포인트컷, 어드바이스, 어드바이저
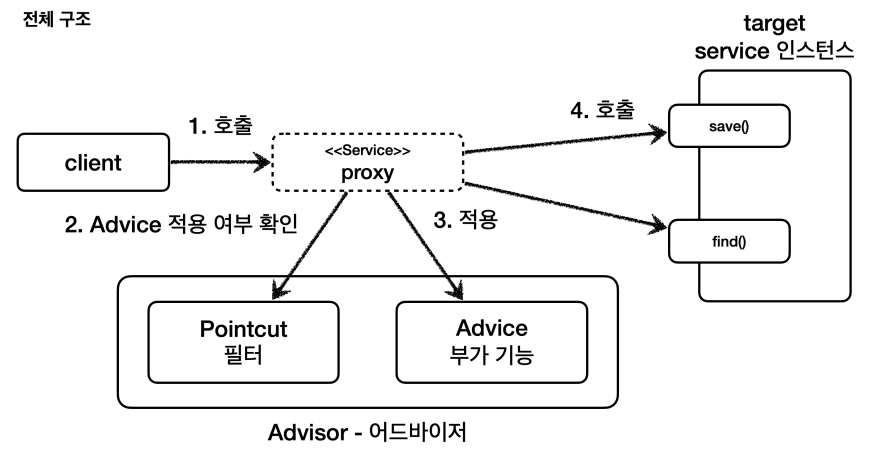
포인트컷( Pointcut ): 어디에 부가 기능을 적용할지, 어디에 부가 기능을 적용하지 않을지 판단하는 필터링 로직이다. 주로 클래스와 메서드 이름으로 필터링 한다. 이름 그대로 어떤 포인트(Point)에 기능을 적용할지 하지 않을지 잘라서(cut) 구분하는 것이다.어드바이스( Advice ): 프록시가 호출하는 부가 기능이다. 단순하게 프록시 로직이라 생각하면된다.어드바이저( Advisor ): 단순하게 하나의 포인트컷과 하나의 어드바이스를 가지고 있는 것이다. 쉽게 이야기해서 포인트컷1 + 어드바이스1이다.포인트컷은 대상 여부를 확인하는 필터 역할만 담당한다.어드바이스는 깔끔하게 부가 기능 로직만 담당한다.- 둘을 합치면
어드바이저가 된다. 스프링의 어드바이저는 하나의 포인트컷 + 하나의 어드바이스로 구성된다
어드바이저 예)
- TEST
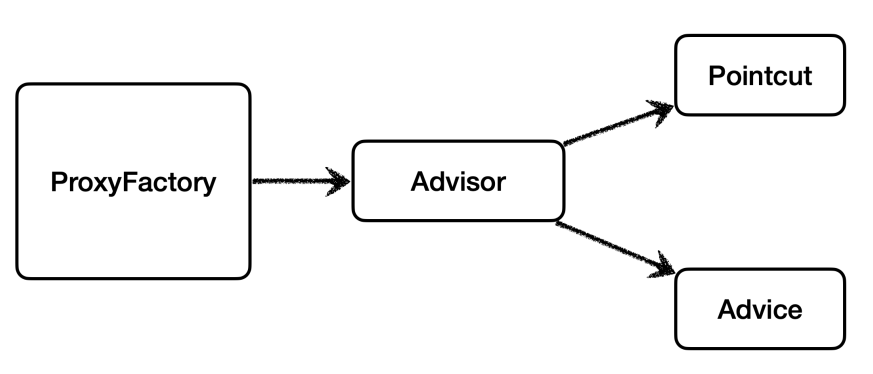
new DefaultPointcutAdvisor : Advisor 인터페이스의 가장 일반적인 구현체이다. 생성자를 통해 하나
의 포인트컷과 하나의 어드바이스를 넣어주면 된다. 어드바이저는 하나의 포인트컷과 하나의 어드바이스로 구성
된다.Pointcut.TRUE : 항상 true 를 반환하는 포인트컷이다.new TimeAdvice() : 앞서 개발한 TimeAdvice 어드바이스를 제공한다.proxyFactory.addAdvisor(advisor) : 프록시 팩토리에 적용할 어드바이저를 지정한다. 어드바이저는 내부에 포인트컷과 어드바이스를 모두 가지고 있다. 따라서 어디에 어떤 부가 기능을 적용해야 할지 어드바이저 하나로 알 수 있다. 프록시 팩토리를 사용할 때 어드바이저는 필수이다.- 그런데 생각해보면 이전에 분명히
proxyFactory.addAdvice(new TimeAdvice()) 이렇게 어드바이저
가 아니라 어드바이스를 바로 적용했다. 이것은 단순히 편의 메서드이고 결과적으로 해당 메서드 내부에서 지금 코드와 똑같은 다음 어드바이저가 생성된다. DefaultPointcutAdvisor(Pointcut.TRUE, new TimeAdvice())
@Test
void advisorTest1() {
ServiceInterface target = new ServiceImpl();
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory(target);
DefaultPointcutAdvisor advisor = new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(Pointcut.TRUE, new TimeAdvice());
proxyFactory.addAdvisor(advisor);
ServiceInterface proxy = (ServiceInterface) proxyFactory.getProxy();
proxy.save();
proxy.find();
}
포인트컷 예)
- TEST
- MyPointcut
- 직접 구현한 포인트컷이다. Pointcut 인터페이스를 구현한다.
