점심을 미리 먹고 옴
10:54 입실
가상 메모리 진짜 어렵지만 그래도 한 발자국씩 앞으로 야금야금 걸어가는 중..🏃🏃🏃🏃🏃
Pintos
새로운 문제
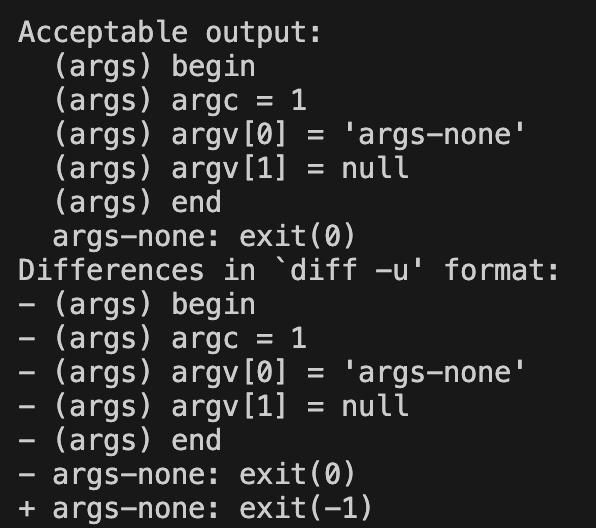
커널 패닉이 뜨지는 않고 이제 새로운 형태의 에러
exit(-1)이면 폴트 핸들러가 작동하지 않아서 그런가?
원인을 찾아보자..
pg_round 누락
❌ page->va = va;
✅ page->va = pg_round_down(va);
va가 속한 페이지를 찾기 위해서는 va에서 페이지 번호만 추출해야 한다. 이때 pg_round_down을 통해 va에서 오프셋을 0으로 만들면 페이지 번호를 추출할 수 있다.
즉, va를 통해 va가 속한 페이지를 찾기 위해서 pg_round_down이 필요하다.
spt 해시 테이블 잘못 지정 문제
struct hash_elem *
hash_find (struct hash *h, struct hash_elem *e) {
return find_elem (h, find_bucket (h, e), e);
}❌ e = hash_find(&spt, &page->hash_elem);
✅ e = hash_find(&spt->spt_hash, &page->hash_elem);
&spt->spt_hash가 들어가야 할 자리에 &spt를 넘겨서 오류 발생
kva 미할당으로 커널 패닉 발생
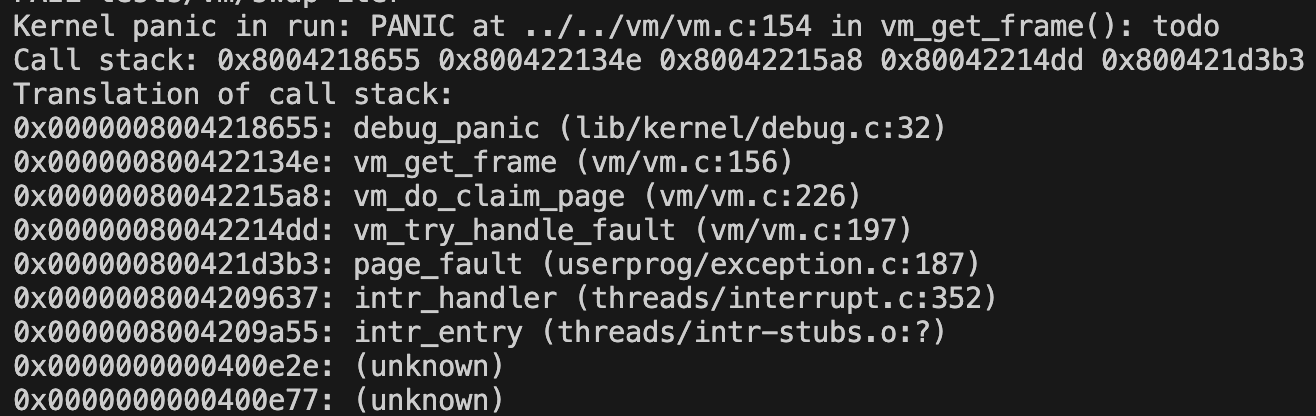
vm_get_frame(void)
{
struct frame *frame = NULL;
/* TODO: Fill this function. */
void *kva = palloc_get_page(PAL_USER);
if (kva == NULL)
PANIC("todo"); // 여기 실행
frame = malloc(sizeof(struct frame));
frame->kva = kva;
frame->page = NULL;
ASSERT(frame != NULL);
ASSERT(frame->page == NULL);
return frame;
}make check를 한 번 더 돌리면 테스트가 우선 실행은 된다???
