과제1.
https://velog.io/@kungsboy/숙제-정렬을-구현하여-보자
삽입 정렬의 전체적인 과정은 이렇다. (오름차순을 기준으로 설명)
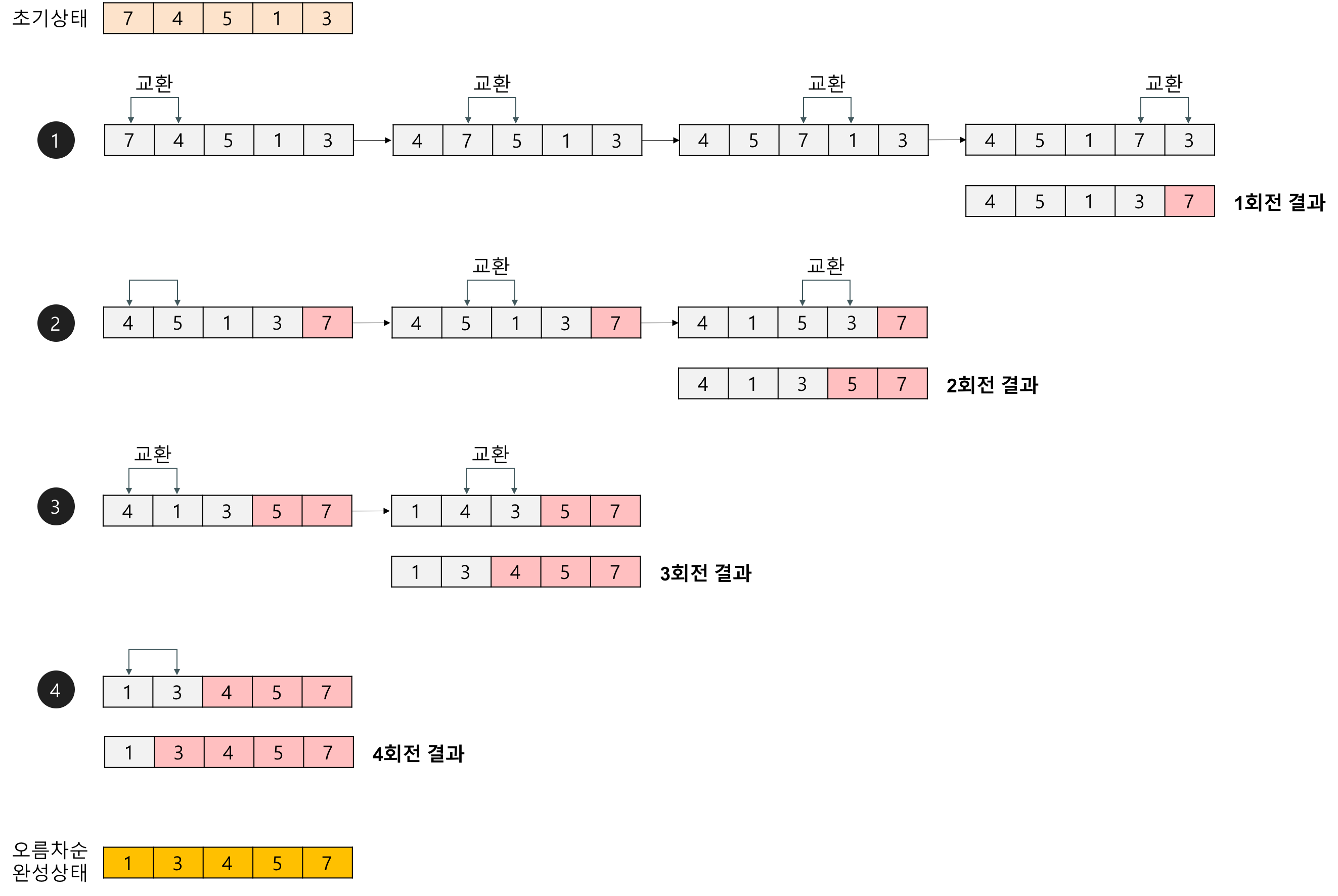
public int[] solution(int n, int[] arr)- 현재 타겟이 되는 숫자와 이전 위치에 있는 원소들을 비교한다. (첫 번째 타겟은 두 번째 원소부터 시작한다.)
- 타겟이 되는 숫자가 이전 위치에 있던 원소보다 작다면 위치를 서로 교환한다.
- 그 다음 타겟을 찾아 위와 같은 방법으로 반복한다.
○ 나의 답
import java.util.Arrays;
public class InsertionSortTest {
public static void insertionSort(int num, int[] arr) {
for (int i = 1; i < num; i++) {
for (int j = i; j > 0; j--) {
if (arr[j] < arr[j-1]) {
int tmp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j-1];
arr[j-1] = tmp;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {5,3,6,4,8,9,1,2,7};
int num = arr.length;
insertionSort(num, arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
}○ 알아간 것
- 자바는 call by value
- 아래 부분을
swap()으로 함수로 따로 빼기는 하지만 크게 이점은 없어보인다.
int tmp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j-1];
arr[j-1] = tmp;과제 2.
다음은 물건을 구입하는 사람을 정의한 Buyer클래스이다. 이 클래스는 멤버변수로 돈(money)과 장바구니(cart)를 가지고 있다. 제품을 구입하는 기능의 buy메서드와 장바구니에 구입한 물건을 추가하는 add메서드, 구입한 물건의 목록과 사용금액, 그리고 남은 금액을 출력하는 summary메서드를 완성하시오.
