9:35 스타벅스
오늘은 일요일이니까 이것 저것 해보기!
- 랭체인 공부하기!
- C로 양방향 연결 리스트, 스택, 큐, 트리 구현해보기!
- 기초 자료 구조 복습
- 기초 알고리즘 복습
- 블로그 정리하기
랭체인
서로 다른 AI API의 요청과 응답을 통일된 형태로 사용할 수 있게 해주는 프레임워크
마치 제이쿼리같다!
https://python.langchain.com/docs/get_started/introduction
환경 변수 세팅
주피터 노트북 환경에서 API 키는 다음 양식으로 해야 됨!
OPENAI_API_KEY="sk-*****"
LLM vs CHAT
llm 모듈은 단일 문장 예측에 사용
chat 모듈은 대화 상황에 대한 예측에 사용
from langchain.llms.openai import OpenAI
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
llm = OpenAI()
chat = ChatOpenAI()ChatOpenAI()
대화형 모듈을 사용해 본다.
여러 파라미터가 있다.
temperature는 창의성, 무작위성 값을 지정.
0~1사이의 값을 가지며, 낮을수록 일관되고 안정적인 반응.
높을 수록 창의적이고 무작위함.
chat = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0.1)schema
대화를 구성하는 스키마를 작성
SystemMessage()로 설정값 주입
AIMessage()는 인공지능의 대답을 설정
HumanMessage()는 사용자의 질문을 설정
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.schema import HumanMessage, AIMessage, SystemMessage
chat = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0.1)
messages = [
SystemMessage(
content="You are a computer science expert.",
),
AIMessage(content="Hi, Nice to meet you!"),
HumanMessage(content="What is Computer?"),
]
chat.predict_messages(messages)위 코드에 대한 응답
AIMessage(content='A computer is an electronic device that is capable of receiving, processing, and storing data. It can perform various operations and calculations based on instructions provided by a user or a program. Computers consist of hardware components such as the central processing unit (CPU), memory, storage devices, input/output devices, and software that enables them to perform specific tasks. They are used in various fields, including business, education, entertainment, research, and many others.')
프롬프트 템플릿
PromptTemplate은 문자열로 템플릿을 만들고,
ChatPromptTemplate 은 메시지에서 템플릿을 만든다.
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate, ChatPromptTemplate
template = PromptTemplate.from_template(
"What is the {subject}?",
)
prompt = template.format(subject="lazy evaluation")
chat.predict(prompt)
chat_template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "You are a computer {category} expert."),
("ai", "Hi, Nice to meet you!"),
("human", "What is {keyword}?")
])
chat_template.format_messages(
category="computer",
subject="virtual memory"
)템플릿으로 스키마를 쉽게 설정할 수 있음.
Output Parser
응답 결과를 파싱함.
파싱한 내용을 새로운 형태로 바꿀 수 있음.
(예를 들어 배열, json 등)