pass tests/userprog/args-none
pass tests/userprog/args-single
pass tests/userprog/args-multiple
pass tests/userprog/args-many
pass tests/userprog/args-dbl-space
pass tests/userprog/halt
pass tests/userprog/exit
pass tests/userprog/create-normal
pass tests/userprog/create-empty
pass tests/userprog/create-null
pass tests/userprog/create-bad-ptr
pass tests/userprog/create-long
pass tests/userprog/create-exists
pass tests/userprog/create-bound
pass tests/userprog/open-normal
pass tests/userprog/open-missing
pass tests/userprog/open-boundary
pass tests/userprog/open-empty
pass tests/userprog/open-null
pass tests/userprog/open-bad-ptr
pass tests/userprog/open-twice
pass tests/userprog/close-normal
pass tests/userprog/close-twice
pass tests/userprog/close-bad-fd
pass tests/userprog/read-normal
pass tests/userprog/read-bad-ptr
FAIL tests/userprog/read-boundary
pass tests/userprog/read-zero
pass tests/userprog/read-stdout
pass tests/userprog/read-bad-fd
pass tests/userprog/write-normal
pass tests/userprog/write-bad-ptr
pass tests/userprog/write-boundary
pass tests/userprog/write-zero
pass tests/userprog/write-stdin
pass tests/userprog/write-bad-fd
FAIL tests/userprog/fork-once
FAIL tests/userprog/fork-multiple
FAIL tests/userprog/fork-recursive
FAIL tests/userprog/fork-read
FAIL tests/userprog/fork-close
FAIL tests/userprog/fork-boundary
FAIL tests/userprog/exec-once
FAIL tests/userprog/exec-arg
FAIL tests/userprog/exec-boundary
pass tests/userprog/exec-missing
pass tests/userprog/exec-bad-ptr
FAIL tests/userprog/exec-read
FAIL tests/userprog/wait-simple
FAIL tests/userprog/wait-twice
FAIL tests/userprog/wait-killed
pass tests/userprog/wait-bad-pid
FAIL tests/userprog/multi-recurse
FAIL tests/userprog/multi-child-fd
pass tests/userprog/rox-simple
FAIL tests/userprog/rox-child
FAIL tests/userprog/rox-multichild
pass tests/userprog/bad-read
pass tests/userprog/bad-write
pass tests/userprog/bad-read2
pass tests/userprog/bad-write2
pass tests/userprog/bad-jump
pass tests/userprog/bad-jump2
pass tests/vm/pt-grow-stack
pass tests/vm/pt-grow-bad
pass tests/vm/pt-big-stk-obj
pass tests/vm/pt-bad-addr
pass tests/vm/pt-bad-read
pass tests/vm/pt-write-code
FAIL tests/vm/pt-write-code2
FAIL tests/vm/pt-grow-stk-sc
pass tests/vm/page-linear
FAIL tests/vm/page-parallel
FAIL tests/vm/page-merge-seq
FAIL tests/vm/page-merge-par
FAIL tests/vm/page-merge-stk
FAIL tests/vm/page-merge-mm
pass tests/vm/page-shuffle
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-read
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-close
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-unmap
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-overlap
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-twice
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-write
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-ro
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-exit
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-shuffle
pass tests/vm/mmap-bad-fd
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-clean
