
POTS and Dial-up
Dial-up Connection
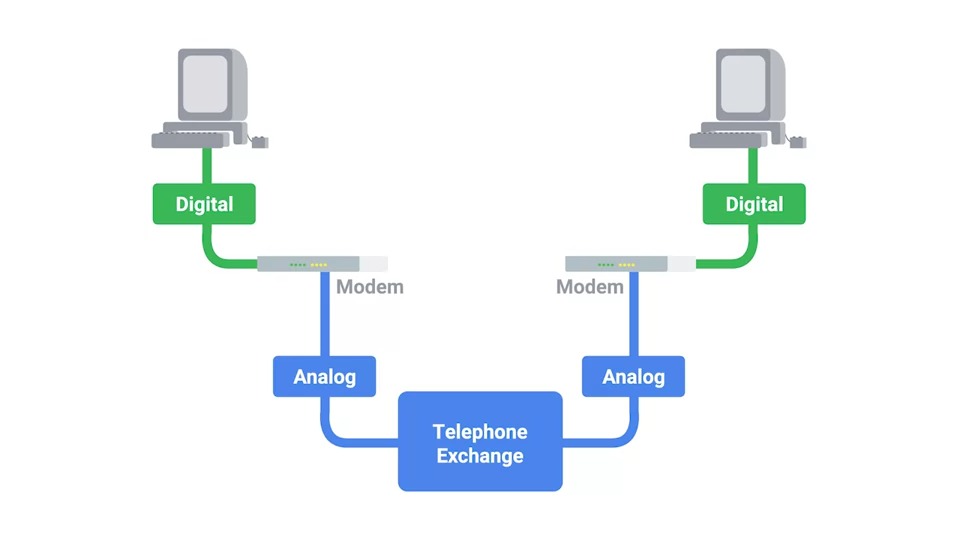
A dial-up connection uses POTS(
Plain Old Telephone Service) for data tranfer and gets its name becuase the connection is established by actually dialing a phone number.
Modem
Modem stands for modulator and demodulator.
They take data that computers can understand and turn them into a audible wavelengths that can be transmitted over POTS.
Baud Rate
A mesaurement of how many bits can be passed across a phone line in a second.
Broadband Connections
Broadband
Any connectivity technology that isn't dial-up internet.
Broadband connections are long lasting connections that don't need to be established with each use.
T-carrier technologies
Originally invented by AT&T in order to transmit multiple phone calls over a single link.
- Transmission System 1 or T1 for short : With this, AT&T invented a way to carry up to 24 simultaneous phone calls across a single piece of twisted pair copper.
1.544 megabits per second. - T3 : 44.736 megabits per second.
Digital Subscriber Lines (DSL)
DSL technology was able to send much more data across the wire than traditional dial-up technologies.
This allowed for normal void phone calls and data transfer to occur at the same time on the same line.
Digital Subsriber Line Access Multiplexer (DSLAMS)
These devices establish data connections across phone lines, but long runnign.
The connection is established when the DSLAM is powered on.
-
ADSL : A for Asymmetric. Faster download speeds, slower upload speeds.
-
SDSL : S for Symmetric. Downloads speeds and upload speeds are the same,.
SDSL now for common for home users and bisunesses because of decreased cost of the Internet.
FTTX or Fiber to the x
-
Fiber to the neighborhood : fiber technologies are used to deliver data to a single physical cabinet that severs a certain amount of the population.
-
Fiber to the building : It's a setup where fiber technologies are used fo rdata delivery to an individual building.
-
Fiber to the home : This is used in instances where fiber is actually run to each individual residents in a neighbothood or apartment building.
Optical Network Terminator
In ONT, converts data from protocols, the fiber network can understand to those taht more traditional twisted pair copper network can understand.
WAN
WAN or Wide Area Network
Acts like a single network, but spans across multiple physical locations.
WAN works by using a number of different protocols at the data link layer to transport your data from one site to another.
Point-to-Point VPNs
Establishes a VPN tunnel between two sites.
Wireless Networking
Different 802.11 standars generally use the same basic protocol,
but might operate at different frequency bands.
Frequency Band
A certain section of a radio spectrum that's been agreed upon to be used for certain communications. Specific frequency band is called the FM broadcast band.
