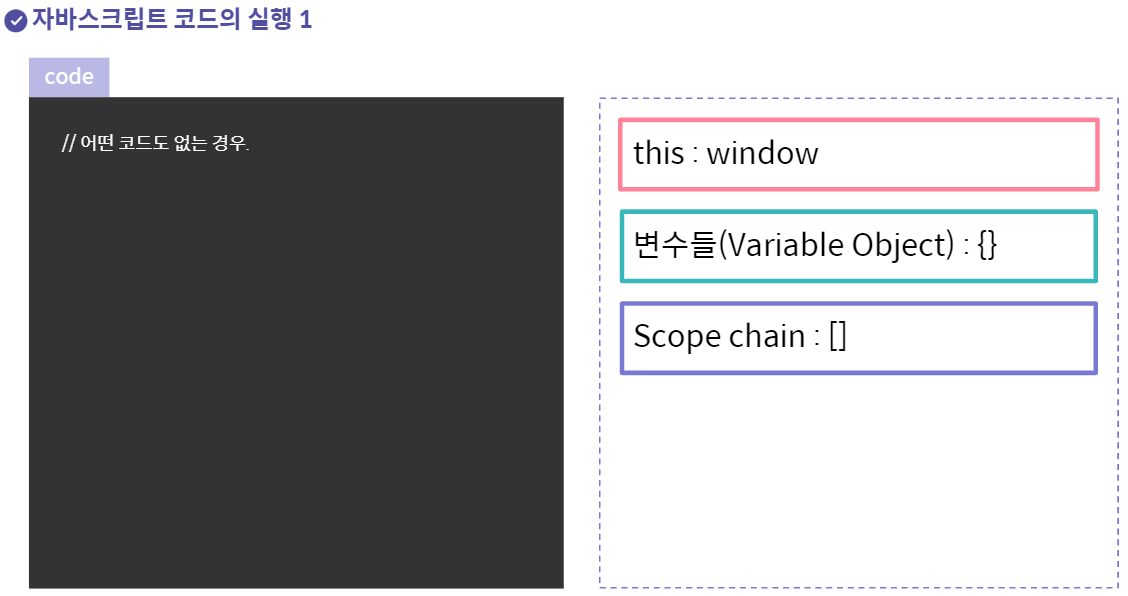
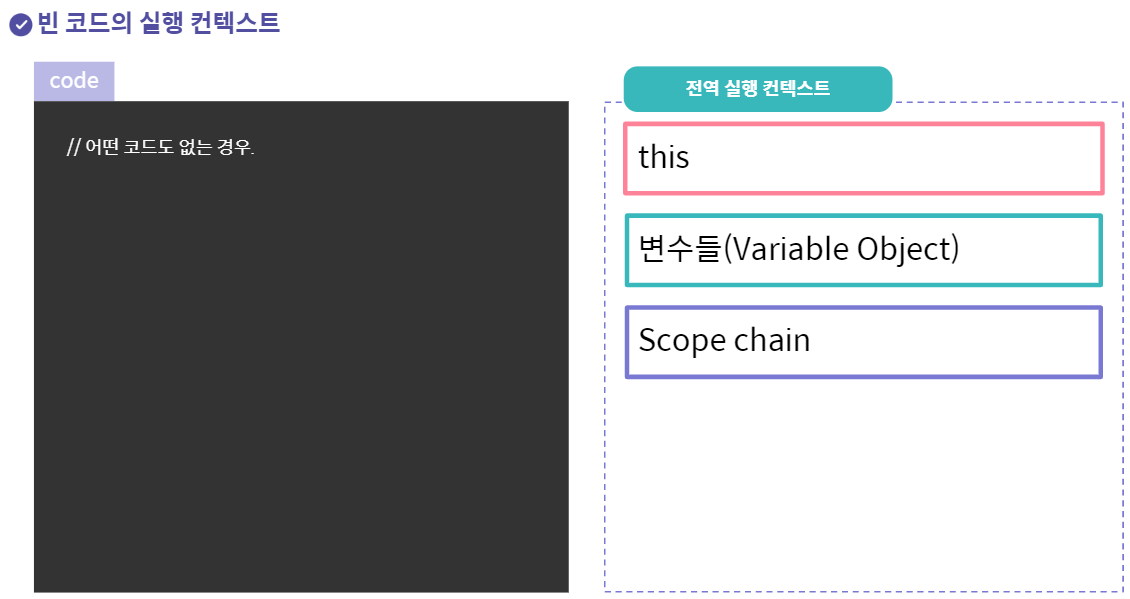
아무런 코드가 없을경우 this는 window를 가리킨다
자바스크립트 엔진은 코드가 없어도 실행환경(실행 컨텍스트)을 초기화한다.