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-inherit
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-misalign
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-null
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-over-code
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-over-data
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-over-stk
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-remove
pass tests/vm/mmap-zero
pass tests/vm/mmap-bad-fd2
pass tests/vm/mmap-bad-fd3
pass tests/vm/mmap-zero-len
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-off
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-bad-off
FAIL tests/vm/mmap-kernel
FAIL tests/vm/lazy-file
pass tests/vm/lazy-anon
FAIL tests/vm/swap-file
FAIL tests/vm/swap-anon
FAIL tests/vm/swap-iter
FAIL tests/vm/swap-fork
pass tests/filesys/base/lg-create
pass tests/filesys/base/lg-full
pass tests/filesys/base/lg-random
pass tests/filesys/base/lg-seq-block
pass tests/filesys/base/lg-seq-random
pass tests/filesys/base/sm-create
pass tests/filesys/base/sm-full
pass tests/filesys/base/sm-random
pass tests/filesys/base/sm-seq-block
pass tests/filesys/base/sm-seq-random
FAIL tests/filesys/base/syn-read
pass tests/filesys/base/syn-remove
FAIL tests/filesys/base/syn-write
pass tests/threads/alarm-single
pass tests/threads/alarm-multiple
pass tests/threads/alarm-simultaneous
pass tests/threads/alarm-priority
pass tests/threads/alarm-zero
pass tests/threads/alarm-negative
pass tests/threads/priority-change
pass tests/threads/priority-donate-one
pass tests/threads/priority-donate-multiple
pass tests/threads/priority-donate-multiple2
pass tests/threads/priority-donate-nest
pass tests/threads/priority-donate-sema
pass tests/threads/priority-donate-lower
pass tests/threads/priority-fifo
pass tests/threads/priority-preempt
pass tests/threads/priority-sema
pass tests/threads/priority-condvar
pass tests/threads/priority-donate-chain
FAIL tests/vm/cow/cow-simple
53 of 141 tests failed.pg_round_down
오프셋 지우고 페이지 번호만 반환
#define pg_round_down(va) (void *) ((uint64_t) (va) & ~PGMASK)폴트 핸들러
bool vm_try_handle_fault(struct intr_frame *f, void *addr,
bool user, bool write, bool not_present)가장 기본적인 기능은 addr(페이지 폴트가 발생한 주소)에서 페이지 폴트가 발생하면 여러 조건을 따져 최종적으로는 addr을 기준으로 round_down을 통해 다음 페이지 경계 주소까지 페이지를 할당함.
이때 스택이 부족하면 stack_growth를 통해 스택을 넓히는 작업도 수행함.
스택 범위
if ((USER_STACK - (1 << 20) <= rsp - 8 && rsp - 8 <= addr && addr <= USER_STACK)){
vm_stack_growth(addr);
}#define USER_STACK 0x47480000
이 영역부터 유저 스택임.
1 << 20 은 1MB를 의미함.
즉, 유저 스택의 한계를 USER_STACK으로부터 1MB까지로 한정하고 있고, 페이지 폴트가 발생한 주소인 addr이 stack 유효 범위 안에 있을 때만 스택을 한 페이지 늘림.
스택을 늘리려면 아래 조건을 모두 만족해야 함.
그렇지 않으면 스택이 충분히 확보된 상황이거나,
스택을 늘릴 수 없는 상황이므로 stack_growth를 실행하지 않음.
USER_STACK - (1 << 20) <= rsp - 8
rsp-8이 스택 한계보다 위에 있어야 함.
rsp - 8 <= addr
페이지 폴트가 발생한 addr이 rsp-8의 바깥에 있어야 함.
(즉, 현재 스택이 충분히 확보되지 않은 상태)
addr <= USER_STACK
페이지 폴트가 발생한 addr이 스택 한계 안에 있어야 함.
rsp - 8을 쓰는 이유
64비트 시스템에서는 스택에 기본적으로 64비트(8바이트) 단위로 데이터가 입출력된다.
즉, push가 발생할 수 있는 최소한의 다음 메모리 주소는 rsp - 8이다.