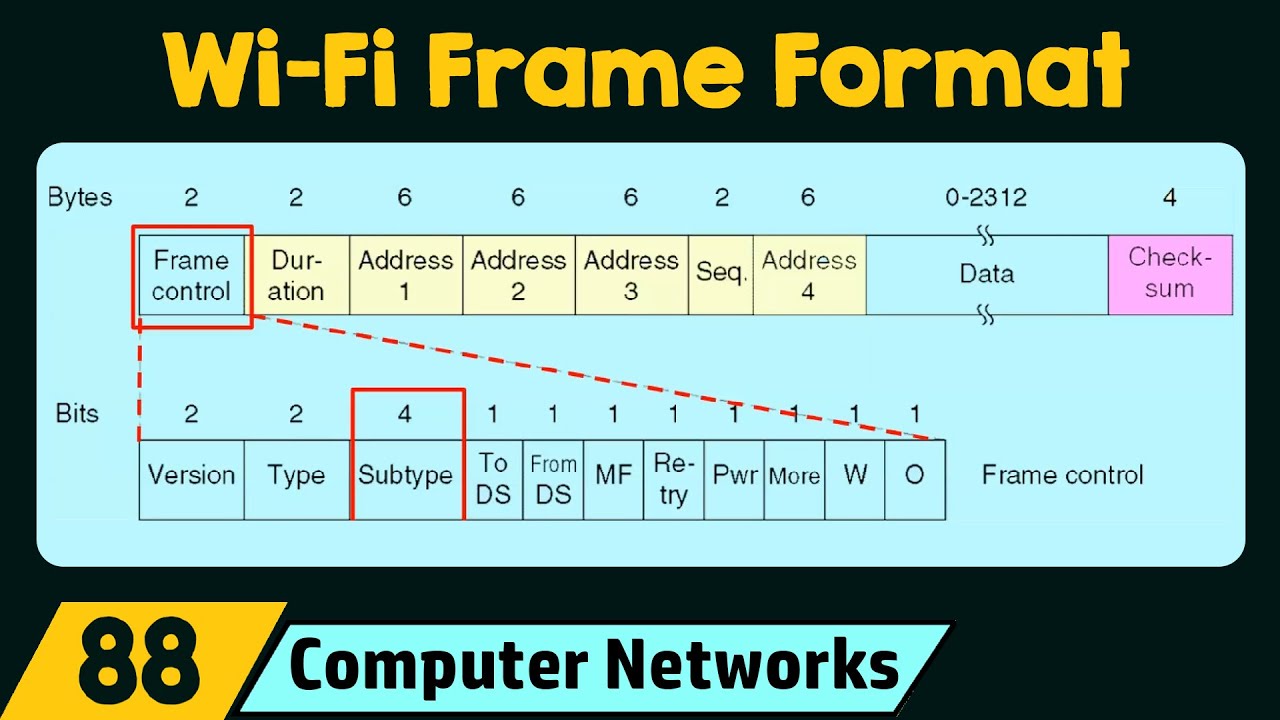
802.11 frame
-
Frame control field : 16 bits long and contains a number of subfields that are used to describe how the frame itself should be processed.
-
Duration field : It specifies how long the total frame is, so the receiver knows how long it should expect to have to listen to this transmission.
Wireless access point : A device that bridges the wireless and wired portions of a network.
3. Four address fields
Source address field : the MAC address of sending device
Intended destination :
Receiving address : the MAC address of the access point that sould recieve the frame.
Transmitter address : the MAC address of whatever has just transmitted the frame.
usually, source address = transmitter address, receiving address = destination address-
Sequence control field : Contains a sequence number used to keep track of ordering the frames.
-
Data payload section : All of the data of the protocols further up the stack.
-
Frame check sequence : contains a checksum used for a CRC.
Wireless network configuration
-
Ad-hoc networks : Where all nodes speacks directly each other.
-
Wireless LANS (WLANS) : Where one or more access points act as a bridge between a wireless and a wired network. The most common.
-
Nesh Networks : Kind of a hybrid of the two.
Wireless Channels
- Channels : Individual, smaller sections of the overall frequency vands used by a wireless network.
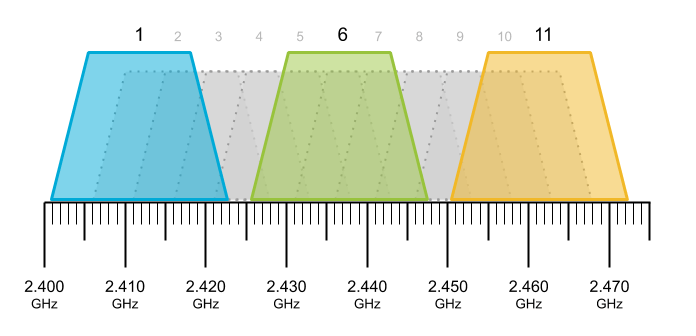
Channels help solving colision domain.
Wireless Security
-
WEP : WEP stands for Wireless Equivalent
Privacy, and it's an encryption technology that provides a very low level of privacy.
Uses 40 bits for its encryption key : very weak. -
WPA : Wi-Fi Protected Access
Uses 128-bit key. WPA 2 uses 256-bit krey. -
MAC Filtering : You configure your access points to only allow for connections from a specific set of MAC addresses belonging to devices you trust
Cellular Networking (Mobile Networking)
The Biggest Difference between cellular networking and 802.11 networking is
the frequencies of cellular networking can travel over longer distances more easily.