스코프는 코드가 현재 실행되는 환경, 맥락(context)를 의미한다.
this 포인터, 스코프에 저장된 변수들, 스코프 체인 등이 환경에 포함도니다.
this 포인터의 경우 글로벌 스코프에서는 window를 가리킨다.
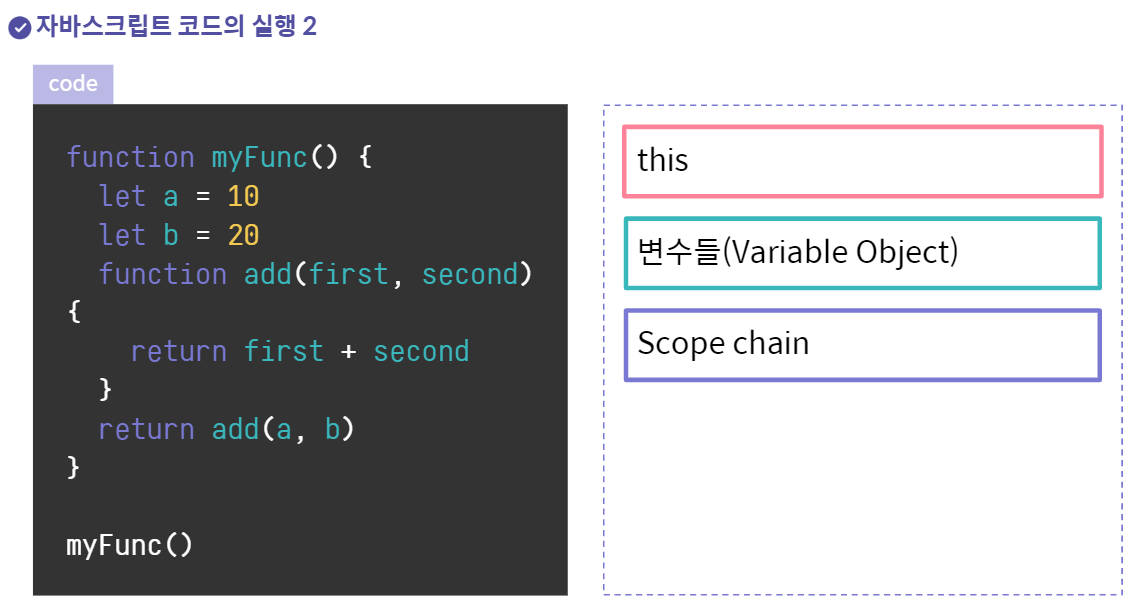
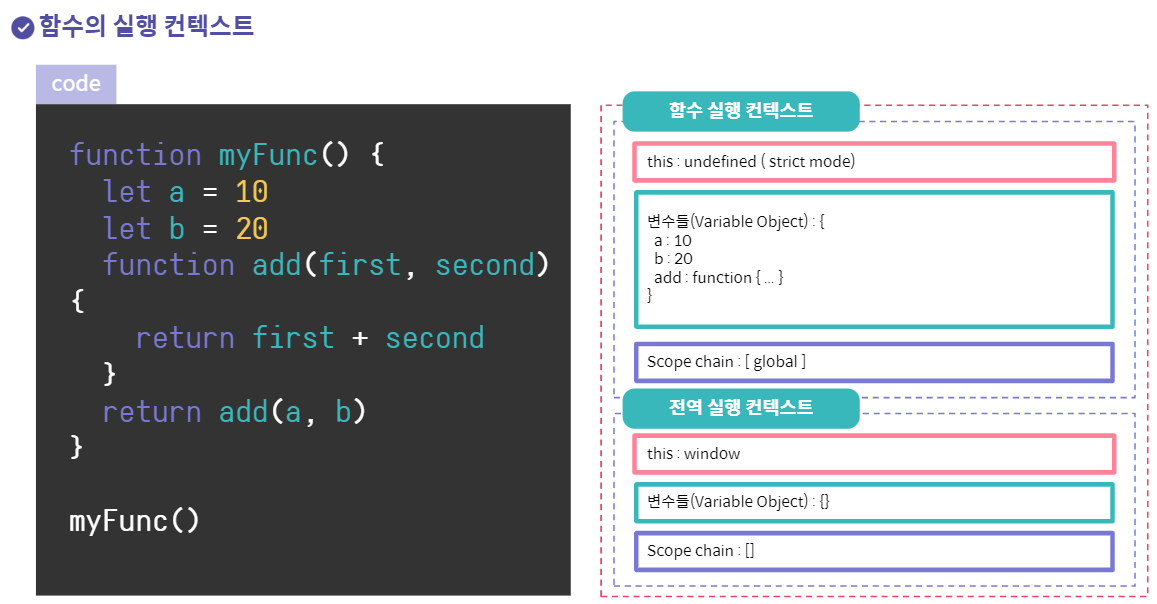
function myFunc() {
let a = 10;