그렇다면, push이 전에 해당 스택 공간에 데이터를 push할 수 있을지 체크하려면 현재 rsp가 아니라 rsp - 8의 위치를 확인해야 한다.
그래서 각종 조건을 체크할 때 현재 위치인 rsp가 아니라 다음 push가 발생할 최소한의 주소인 rsp - 8을 기준으로 한다.
즉, push 인스트럭션의 특성 상 rsp - 8 위치에서 데이터 입력이 발생하기 때문에 rsp - 8 위치에서 폴트가 발생할 경우 스택을 늘려주어야 한다.
64비트 시스템에서는 데이터가 64비트(8바이트) 단위로 I/O 된다는 사실을 기억하기!
중첩 구조체
두 함수 모두 실행되는 게 이상하지 않나?
// 구조체는 이렇게 생김
struct supplemental_page_table {
struct hash spt_hash
};
// hash_init
void supplemental_page_table_init (struct supplemental_page_table *spt);
// 1. 구조체 안에 구조체 명시
void supplemental_page_table_init(struct supplemental_page_table *spt)
{
hash_init(&spt->spt_hash, page_hash, page_less, NULL);
}
// 2. 외부 구조체만 명시
void supplemental_page_table_init(struct supplemental_page_table *spt)
{
hash_init(spt, page_hash, page_less, NULL);
}동작하는 이유는?
hash_init의 첫 번째 인자로는 spt의 포인터가 넘어가야 한다.
기본적으로 구조체는 첫 번째 시작 주소를
반환한다.
1번 코드에서는 spt 주소로 접근해서 그 안에 있는 hash_table의 주소를 반환한다.
2번 코드에서는 spt 주소 자체를 반환한다.
이중 구조체의 형태를 보면 구조체 안에 구조체가 들어가 있는 형태이므로, spt와 &spt->spt_hash는 같은 주소 값을 반환한다고 볼 수 있다.
