빈 스코프
- 번역 그대로 빈이 존재할 수 있는 범위를 뜻함
스코프 종류
- 싱글톤: 기본 스코프, 스프링 컨테이너의 시작과 종료까지 유지되는 가장 넓은 범위의 스코프이다.
- 프로토타입: 스프링 컨테이너는 프로토타입 빈의 생성과 의존관계 주입까지만 관여하고 더는 관리하지 않는 매우 짧은 범위의 스코프이다.
- 웹 관련 스코프
- request: 웹 요청이 들어오고 나갈때 까지 유지되는 스코프이다.
- session: 웹 세션이 생성되고 종료될 때 까지 유지되는 스코프이다.
- application : 웹의 서블릿 컨텍스트와 같은 범위로 유지되는 스코프이다.
싱글톤
- 스프링 컨테이너의 시작과 종료까지 함께함
- 빈을 가져올 때 같은 빈을 가져옴
- Test
package hello.core.scope;
import jakarta.annotation.PostConstruct;
import jakarta.annotation.PreDestroy;
import org.assertj.core.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
public class SingletonTest {
@Test
void singletonBeanFind() {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SingletonBean.class);
SingletonBean singletonBean1 = ac.getBean(SingletonBean.class);
SingletonBean singletonBean2 = ac.getBean(SingletonBean.class);
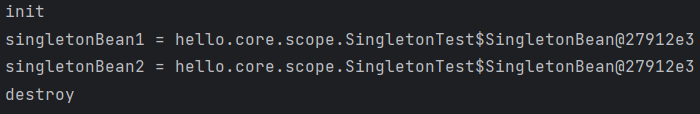
System.out.println("singletonBean1 = " + singletonBean1);
System.out.println("singletonBean2 = " + singletonBean2);
Assertions.assertThat(singletonBean1).isSameAs(singletonBean2);
ac.close();
}
@Scope("singleton")
static class SingletonBean {
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("init");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("destroy");
}
}
}
프로토타입
- 싱글톤 빈은 스프링 컨테이너 생성 시점에 초기화 메서드가 실행 되지만, 프로토타입 스코프의 빈은 스프링 컨테이너에서 빈을 조회할 때 생성되고, 초기화 메서드도 실행된다.
- 프로토타입 빈을 2번 조회하면 서로 다른 빈이 생성되고 초기화도 2번 이루어 진다
- 싱글톤 빈은 스프링 컨테이너가 관리하기 때문에 스프링 컨테이너가 종료될 때 빈의 종료 메서드가 실행되지만, 프로토타입 빈은 스프링 컨테이너가 생성과 의존관계 주입 그리고 초기화 까지만 관여하고, 더는 관리하지 않는 다. 따라서 프로토타입 빈은 스프링 컨테이너가 종료될 때
@PreDestroy 같은 종료 메서드가 전혀 실행되지 않는다.
- 종료하는 것은 클라이언트의 몫으로 넘어간다.(자체적으로 종료 메소드를 호출해야함)
- Test
package hello.core.scope;
import jakarta.annotation.PostConstruct;
import jakarta.annotation.PreDestroy;
import org.assertj.core.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
public class PrototypeTest {
@Test
void prototypeBeanFind() {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(PrototypeBean.class);
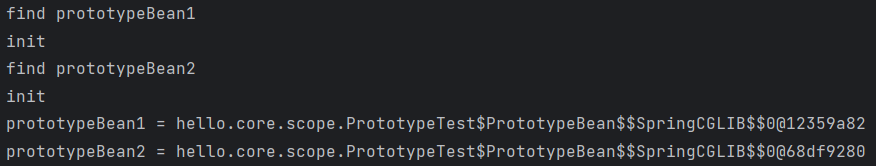
System.out.println("find prototypeBean1");
PrototypeBean prototypeBean1 = ac.getBean(PrototypeBean.class);
System.out.println("find prototypeBean2");
PrototypeBean prototypeBean2 = ac.getBean(PrototypeBean.class);
System.out.println("prototypeBean1 = " + prototypeBean1);
System.out.println("prototypeBean2 = " + prototypeBean2);
Assertions.assertThat(prototypeBean1).isNotSameAs(prototypeBean2);
ac.close();
}
@Configuration
@Scope("prototype")
static class PrototypeBean {
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("init");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("destroy");
}
}
}