let b = 20;
function add(first, second) {
return first+second
}
return add(a,b);
}
myFunc();
myFunc의 스코프
add()의 스코프
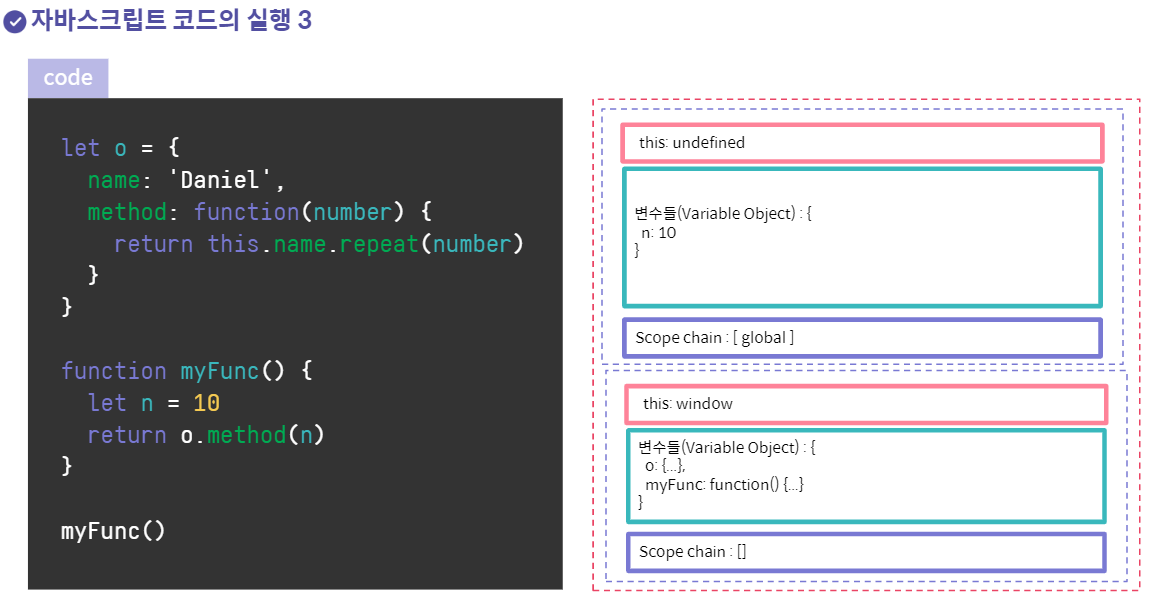
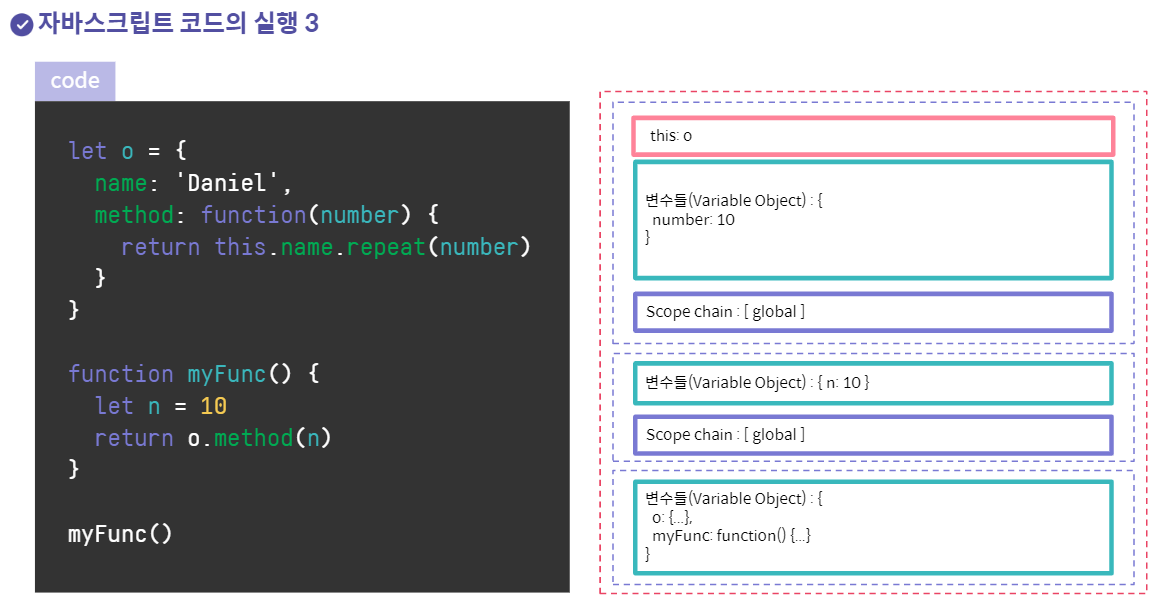
위: myFunc(), 아래: window