따라서 두 코드 모두 정상 작동한다.
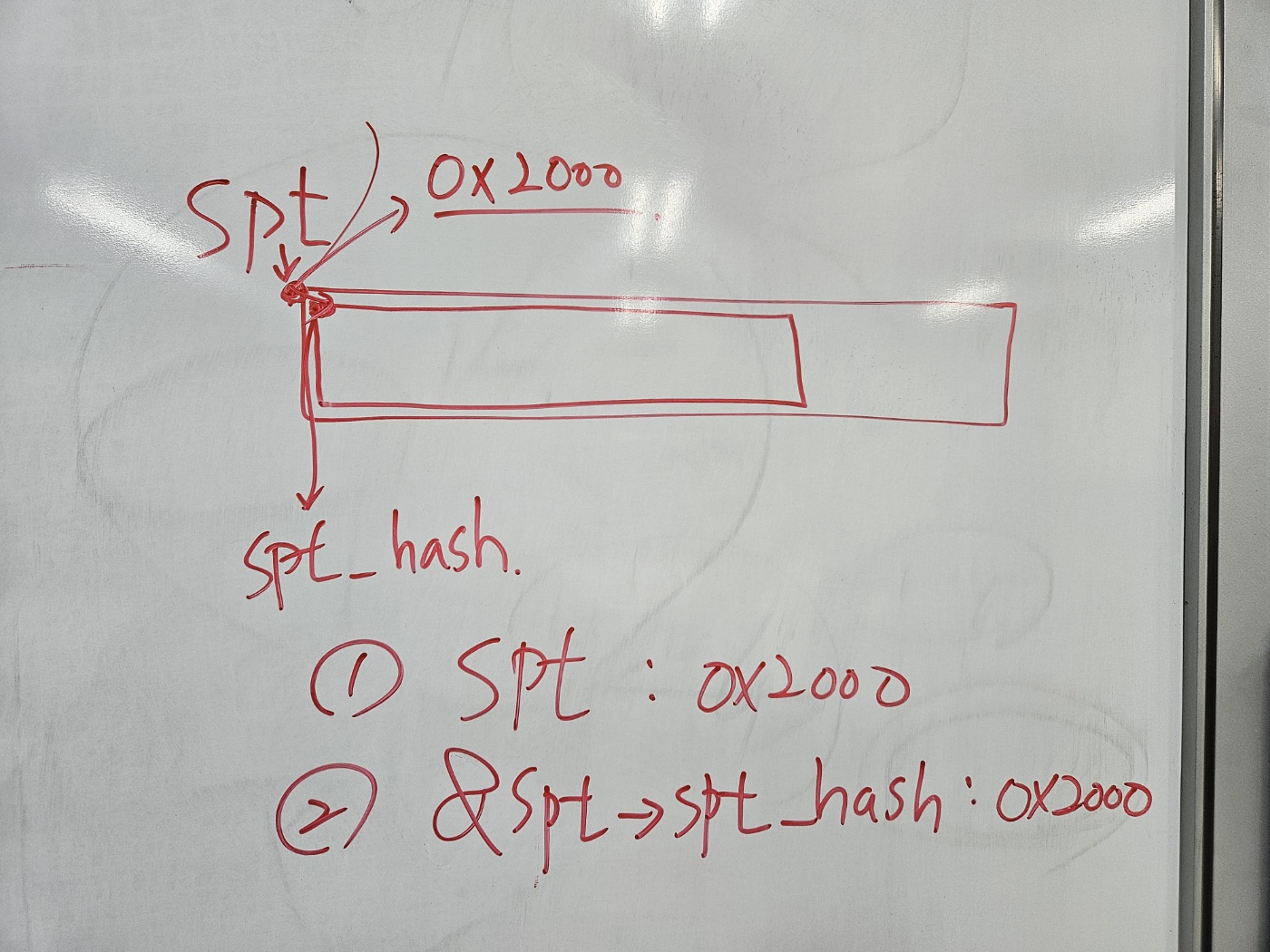
중첩된 구조체의 경우, 구조체 포인터와 구조체 내부의 멤버 포인터가 동일한 메모리 주소를 가리킨다.
해시 테이블 copy
process fork시에 자식 프로세스는 부모의 페이지 테이블을 copy한다.
(쓰기 시 복사는 옵션으로 구현)
srt의 테이블을 dst로 복사한다.
단순히 복사는 안되고 srt테이블을 순회하면서 일일이 복사해야 한다.
fork시 새롭게 페이지를 할당하고, 프레임에 연결해주는 작업이 필요함.
즉, copy는 페이지 프레임만 카피하는 게 아니라 페이지 프레임을 복사하고
그에 맞는 page 구조체 자체로 새롭게 복사해야 함.
이때 page가 frame과 연결되어 있다면 그것도 똑같이 적재시켜 줘야 함.
- 새로운 페이지 할당
- 페이지 프레임 복사
- 페이지 프레임 연결
포크 과정을 이해하니까 쓰기 시 복사가 왜 필요한지 이해함!
해시 테이블 kill
프로세스가 종료될 때 호출된다.
1. 만약 내용 변경된 파일 기반 페이지는 디스크 동기화 해야 함.
2. 페이지를 메모리에서 해제
Memory Mapped Files
관련 함수
do_mmap(): 메모리에 파일 매핑시키기
do_munmap() : 메모리 해제
vm_file_init() : 파일 페이지 초기화
file_backed_initializer(): 파일 기반 메모리 구조체 초기화
file_backed_destroy(): 파일닫아서 페이지 파괴, 만약 메모리 내용이 수정되었다면 파일에 동기화 시켜야 함.
https://youtu.be/SQYio0aKbgM?si=pEs20cVY7vP-MxmG
드디어.. 파일 기반 메모리로 간다.
mmap과 munmap을 구현해야 함.
mmap은 마찬가지로 lazy한 방식으로 구현되고, 매핑된 파일이 백업 저장소 역할을 한다.
file.c에서 do_mmap과 do_munmmap을 구현하면 됨.
