서블릿 필터Servlet Filter
요청/응답과 관련된 작업을 미리 처리한다. 이를테면 setCharacterEncoding()같은 귀찮은 작업을 필터에 설정해두면 요청/응답할 때 알아서 한다.
Request Filter - Response Filter
필터는 크게 요청 필터와 응답 필터로 나눌 수 있다.
요청 필터
- 사용자 인증 및 권한 검사
- 요청 시 요청 관련 로그 작업
- 인코딩
응답 필터
- 응답 결과에 대한 암호화
- 서비스 시간 측정
관련 API
- javax.servlet.Filter
- javax.servlet.FilterChain
- javax.servlet.FilterConfig
Filter인터페이스의 메서드
| Method | 기능 |
|---|---|
| destroy() | 필터 소멸 시 컨테이너에 의해 호출되어 종료 작업 수행 |
| doFilter() | 요청/응답 시 컨테이너에 의해 호출되어 기능 수행 |
| init() | 필터 생성 시 컨테이너에 의해 호출되어 초기화 작업 수행 |
FilterConfig의 메서드
| Method | 기능 |
|---|---|
| getFilterName() | 필터 이름 반환 |
| getInitParameter(String name) | 매개변수 name에 대한 값을 반환 |
| getServletContext() | 서블릿 컨텍스트 객체를 반환 |
사용자 정의 필터
사용자 정의 필터는 반드시 Filter 인터페이스를 구현해야 한다.
사용자 정의 필터를 생성하면 필터를 각각 요청에 맞게 적용하기 위해 매핑이 필요하다. xml을 이용해서 할 수도 있고 애너테이션을 이용해서 할 수도 있다. 역시 애너테이션이 편하다.
요청 필터 사용해보기
지금껏 한글 인코딩reqeust.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8")이 늘 지겹도록 반복됐다.
이것을 Filter로 설정해두고, 모든 요청이 해당 Filter를 거치도록 만들어본다.
login.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Login</title>
</head>
<body>
<form name="login" method="post" action="/filterLogin">
아이디 : <input type="text" name="id"><br>
비밀번호:<input type="password" name="password">
<button>확인</button>
</form>
</body>
</html>FilterLogin.java
@WebServlet("/filterLogin")
public class FilterLogin extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//setCharacterEncoding() 생략
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
String id = request.getParameter("id");
String pwd = request.getParameter("password");
out.print("<h1>한글 id : " + id +"<br> pwd : " + pwd+"</h1>");
}
}이렇게 셋캐릭터인코딩을 하지 않은 상태로 한글 아이디를 입력해 로그인하게 되면 다음과 같은 일이 일어난다.
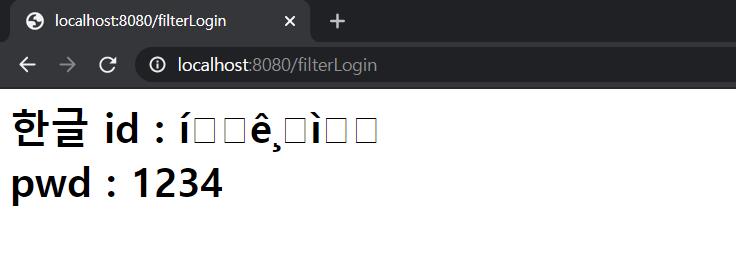
이것을 Filter를 사용해서 인코딩할 것이다.
우선 서블릿과 같은 패키지에 filter를 만든다.

EncoderFilter.java
@WebFilter("/*") //모든 요청은 해당 필터를 거친다.
public class EncoderFilter implements Filter {
private ServletContext context;
public void init(FilterConfig fConfig) throws ServletException {
System.out.println("filter........");
System.out.println("utf-8 encoding.........");
context = fConfig.getServletContext();
}
//실제로 필터 역할을 하는 메서드
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
System.out.println("doFilter()..........");
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
//웹 어플리케이션의 컨텍스트 이름
String context = ((HttpServletRequest)request).getContextPath();
//웹 브라우저에서 요청한 요청 URI
String pathinfo = ((HttpServletRequest)request).getRequestURI();
//요청 URI의 절대 경로
String realPath = request.getRealPath(pathinfo);
String msg = "Context : " + context +" \n URI : : " + pathinfo + "\n 절대 경로 : " + realPath;
System.out.println(msg);
//다음 필터로 넘기는 작업을 수행
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("destroy().....");
}
}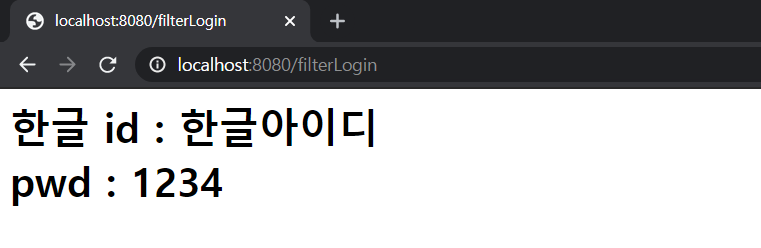
utf-8로 아주 잘 인코딩 된 것을 볼 수 있다.
응답 필터도 써보기
응답 필터라고 요청 필터와 다르지 않다. 위 EncoderFilter.java에서 doFilter() 마지막 줄에서
chain.doFilter(request, response);이 코드를 볼 수 있다. 이 코드를 기준으로 위쪽에 있는 코드는 요청 필터, 아래 있는 코드는 응답 필터다.
응답 필터로 작업 시간을 구하는 예제다.
EncoderFilter.java의 doFilter()만 약간 수정하면 된다.
//실제로 필터 역할을 하는 메서드
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
...
...
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
//다음 필터로 넘기는 작업을 수행
chain.doFilter(request, response);
System.out.println("response filter..........");
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("작업 시간 : " + (end - begin)+"ms");
}간단한 작업이므로 결과는 0ms를 얻는다.
공통으로 처리해야 하는 작업을 Filter로 처리하면 쉽게 중복을 제거하고 귀찮은 일을 덜 수 있단느 것을 기억하자!