위: method funciton
객체의 메서드의 경우 메서드 환경의 this는 해당 객체를 가리키게 된다.
하지만 this가 가리키는 것은 환경에 따라 변할 수 있다.
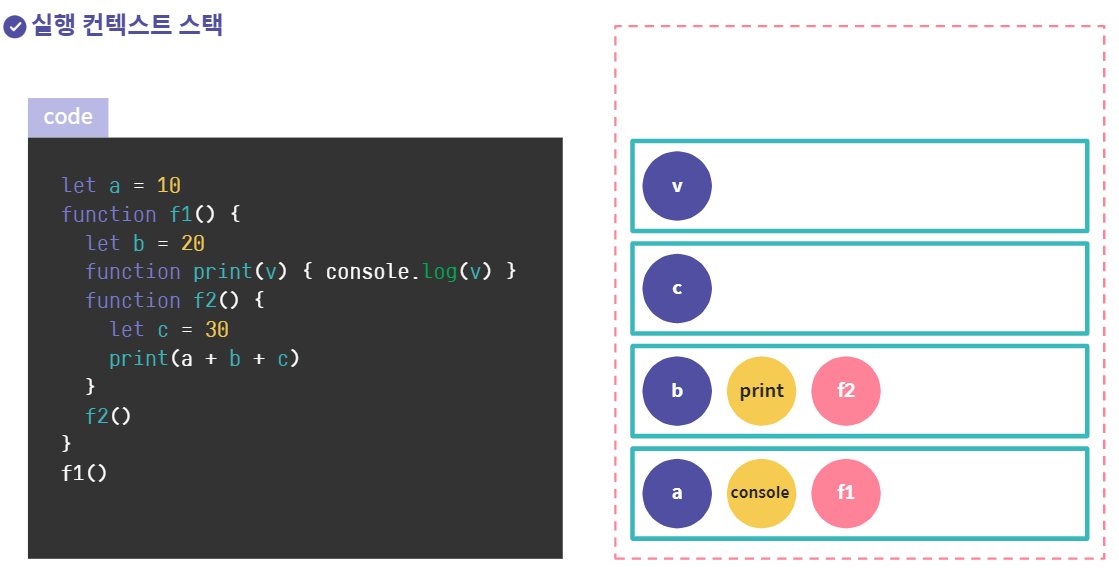
실행컨텍스트(Execution context)
실행컨텍스트: 자바스크립트 코드가 실행되는 환경
코드에서 참조하는 변수, 객체(함수 포함), this 등에 대한 레퍼런스가 있다.
