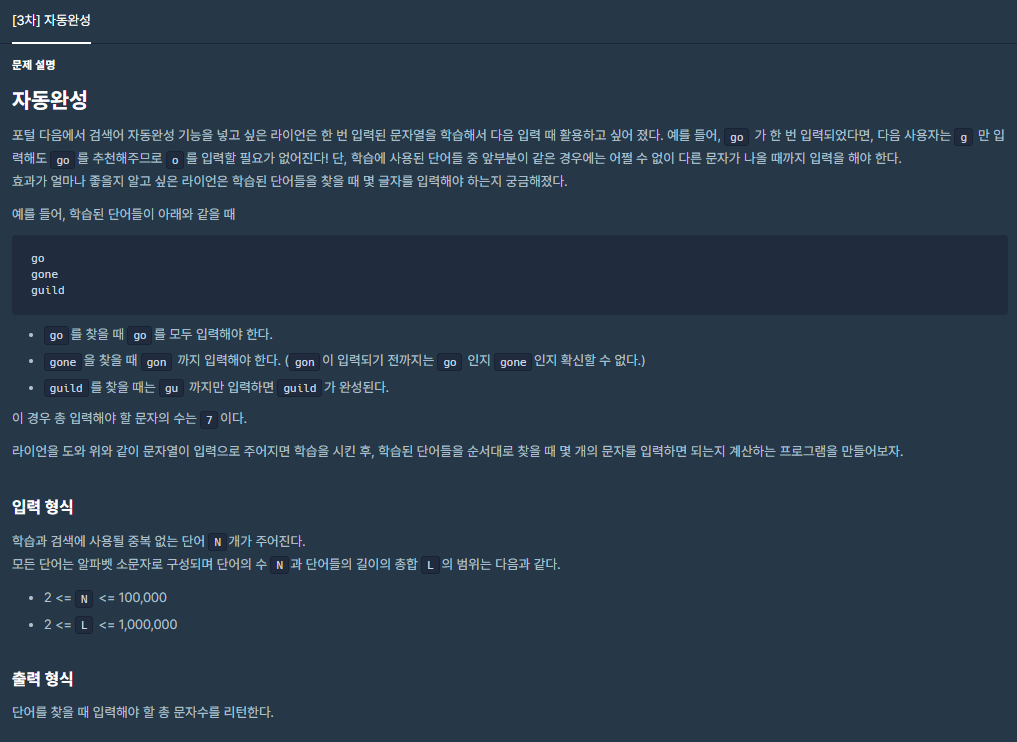
1. 문제 설명
- trie 구조를 사용하여 해결한다.
- 각각의 노드마다 하위 단어가 몇개인지 저장해준다.
- 하위 trie개수를 보고 더 탐색을 할지 말지 결정한다.
2. 풀이
- root를 [하위노드 개수,{자식노드}]의 구조로 생성해준다.
👉모든 노드는 아래의 구조로 생성한다.
root=[0,dict()]
- 단어와 root를 파라미터로 받아서 trie를 생성해주는 make_trie 함수를 생성한다.
def make_trie(root,word):
cur_node=root
for c in word:
if c not in cur_node[1]:
cur_node[1][c]=[0,dict()]
cur_node[0]+=1
cur_node=cur_node[1][c]
cur_node[0]+=1
- make_trie 함수를 사용해서 trie를 생성해준다.
for word in words:
make_trie(root,word)
- 생성된 trie를 탐색하는 search_target 함수를 생성해준다.
def search_target(root,word):
ret=0
cur_node=root
for c in word:
if cur_node[0]==1:
return ret
ret+=1
cur_node=cur_node[1][c]
return ret
for word in words:
answer += search_target(root,word)
3. 코드
import sys
from collections import defaultdict
sys.setrecursionlimit(10**6)
def make_trie(root,word):
cur_node=root
for c in word:
if c not in cur_node[1]:
cur_node[1][c]=[0,dict()]
cur_node[0]+=1
cur_node=cur_node[1][c]
cur_node[0]+=1
def search_target(root,word):
ret=0
cur_node=root
for c in word:
if cur_node[0]==1:
return ret
ret+=1
cur_node=cur_node[1][c]
return ret
def solution(words):
answer = 0
root=[0,dict()]
for word in words:
make_trie(root,word)
for word in words:
answer += search_target(root,word)
return answer