LangChain expression language(LCEL)
랭체인은 결과를 변수에 담고, 또 그걸 메서드로 호출하고 그런 작업을 하나로 연결해 준다.
마치 리눅스의 파이프같은 개념.
chain = template | chat | OutputParser()
chain.invoke({
"max_items": 10,
"keyword": "OSI 7 Layer"
})LCEL 추가 문법
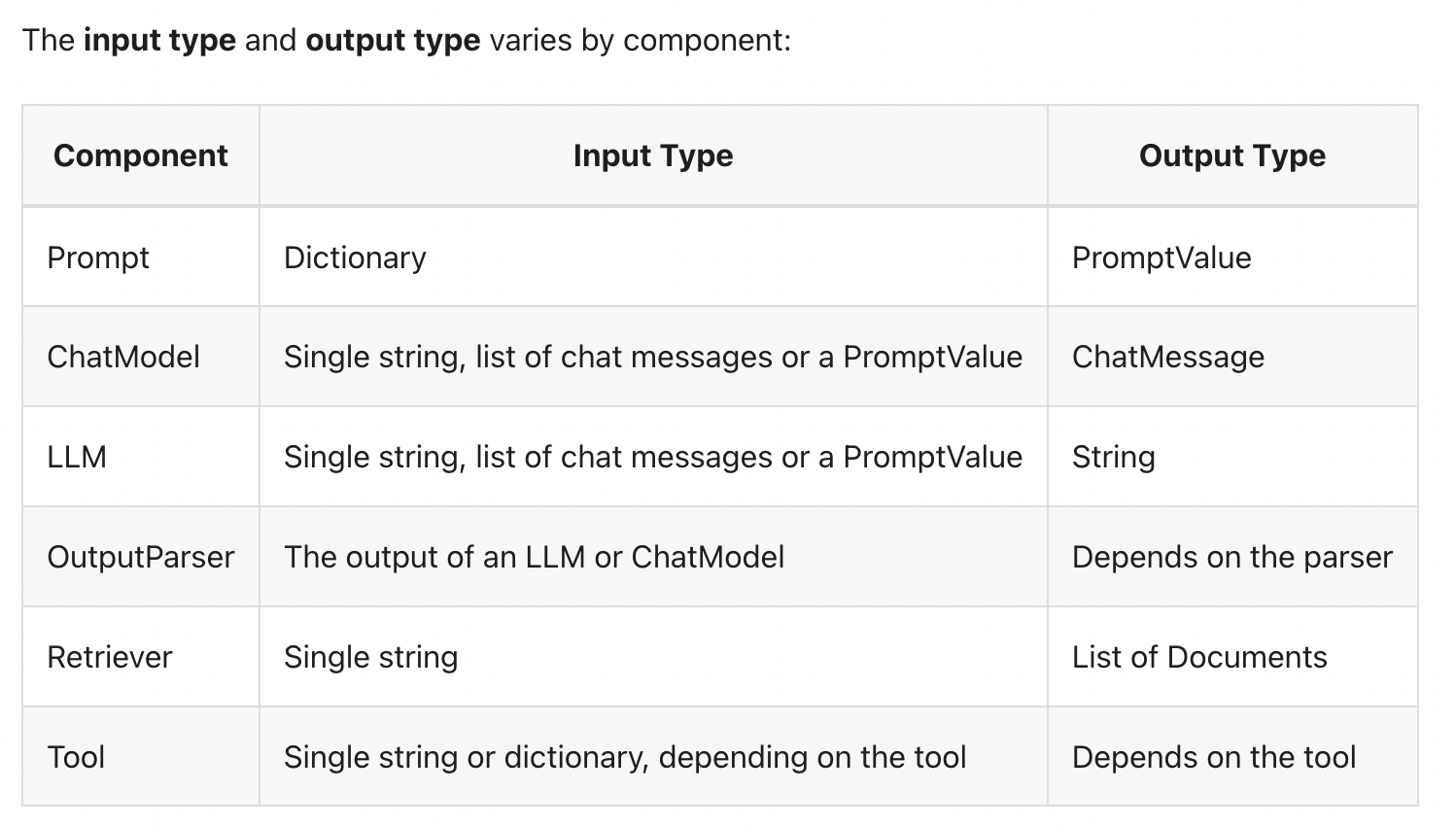
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain.callbacks import StreamingStdOutCallbackHandler
chat = ChatOpenAI(
temperature=0.1,
streaming=True,
callbacks=[StreamingStdOutCallbackHandler]
)
cs_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "You are computer science expoert."),
("human", "What is the {keyword}?")
])
cs_chain = cs_prompt | chat
story_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
"system", "You specialize in figuratively expressing the concepts of the questions you are asked through simple stories.",
"human", "{ask}"
])
story_chain = story_prompt | chat
final_chain = {"ask": cs_chain} | story_chain
final_chain.invoke({
"keyword": "OOP",
})FewShotPromptTemplate
FewShot은 예제를 주는 것
예를 들어 대답해야 하는 형식을 프롬프트로 지정해 주는 게 아니라
기존에 이미 정해진 FewShot을 통해 알려주는 것
FewShot은 몇 장의 사진과 같은 것이다.
즉 예제를 알려주는 거!
예를 들어 몇 개의 json를 형식화해서 알려주면,
그 형식에 맞춰서 결과를 생성해 줌.
example = [
{
"question": "What do you know about USA",
"answer": """
I Know this:
Capital: Washington D.C.
Language: English
Food: Hamburger
Currency: Dollar
"""
},
{
"question": "What do you know about Korea?",
"answer": """
I Know this:
Capital: Seoul
Language: Korean
Food: Kimchi
Currency: Won
"""
},
{
"question": "What do you know about Japan?",
"answer": """
I Know this:
Capital: Tokyo
Language: Japanese
Food: shusi
Currency: Yen
"""
}
]
example_template = """
Human: {question}
AI: {answer}
"""
example_prompt = PromptTemplate.from_template(example_template)
prompt = FewShotPromptTemplate(
example_prompt=example_prompt,
examples=example,
suffix="Human: What do you know about {country}?",
input_variables=["country"]
)
# prompt.format(country="China")
chain = prompt | chat
chain.invoke({
"country": "China"
})그니까 프롬프트로 추상적으로 명령을 내리는 게 아니라(연역적)
구체적인 결과를 먼저 보여주는 것(귀납적)
예제 선택기
example을 다 넘기면 비효율적
셀렉터를 통해 예제를 선택할 수 있음.
from lengchain.prompts.example_selector import LengthBaseExampleSelector이건 길이 기반으로 예제를 선택하는거고, BaseSelector를 상속받아서 custom selector를 사용할 수도 있음.
직렬화
from langchain.prompts import load_prompt
prompt = load_prompt("./prompt.yaml")prompt를 json이나 yaml로 파일로 관리할 수 있음.
