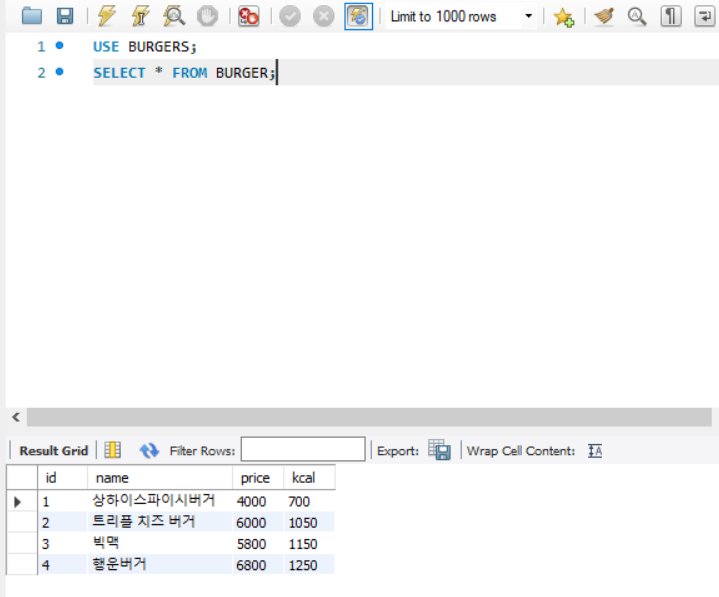
1. JDBC를 이용하여 MySQL의 BURGERS 테이블을 조회해보자.
JDBC 실행 순서별 설명
- Class.forName() 메서드를 이용해서 JDBC 드라이버를 로딩
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");- 데이터 베이스 연결
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/BURGERS?serverTimezone=UTC"; //DB연결 (로컬호스트 뒤에 연결 할 DB명)
String user = "아이디"; //mysql 워크벤치 아이디
String pass = "비밀번호"; //mysql 워크벤치 비밀번호- Connection 객체 생성으로 계정 연결
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, pass);- DB와 연결된 con 객체로 부터 Statement 객체 획득.
Statement stmt = con.createStatement();- SQL문 실행 및 결과처리
ResultSet result = stmt.executeQuery("select * from BURGER");
while(result.next()) {
// 컬럼 이름을 이용해서 데이터를 뽑는게 더 안전하다.
// getString("컬럼이름")
int id = Integer.parseInt(result.getString("id"));
String name = result.getString("name");
int price = Integer.parseInt(result.getString("price"));
int kcal = Integer.parseInt(result.getString("kcal"));
System.out.println("번호:" + id);
System.out.println("메뉴명:" + name);
System.out.println("가격:" + price);
System.out.println("칼로리:" + kcal);
System.out.println();
}- JDBC 연결 과정에서 필요했던 객체들을 close
public static void close(Connection conn) {
if(conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void close(Statement conn) {
if(conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void close(PreparedStatement conn) {
if(conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void close(ResultSet rs) {
if (rs != null) { try { rs.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
}전체 코드
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class dbtest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("MySQL연결");
// 8.x 버전
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); // Class.forName() 메서드를 이용해서 JDBC 드라이버를 로딩
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/BURGERS?serverTimezone=UTC"; //DB연결
String user = "아이디"; //mysql 워크벤치 아이디
String pass = "비밀번호"; //mysql 워크벤치 비밀번호
// 데이터베이스 실제 연결을 도와주는 클래스
// Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, pass);
try {
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, pass);
if(con != null) {
System.out.println("DB연결 성공!");
}
// //DB와 연결된 conn 객체로 부터 Statement 객체 획득.
// //내가 데이터베이스에게 질의를 할 수 있다.
// Statement stmt = con.createStatement();
//
Statement stmt = con.createStatement(); //DB와 연결된 con 객체로 부터 Statement 객체 획득.
//조회 select
// 쿼리문이 데이터를 가지고 온다. 객체 형식으로
// next() 다음 데이터가 있으면 true, 없으면 false
ResultSet result = stmt.executeQuery("select * from BURGER");
while(result.next()) {
// 컬럼 이름을 이용해서 데이터를 뽑는게 더 안전하다.