- 메서드명 : buy
기능 : 지정된 물건을 구입한다. 가진 돈(money)에서 물건의 가격을 빼고, 장바구니(cart)에 담는다.
만일 가진 돈이 물건의 가격보다 적다면 바로 종료한다.반환타입 : 없음매개변수 : Product p - 구입할 물건 - 메서드명 : add
기능 : 지정된 물건을 장바구니에 담는다.만일 장바구니에 담을 공간이 없으면, 장바구니의 크기를 2배로 늘린 다음에 담는다.
반환타입 : 없음매개변수 : Product p - 구입할 물건
- 메서드명 : summary
기능 : 구입한 물건의 목록과 사용금액, 남은 금액을 출력한다.
반환타입 : 없음매개변수 : 없음
class PolyExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Buyer b = new Buyer();
b.buy(new Tv());
b.buy(new Computer());
b.buy(new Tv());
b.buy(new Audio());
b.buy(new Computer());
b.buy(new Computer());
b.buy(new Computer());
b.summary();
}
}
class Buyer {
int money = 1000;
Product[] cart = new Product[3]; // 구입한 제품을 저장하기 위한 배열
int i = 0; // Product배열 cart에 사용될 index
void buy(Product p) {
/*
* (1) 아래의 로직에 맞게 코드를 작성하시오 . 1.1 가진 돈과 물건의 가격을 비교해서 가진 돈이 적으면 메서드를
* 종료한다. 1.2 가진 돈이 충분하면, 제품의 가격을 가진 돈에서 빼고 1.3 장바구니에 구입한 물건을 담는다.(add
* 메서드 호출 )
*/
}
void add(Product p) {
/*
* (2) 아래의 로직에 맞게 코드를 작성하시오. 1.1 i의 값이 장바구니의 크기보다 같거나 크면 1.1.1 기존의
* 장바구니보다 2배 큰 새로운 배열을 생성한다. 1.1.2 기존의 장바구니의 내용을 새로운 배열에 복사한다. 1.1.3 새로운
* 장바구니와 기존의 장바구니를 바꾼다. 1.2 물건을 장바구니(cart)에 저장한다. 그리고 i의 값을 1 증가시킨다.
*/
} // add(Product p)
void summary() {
/*
* (3) 아래의 로직에 맞게 코드를 작성하시오 . 1.1 장바구니에 담긴 물건들의 목록을 만들어 출력한다 . 1.2 장바구니에
* 담긴 물건들의 가격을 모두 더해서 출력한다. 1.3 물건을 사고 남은 금액 를 출력한다(money).
*/
} // summary()
}
class Product {
int price; // 제품의 가격
Product(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
}
class Tv extends Product {
Tv() {
super(100);
}
public String toString() {
return "Tv";
}
}
class Computer extends Product {
Computer() {
super(200);
}
public String toString() {
return "Computer";
}
}
class Audio extends Product {
Audio() {
super(50);
}
public String toString() {
return "Audio";
}
}
[실행결과]
잔액이 부족하여 Computer을/를 살 수 없습니다.
구입한 물건 : Tv, Computer, Tv, Audio, Computer, Computer,
사용한 금액 : 850
남은 금액 : 150○ 나의 답
void buy(Product p) {
if (money < p.price) {
System.out.println("잔액이 부족하여 "+ p.toString() + "을/를 살 수 없습니다.");
return; //1. 돈이 부족하면 프로그램 종료
} else {
money -= p.price; //2. 제품 가격을 가진 돈에서 뺀다
add(p); //3. 장바구니에 구입한 물건을 담는다.
}
}
void add(Product p) {
if (i >= cart.length) { //1. 장바구니가 넘치면
Product[] newCart = new Product[cart.length*2]; //2배 큰 배열을 생성한다.
for (int i = 0; i < cart.length; i++) { //기존의 장바구니에 있던 것 옮겨 담는다
newCart[i] = cart[i];
}
this.cart = newCart; //새 장바구니로 교체한다.
}
cart[i++] = p; //2. 카트에 물건을 담고, i값을 증가시킨다.
}
void summary() {
int sum = 0;
System.out.print("구입한 물건 : "); //1. 장바구니 안의 물건 목록 출력
for (Product p : cart) {
System.out.print(p.toString()+ ", ");
sum += p.price;
}
System.out.println("\n\n사용한 금액 : " + sum); //2. 물건 가격 합 출력
System.out.println("남은 금액 : " + money); //3. 남은 돈 출력
}○ 배운 것
배열 복사하기
참고 : https://coding-factory.tistory.com/548
Object.clone()
int[] a = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
int[] b = a.clone();Arrays.copyOf()
배열의 시작점 ~ 원하는 length까지 배열의 깊은 복사를 할 수 있다.
int[] a = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
int[] b = Arrays.copyOf(a, a.length);Arrays.copyOfRange()
복사할 배열의 시작점도 지정할 수 있다.
int[] a = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
int[] b = Arrays.copyOfRange(a, 1, 3);System.arraycopy()
지정된 배열을 대상 배열의 지정된 위치에 복사한다.
int[] a = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
int[] b = new int[a.length];
System.arraycopy(a, 0, b, 0, a.length);