- 현재 메서드 기준으로 로직을 적용하면 된다. 클래스 필터는 항상 true 를 반환하도록 했고, 메서드 비교 기능은 MyMethodMatcher 를 사용한다.
- MyMethodMatcher
- 직접 구현한 MethodMatcher 이다. MethodMatcher 인터페이스를 구현한다.
- matches() : 이 메서드에 method , targetClass 정보가 넘어온다. 이 정보로 어드바이스를 적용할지 적용하지 않을지 판단할 수 있다.
- 여기서는 메서드 이름이 "save" 인 경우에 true 를 반환하도록 판단 로직을 적용했다.
- isRuntime() , matches(... args) : isRuntime() 이 값이 참이면 matches(... args) 메서드가 대신 호출된다. 동적으로 넘어오는 매개변수를 판단 로직으로 사용할 수 있다.
- isRuntime() 이 false 인 경우 클래스의 정적 정보만 사용하기 때문에 스프링이 내부에서 캐싱을 통해 성능 향상이 가능하지만, isRuntime() 이 true 인 경우 매개변수가 동적으로 변경된다고 가정하기 때문에 캐싱을 하지 않는다.
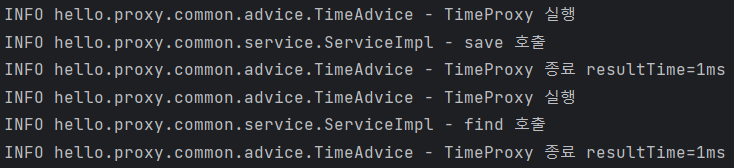
- new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(new MyPointcut(), new TimeAdvice())
@Test
@DisplayName("직접 만든 포인트컷")
void advisorTest2() {
ServiceImpl target = new ServiceImpl();
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory(target);
DefaultPointcutAdvisor advisor = new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(new MyPointcut(), new TimeAdvice());
proxyFactory.addAdvisor(advisor);
ServiceInterface proxy = (ServiceInterface) proxyFactory.getProxy();
proxy.save();
proxy.find();
}
static class MyPointcut implements Pointcut {
@Override
public ClassFilter getClassFilter() {
return ClassFilter.TRUE;
}
@Override
public MethodMatcher getMethodMatcher() {
return new MyMethodMatcher();
}
}
static class MyMethodMatcher implements MethodMatcher {
private String matchName = "save";
@Override
public boolean matches(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) {
boolean result = method.getName().equals(matchName);
log.info("포인트컷 호출 method={} targetClass={}", method.getName(),
targetClass);
log.info("포인트컷 결과 result={}", result);
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean isRuntime() {
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean matches(Method method, Class<?> targetClass, Object... args)
{
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
}
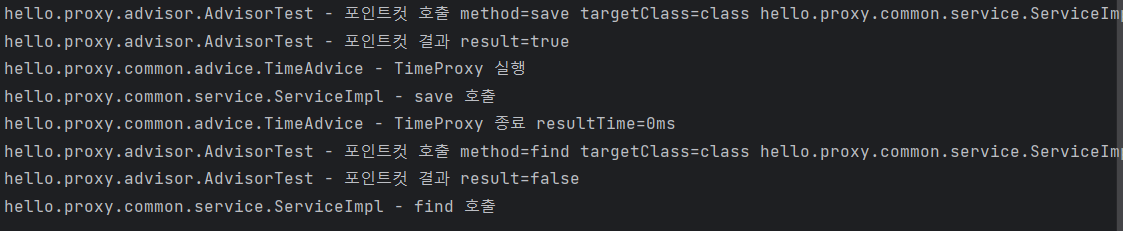
스프링이 제공하는 포인트컷
- TEST
- NameMatchMethodPointcut 을 생성하고 setMappedNames(...) 으로 메서드 이름을 지정하면 포인트컷이 완성된다
@Test
@DisplayName("스프링이 제공하는 포인트컷")
void advisorTest3() {
ServiceImpl target = new ServiceImpl();
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory(target);
NameMatchMethodPointcut pointcut = new NameMatchMethodPointcut();
pointcut.setMappedName("save");
DefaultPointcutAdvisor advisor = new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(pointcut, new TimeAdvice());
proxyFactory.addAdvisor(advisor);
ServiceInterface proxy = (ServiceInterface) proxyFactory.getProxy();
proxy.save();
proxy.find();
}
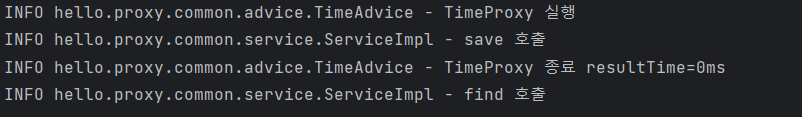
- 대표적인 포인트컷
- NameMatchMethodPointcut : 메서드 이름을 기반으로 매칭한다. 내부에서는 PatternMatchUtils 를 사용한다.