// getString("컬럼이름")
int id = Integer.parseInt(result.getString("id"));
String name = result.getString("name");
int price = Integer.parseInt(result.getString("price"));
int kcal = Integer.parseInt(result.getString("kcal"));
System.out.println("번호:" + id);
System.out.println("메뉴명:" + name);
System.out.println("가격:" + price);
System.out.println("칼로리:" + kcal);
System.out.println();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("연결 에러");
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 에러");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 데이터베이스 작업에 사용한 객체를 닫는 메서드
public static void close(Connection conn) {
if(conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void close(Statement conn) {
if(conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void close(PreparedStatement conn) {
if(conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void close(ResultSet rs) {
if (rs != null) { try { rs.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
}
}
실행 결과
MySQL의 BURGER 테이블
JDBC로 BURGER 테이블 불러오기 성공
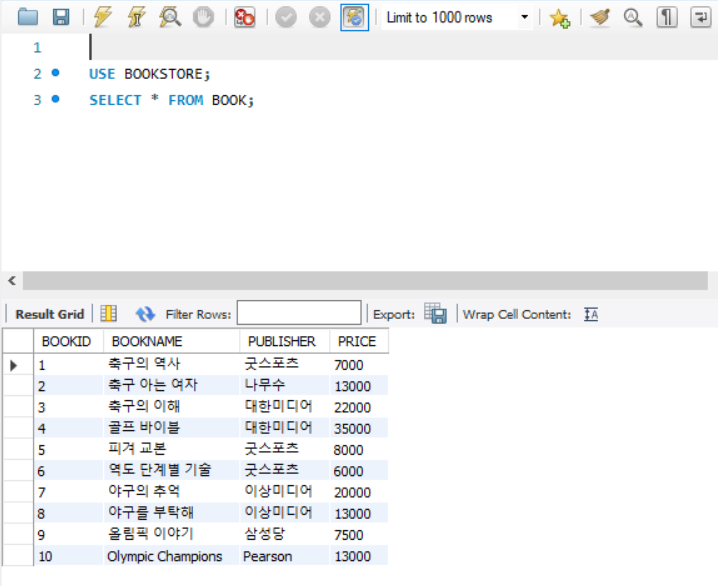
2. JDBC를 이용하여 MySQL의 BOOKSTORE 테이블을 조회해보자.
전체 코드
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class dbtest3
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("MySQL 연결");
// - Class.forName() 메서드를 이용해서 JDBC 드라이버를 로딩
// 8.x 버전
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); // Class.forName() 메서드를 이용해서 JDBC 드라이버를 로딩
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/BOOKSTORE?serverTimezone=UTC"; //DB연결
String user = "아이디"; //mysql 워크벤치 아이디
String pass = "비밀번호"; //mysql 워크벤치 비밀번호
// 데이터베이스 실제 연결을 도와주는 클래스
// Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, pass);
try {
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, pass);
if(con != null) {
System.out.println("DB연결 성공!");
}
// //DB와 연결된 conn 객체로 부터 Statement 객체 획득.
// //내가 데이터베이스에게 질의를 할 수 있다.
// Statement stmt = con.createStatement();
//
Statement stmt = con.createStatement(); //DB와 연결된 con 객체로 부터 Statement 객체 획득.
//조회 select
// 쿼리문이 데이터를 가지고 온다. 객체 형식으로
// next() 다음 데이터가 있으면 true, 없으면 false
ResultSet result = stmt.executeQuery("select * from BOOK");
while(result.next()) {
// 컬럼 이름을 이용해서 데이터를 뽑는게 더 안전하다.
// getString("컬럼이름")
int BOOKID = Integer.parseInt(result.getString("BOOKID"));
String BOOKNAME = result.getString("BOOKNAME");
String PUBLISHER = result.getString("PUBLISHER");
int PRICE = Integer.parseInt(result.getString("PRICE"));
System.out.println("BOOKID:" + BOOKID);
System.out.println("BOOKNAME:" + BOOKNAME);
System.out.println("PUBLISHER:" + PUBLISHER);
System.out.println("PRICE :" + PRICE );
System.out.println();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("연결 에러");
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 에러");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 데이터베이스 작업에 사용한 객체를 닫는 메서드
public static void close(Connection conn) {
if(conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void close(Statement conn) {
if(conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void close(PreparedStatement conn) {
if(conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void close(ResultSet rs) {
if (rs != null) { try { rs.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
}
}
실행 결과
MySQL의 BOOK 테이블
JDBC로 BOOK 테이블 불러오기 성공