실행 컨텍스트는 전역에서 시작해 함수가 호출될때 스택에 쌓이게 된다.
자바스크립트가 실행될때 전역 실행 컨텍스트(global)가 만들어진다.
함수가 실행될때 함수 실행 컨텍스트 (function)가 만들어진다.
this가 가리키는 것
함수 호출되는 상황 4가지
- 함수 호출 - 함수를 직접 호출한다
- 메서드 호출 - 객체의 메서드를 호출한다.
- 생성자 호출 - 생성자 함수를 호출한다.
- 간접 호출 - call, apply 등으로 함수를 간접 호출한다.
그 외 콜백 함수의 호출이 있다.
콜백 함수는 특정 동작 이후 불려지는 함수이다.
보통 다른 함수의 인자로 보내지는 함수를 의미한다.
함수의 호출 환경에 따라 this는 동적으로 셋팅된다.
this가 환경에 따라 바뀌는 것을 동적 바인딩(dynamic binding)이라고 한다.
bind, apply, call 등으로 this가 가리키는 것을 조작할 수 있다.
최상단 스코프의 실행 컨텍스트는 전역이다.
setTimeout으로 함수의 실행 환경을 바꾼다.
여기서 내이름은 undefined 인 이유: 그 전 캡처를 보면 객체 내부의 function은 원래 this가 객체를가리키지만 setTimeout에서 this를 전역으로 바꿔버린다. global에는 name이 없으므로 undefined
const myCar = {
name: 'hola',
oil: 'gasoline',
getname: function() {
return this.name;},
getOil: function() {
reuturn this.oil;}
}const toy = {
brand: 'lego',
type: 'robot',
getBrand: function(){return this.brand},
getType: function(){return this.type},
changeBrand: function(newBrand){this.brand = newBrand},
changeType: function(newType){this.type = newType}
}function hello(arr) {
let newstr = ``;
arr.forEach(function (e) {
newstr += `<li>${e.name}</li>`;
}
return newstr;
}let height = people.filter(e => e.height >= 175);화살표 함수 vs. 일반 함수
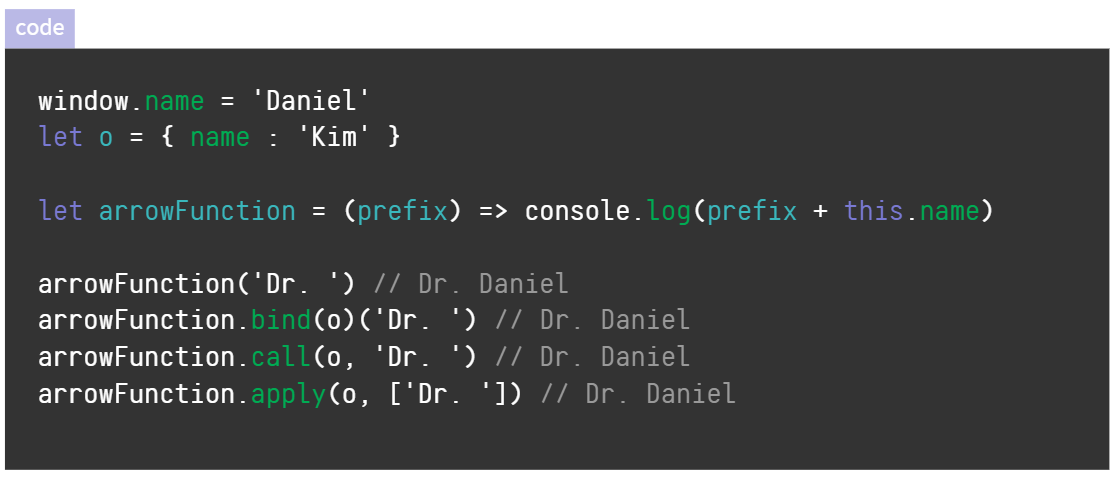
- 화살표 함수의 this는 호출된 함수를 둘러싼 실행 컨텍스트를 가리킨다.