- JdkRegexpMethodPointcut : JDK 정규 표현식을 기반으로 포인트컷을 매칭한다.
- TruePointcut : 항상 참을 반환한다.
- AnnotationMatchingPointcut : 애노테이션으로 매칭한다.
- AspectJExpressionPointcut : aspectJ 표현식으로 매칭한다
어드바이저 여러개
- 프록시 여러개
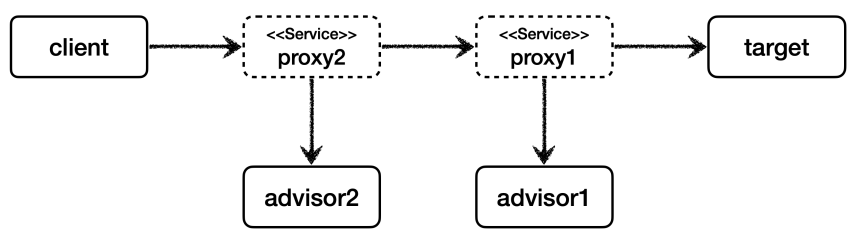
- 적용해야 하는 어드바이저가 10개라면 10개의 프록시를 생성해야한다
@Test
@DisplayName("여러 프록시")
void multiAdvisorTest1() {
ServiceInterface target = new ServiceImpl();
ProxyFactory proxyFactory1 = new ProxyFactory(target);
DefaultPointcutAdvisor advisor1 = new
DefaultPointcutAdvisor(Pointcut.TRUE, new Advice1());
proxyFactory1.addAdvisor(advisor1);
ServiceInterface proxy1 = (ServiceInterface) proxyFactory1.getProxy();
ProxyFactory proxyFactory2 = new ProxyFactory(proxy1);
DefaultPointcutAdvisor advisor2 = new
DefaultPointcutAdvisor(Pointcut.TRUE, new Advice2());
proxyFactory2.addAdvisor(advisor2);
ServiceInterface proxy2 = (ServiceInterface) proxyFactory2.getProxy();
proxy2.save();
}
@Slf4j
static class Advice1 implements MethodInterceptor {
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
log.info("advice1 호출");
return invocation.proceed();
}
}
@Slf4j
static class Advice2 implements MethodInterceptor {
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
log.info("advice2 호출");
return invocation.proceed();
}
}
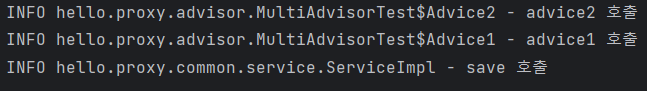
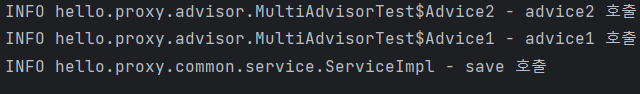
- 하나의 프록시, 여러 어드바이저
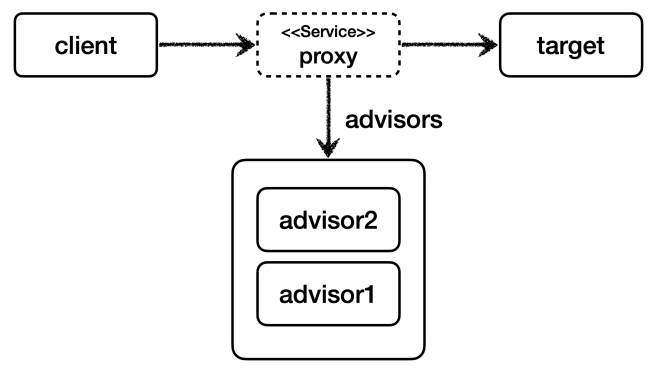
@Test
@DisplayName("하나의 프록시, 여러 어드바이저")
void multiAdvisorTest2() {
DefaultPointcutAdvisor advisor1 = new
DefaultPointcutAdvisor(Pointcut.TRUE, new Advice1());
DefaultPointcutAdvisor advisor2 = new
DefaultPointcutAdvisor(Pointcut.TRUE, new Advice2());
ServiceInterface target = new ServiceImpl();
ProxyFactory proxyFactory1 = new ProxyFactory(target);
proxyFactory1.addAdvisor(advisor2);
proxyFactory1.addAdvisor(advisor1);
ServiceInterface proxy = (ServiceInterface) proxyFactory1.getProxy();
proxy.save();
}