프롬프트 파이프라인
여러 프롬프트를 하나로 합쳐줄 수 있음.
관리해야 하는 프롬프트가 다수일 때 프롬프트 제어에 유용
prompts = [
("intro", intro),
("example", example),
("start", start),
]
full_prompt = PipelinePromptTemplate(
final_prompt=final,
pipeline_prompts=prompts,
)Caching
메모리 캐시
from langchain.globals import set_llm_cache
from langchain.cache import InMemoryCache
set_llm_cache(InMemoryCache())데이터베이스 캐싱
from langchain.cache import SQLiteCache
set_llm_cache(SQLiteCache())debug
실행 중인 상황에 대한 로그를 송출
from langchain.globals import set_debug
set_debug(True)비용 확인하기
chat = ChatOpenAI(
temperature=0.1,
# streaming=True,
# callbacks=[StreamingStdOutCallbackHandler()]
)
with get_openai_callback() as usage:
chat.predict("What is the KOREA?")
print(usage)Tokens Used: 130
Prompt Tokens: 14
Completion Tokens: 116
Successful Requests: 1
Total Cost (USD): $0.000253
메모리
랭체인은 5가지의 메모리가 존재.
메모리가 없으면 챗봇은 이전 대화를 기억하지 못한다.
OpenAI 기본 API는 기본적으로 메모리 미지원.(stateless)
conversation buffer
대화의 모든 부분을 누적해서 기억함
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
memory = ConversationBufferMemory(return_message=True)
memory.save_context({"input": "Hi!"}, {"output": "How are you?"})
memory.load_memory_variables({}){'history': [HumanMessage(content='Hi!'), AIMessage(content='How are you?')]}
기본적으로 input은 "human"처리되고, output은 "AI"로 처리됨.
return_message는 챗 모델을 사용할 때 설정.
이게 설정되면 채팅 형태로 반환되고 없으면 답변이 스트링 형태로 넘어 옴.
conversation buffer window
대화의 특정 부분만 기억함
(용량이 정해져 있음, 큐 형태로 구조)
최근 대화에 집중
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferWindowMemory
memory = ConversationBufferWindowMemory(
return_messages=True,
k=4
)
def add_message(input, output):
memory.save_context({"input": input}, {"output": output})
add_message(1, 1)
add_message(2, 2)
add_message(3, 3)
add_message(4, 4)
add_message(5, 5)
memory.load_memory_variables({}){'history': [HumanMessage(content='2'),
AIMessage(content='2'),
HumanMessage(content='3'),
AIMessage(content='3'),
HumanMessage(content='4'),
AIMessage(content='4'),
HumanMessage(content='5'),
AIMessage(content='5')]}Conversation Summary
llm을 사용해서 기존 대화를 요약한다.
llm을 사용하는 과정에서 API를 호출하고 과금됨.
from langchain.memory import ConversationSummaryMemory
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0.1)
memory = ConversationSummaryMemory(llm=llm)
def add_message(input, output):
memory.save_context({"input": input}, {"output": output})
def get_history():
return memory.load_memory_variables({})
add_message("Hi, I love computer.", "It's amazing!")
add_message("Do you remember what I love?", "ofcourse!")
get_history(){'history': 'The human expresses their love for computers and the AI agrees, finding them amazing. The AI remembers what the human loves.'}뭐야.. AI 요약은 아예 맥락을 만들어서 그 맥락을 기억한다.. 와우..
Conversation Summary Buffer
summary와 buffer가 합해진 형태
리밋 이하 메시지는 그대로 기억하고, 리밋을 넘어가는 대화는 오래된 메시지부터 요약해서 기억
from langchain.memory import ConversationSummaryBufferMemory
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0.1)
memory = ConversationSummaryBufferMemory(llm=llm, max_token_limit=100)ConversationKGMemory
지식 그래프 메모리
대화 중에 지식 그래프를 생성
중요한 것들만 뽑아서 요약본을 만듦
엔티티는 키워드를 뽑아서, 그 키워드에 대한 설명을 저장하는 것과 비슷
from langchain.memory import ConversationKGMemory
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0.1)
memory = ConversationKGMemory(llm=llm, return_messages=True)summary가 문장 형태로 요약해서 기억한다면, KG는 각각의 요소를 그래프 형태(노드와 엣지)로 연결되게 그린다.
체인과 메모리 결합하기
off-the-shelf chain(기성 체인 같은 느낌)
from langchain.memory import ConversationSummaryBufferMemory
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.chains import LLMChain
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0.1)
memory = ConversationSummaryBufferMemory(
llm=llm,
max_token_limit=120,
memory_key="chat_history"
)
template = """
You are a helpful AI talking to a human.
{chat_history}
Human: {question}
You:
"""
chain = LLMChain(
llm=llm,
memory=memory,
prompt=PromptTemplate.from_template(template),
verbose=True,
)
chain.predict(question="I'm classbiu")
memory.load_memory_variables({})