- 일반 함수의 this는 새롭게 생성된 실행 컨텍스트를 가리킨다.
화살표 함수의 this는 정해지면 바꿀 수 없다.
can, bind, apply를 사용해도 안바뀜
setTimeout 등 this가 바뀌는 상황에서 유용하다.
closure
- 일급 객체란, 다른 변수처럼 대상을 다룰 수 있는 것
- 자바스크립트에서 함수는 일급 객체이다
- 즉 자바스크립트에서 함수는 변수처럼 다룰 수 있다.
- 자바스크립트의 클로저는 함수의 일급 객체 성질을 이용한다.
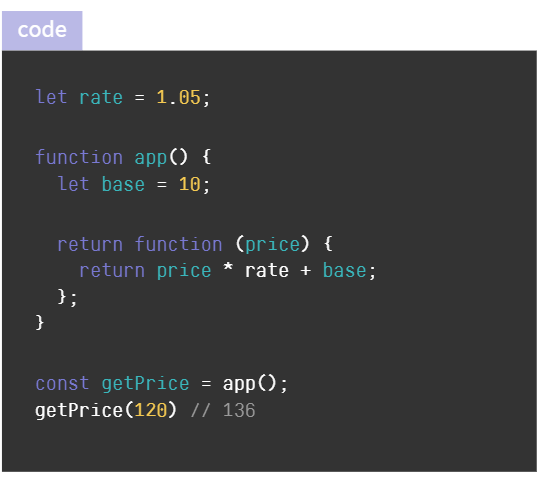
- 함수가 생성될 때 함수내부에서 사용되는 변수들이 외부에 존재하는 경우 그 변수들은 함수의 스코프에 저장된다.
- 함수와 함수가 사용하는 변수들을 저장한 공간을 클로저라고 한다.
- base는 app 함수 내부, rate는 app 함수 외부의 스코프에 존재한다.
함수가 참조하는 변수는 실행 시점에 실행컨텍스트에 의해 스코프가 결정된다.
Rest Operator
- 함수의 인자, 배열, 객체 중 나머지 값을 묶어 사용하도록 한다.
- 함수의 인자 중 나머지를 가리킨다.
- 배열의 나머지 인자를 가리킨다.
- 객체의 나머지 필드를 가리킨다.
function findMin(...rest) {
return rest.reduce((a, b) =>
a < b ? a : b)
}
findMin(7, 3, 5, 2, 4, 1) // 1- 함수 인자 rest operator는 인자들을 배열로 묶는다.
- rest에는 숫자들이 배열로 담긴다.
- reduce 함수로 min 값을 리턴한다.
const o = {
name: "Daniel",
age: 23,
address: "Street",
job: "Software Engineer",
};
const {age, name, ...rest} = o;
findSamePerson(age, name);- 객체의 rest operator는 지정된 필드 외의 나머지필드를 객체로 묶는다.
age, name을 제외한 나머지 필드는 rest 변수로 할당된다.
function sumArray(sum, arr) {
if(arr.length === 0) return sum;
const [head, ...tail] = arr;
return sumArray(sum + head, tail);
}
sumArray(0, [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]);- 배열의 rest operator는 나머지 인자를 다시 배열로 묶는다.
- sumArray의 tail변수는 첫번째 원소 head를 제외한 나머지 값들을 다시 배열로 묶는다.
- tail은 하나씩 줄어들며 길이가 0이 되면 합을 반환한다.
Spread Operator
- 묶인 배열 혹은 객체를 각각의 필드로 변환한다.
- 객체는 또 다른 객체로의 spread를 지원한다.
- 배열은 또 다른 배열의 인자, 함수의 인자로의 spread를 지원한다.